If the log collection feature is enabled for a domain name added to WAF, you can use the feature to query and analyze the collected logs of the domain name in real time. You can configure charts and create alert rules based on the query and analysis results.
Prerequisites
The Log Service for WAF feature is enabled. For more information, see Get started with the Simple Log Service for WAF feature.
Query and analyze logs
Log on to the WAF console. In the top navigation bar, select the resource group and the region in which the WAF instance is deployed. The region can be Chinese Mainland or Outside Chinese Mainland.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
Select a domain name from the domain name drop-down list and turn on Status to enable log collection for the domain name.
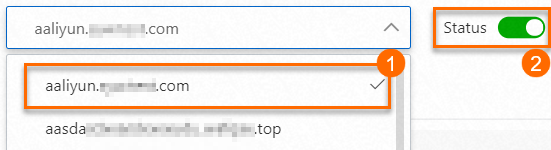
The domain name drop-down list, which is marked as 1 in the preceding figure, contains only the domain names that are protected by WAF. If the domain name for which you want to enable log collection is not contained in the drop-down list, add the domain name to WAF. For more information, see Tutorial.
On the Log Search tab, execute a query statement to query and analyze the logs of the protected object that you selected.

Enter a query statement in the search box that is marked as 1 in the preceding figure.
The query statement that you enter must use the syntax that is specific to Log Service. For more information about the syntax, see Search syntax. The log fields that are included in WAF logs are used as query fields in the query statements. For more information about the log fields that are supported by WAF, see Log fields supported by WAF.
If you are not familiar with the query syntax, we recommend that you use the Advanced Search feature. To use the Advanced Search feature, you need only to expand Advanced Search above the search box, specify search conditions, and then click Search. A query statement is automatically generated in the search box based on the search conditions. The following table describes the search conditions that are supported by the Advanced Search feature.
Search condition
Description
IP
The IP address of the client that sends the request.
Request ID
The unique ID that is generated by WAF for the client request. This ID is provided when WAF returns an error page or a response page that prompts the client to complete slider CAPTCHA verification to the client. You can use this ID to analyze and troubleshoot the error.
Rule ID
The ID of the WAF protection rule that is matched by the request. You can obtain the ID on the Security Report page or by choosing .
Server Response Code
The HTTP status code that the origin server sends in response to the request from WAF.
Status Code Returned by WAF
The HTTP status code that WAF sends in response to the request from the client.
Protection Features
The type of the WAF protection rule that is matched by the request. For more information about WAF protection rules and their configuration methods, see Overview.
If you want to compute and analyze the query results, you must enter an analytic statement following the search statement in the search box. If you only want to query logs that meet the search conditions, skip this step.
Analytic statements and search statements are separated by vertical bars (|). The analytic statements use the standard SQL-92 syntax. For more information about the analytic statements, see Overview of log query and analysis.
Specify the query time range by using the time selector that is marked as 2 in the preceding figure.
Click Search & Analyze that is marked as 3 in the preceding figure.
In the lower section of the page, you can view the query and analysis results in a log histogram and on the Raw Logs and Graph tabs. You can perform various operations based on the query and analysis results. For example, you can conduct quick analysis, generate charts, and configure alerts. For more information, see Manage query and analysis results and Create alert rules.
For more log query and analysis examples, see the "Query and analysis examples" section in this topic.
Manage query and analysis results
Log Service for WAF displays query and analysis results in a log histogram, on the Raw Logs tab, and on the Graph tab. Log Service for WAF also allows you to perform follow-up operations on the results, such as configuring alerts and creating saved searches.
Log histogram
The log histogram shows the breakdown of queried logs in different time ranges.
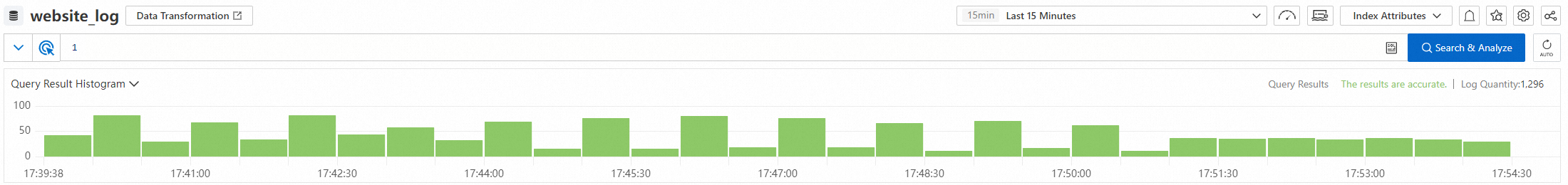
If you move the pointer over a green rectangle, you can view the time range that is represented by the rectangle and the number of logs that are obtained within the time range.
If you click the green rectangle, you can view a more fine-grained log breakdown. You can also view the query and analysis results on the Raw Logs tab.
Raw Logs
You can view the details of each log on the Raw Logs tab.
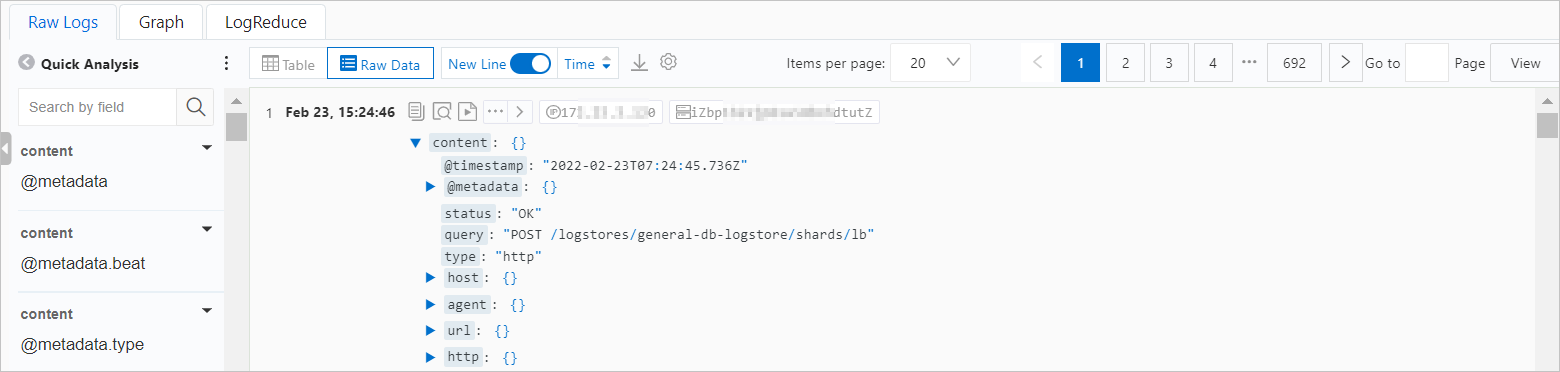
Quick analysis
You can click the
 icon to specify whether to show the names or aliases of fields. You can create aliases when you configure indexes. For example, if the alias of host_name is host, host is displayed in the Quick Analysis list after you select Show Field Aliases. Note
icon to specify whether to show the names or aliases of fields. You can create aliases when you configure indexes. For example, if the alias of host_name is host, host is displayed in the Quick Analysis list after you select Show Field Aliases. NoteIf a field does not have an alias, the name of the field is displayed in the Quick Analysis list even if you select Show Field Aliases.
For more information, see Quick analysis.
View log details
Click Table to view logs in a table.
Click Raw Data to view raw logs.
Click the
 icon to copy logs.
icon to copy logs. Click the
 icon to view the tag details.
icon to view the tag details.
Click New Line to determine whether to display logs in multiple lines.
Click Time to display logs in chronological order.
Click the
 icon to download logs to your computer. Download Log in Current Page, Download All Logs with Cloud Shell, and Download All Logs Using Command Line Tool are supported. For more information, see Download logs.
icon to download logs to your computer. Download Log in Current Page, Download All Logs with Cloud Shell, and Download All Logs Using Command Line Tool are supported. For more information, see Download logs. Click the
 icon and configure Tag Configurations, Column Settings, JSON Configurations, and Event Settings.
icon and configure Tag Configurations, Column Settings, JSON Configurations, and Event Settings.
Graphs
You can view the query and analysis results on the Graph tab. To view charts on the Graph tab, you must enter an analytic statement that uses the standard SQL-92 syntax in the search box.
Change the chart type: Select a chart type based on your business requirements to view the query and analysis results. For more information, see Chart configurations.
Preview a chart: Preview the chart after you change the chart type.
Click Add to New Dashboard to add the current chart to the dashboard. Click Download Log to download logs to your computer. Download Log in Current Page, Download All Logs with Cloud Shell, and Download All Logs Using Command Line Tool are supported. For more information, see Download logs.
Modify the settings of a chart
Operation
Description
Configure global settings for a chart. For example, you can select a color scheme to display the results of all query statements for the chart.
Configure personalized display settings for the results of a single query statement or for a single column of data in the results. For example, if you select a query statement and then select a color scheme, the chart is generated based on the results of the query statement and uses the color scheme that you select.
You can configure an interaction occurrence for the results of a query statement or for a single column of data in the results to analyze data from a fine-grained dimension.
LogReduce tab
On the LogReduce tab, click Enable LogReduce to cluster similar logs. For more information, see LogReduce.
Create alert rules
You can create alert rules based on the query and analysis results. After you create an alert rule, Log Service checks related query and analysis results on a regular basis. If a query and analysis result meets the trigger condition that you specified in the alert rule, Log Service sends an alert notification. This way, the service status is monitored in real time.
On the query and analysis page, you can choose to configure alerts based on the query and analysis results. For more information, see Configure an alert rule.
Query and analysis examples
Query the number of requests blocked by different WAF protection features every quarter hour. The results include the attack time (time), the numbers of requests blocked by Protection Rules Engine (wafmodule), requests blocked by the IP address blacklist and custom protection policies (aclmodule), and requests blocked by HTTP flood protection and custom protection policies (httpfloodmodule).
* | SELECT time_series(__time__, '15m', '%H:%i', '0') as time, COUNT_if(final_plugin = 'waf') as "wafmodule", COUNT_if(final_plugin = 'acl') as "aclmodule", COUNT_if(final_plugin = 'cc') as "httpfloodmodule" GROUP by time ORDER by timeQuery the breakdown of protection features (final_plugin) that perform protection actions. The results include the numbers of times that the protection features are triggered (times), requested domain names (host), and protection features (final_plugin).
* | SELECT count(*) as times, host, final_plugin GROUP by host, final_plugin ORDER by times descQuery the queries per second (QPS) every quarter hour. The results include the query time (time) and QPS (QPS).
* | SELECT time_series(__time__, '15m', '%H:%i', '0') as time, count(*) / 900 as QPS GROUP by time ORDER by timeQuery the domain names that suffer the most HTTP flood attacks. The results include the number of times that HTTP flood attacks are blocked (times) and the requested domain names (host).
* and acl_action :block | SELECT count(*) as times, host GROUP by host ORDER by times descQuery the log details about requests every second. The results include the request time (time), requested domain name (host), request path (request_path), request method (request_method), HTTP status code (status) that WAF responds, HTTP status code (upstream_status) that the origin server responds, and query string (querystring).
* | SELECT date_format(date_trunc('second', __time__), '%H:%i:%s') as time, host, request_path, request_method, status, upstream_status, querystring LIMIT 10Query the latest 10 attacks on the your_domain_name website. The results include the attack time (time), the originating IP address of the client, (real_client_ip), and client type (http_user_agent).
matched_host: your_domain_name and final_action: block | SELECT time, real_client_ip, http_user_agent ORDER by time desc LIMIT 10Query the number of days (days_passed) that have elapsed since an attack on the your_domain_name website was blocked by WAF. The value of days_passed is rounded to one decimal place.
matched_host: your_domain_name and final_action: block | SELECT time, round((to_unixtime(now())-__time__) / 86400, 1) as "days_passed", real_client_ip, http_user_agent ORDER by time desc LIMIT 10Query the trend of the number of attacks on the your_domain_name website by day.
matched_host: your_domain_name and final_action: block | SELECT date_trunc('day', __time__) as dt, count(1) as PV GROUP by dt ORDER by dtThe date_trunc function is used to group the time when attacks occurred by day. For more information about the function, see Date and time functions.
Query the breakdown of countries from which attacks are launched to the your_domain_name website.
matched_host: your_domain_name and final_action: block | SELECT ip_to_country( if(real_client_ip = '-', remote_addr, real_client_ip) ) as country, count(1) as "Number of attacks" GROUP by countryThe
real_client_ipfield in WAF logs indicates the originating IP address of a client. If a proxy server is used or the IP field in a request header is invalid, the originating IP address of the client cannot be obtained. In this case, the value of thereal_client_ipfield is displayed as a hyphen-. You can use the value of theremote_addrfield as the originating IP address of the client. The remote_addr field indicates the IP address that is used to connect to WAF.Query the breakdown of provinces from which attacks are launched to the your_domain_name website.
matched_host: your_domain_name and final_action: block | SELECT ip_to_province( if(real_client_ip = '-', remote_addr, real_client_ip) ) as province, count(1) as "Number of attacks" GROUP by provinceThe ip_to_province function is used to obtain information about the provinces in which the originating IP addresses of clients are located. For more information about the function, see IP functions.