This topic describes common types of HTTP flood attacks and how to defend against them by using protection policies offered by WAF.
Overview
Volumetric and high-rate HTTP flood attacks
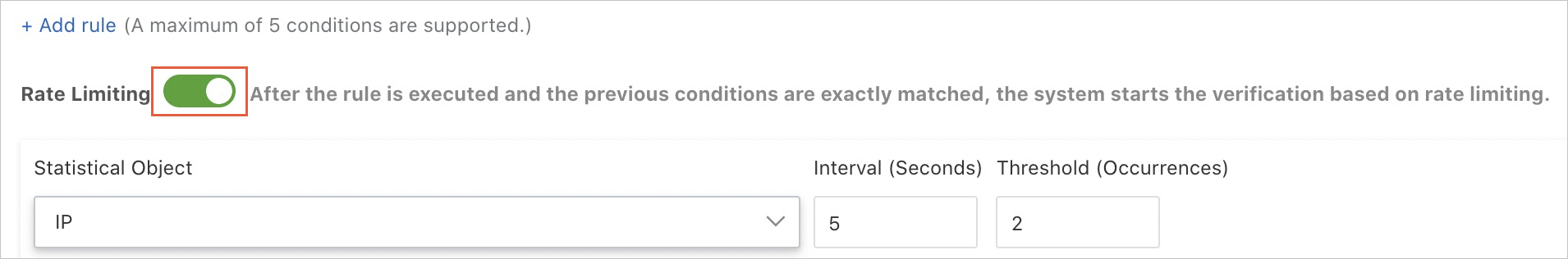
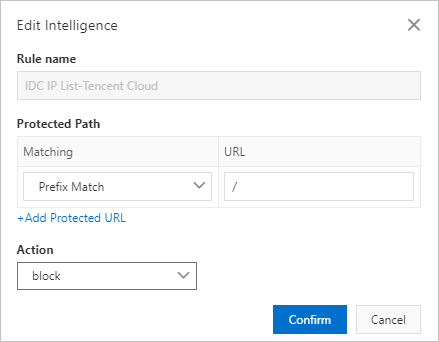
In volumetric HTTP flood attacks, a zombie server sends requests at a higher frequency than a normal server does. To prevent such attacks, the most effective measure is to limit the request rate of request sources. WAF provides the Rate Limiting function for this purpose. You can configure this function from the Custom Protection Policy page. For more information, see Create a custom protection policy.
/login.php, and block IP addresses that send more than 20 requests to access the path within
60 seconds.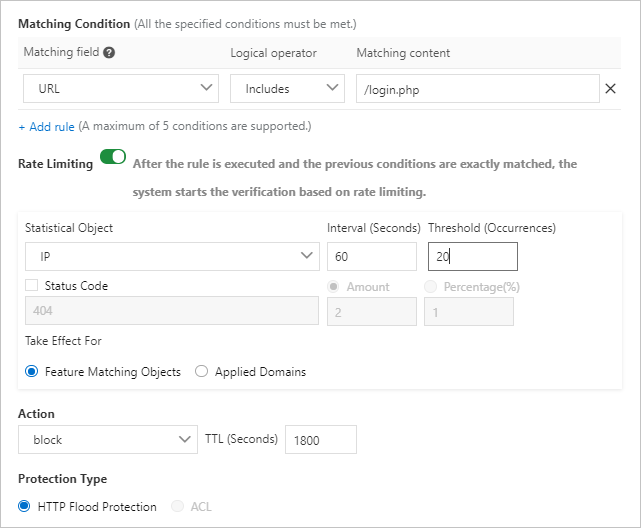
- Captcha and Strict Captcha in the Action drop-down list aim to verify whether requests originate from a human or an automation script. You can use these two actions to protect common and HTML5 web pages, but not native apps or APIs. To protect the native apps and APIs, set Action to block.
- You can configure whitelist policies for APIs or IP addresses that may be mistakenly blocked by HTTP flood protection on the Access Control/Throttling tab. For more information, see Configure a whitelist for Access Control/Throttling.
- Do not select the Protection-emergency mode for native apps or APIs in the HTTP Flood Protection section.
uid=12345.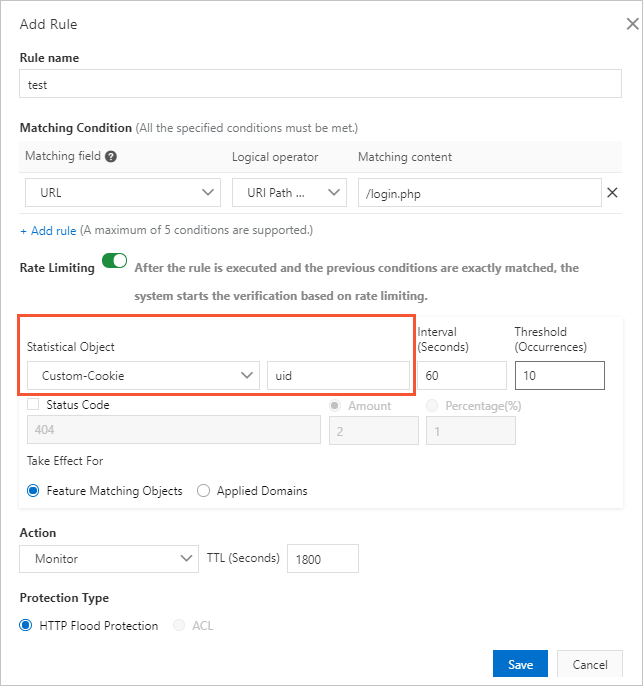
Attacks from regions outside China and public clouds
A large portion of HTTP flood attacks originate from regions outside China, on-premises data centers, and public clouds.
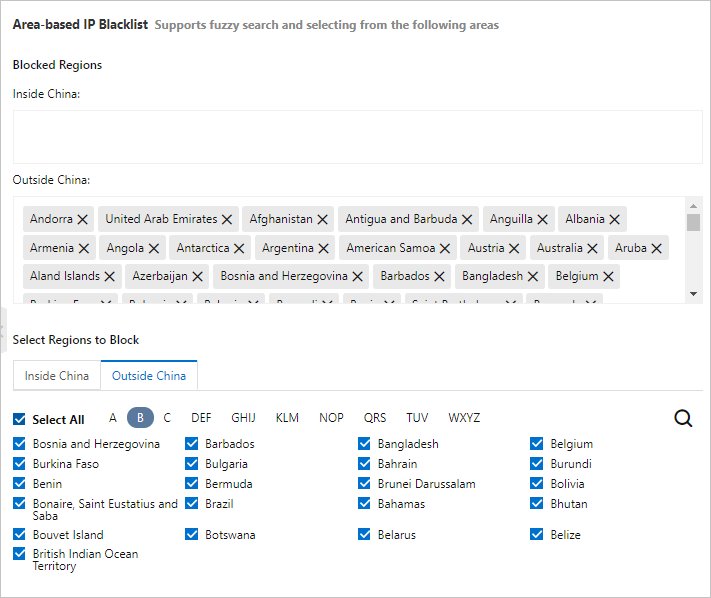
Malformed packets
- Abnormal or malformed User-Agent string: has characteristics of automation tools (such
as Python), is in an incorrect format (such as
Mozilla///), or is impossible to be used in normal requests (such aswww.example.com). If abnormal or malformed User-Agent strings are detected, block the requests. - Unusual User-Agent string: Promotional HTML5 pages that target WeChat users are supposed to be accessed through WeChat. It is unusual if the User-Agent string indicates that the request is sent from a Windows desktop browser, such as Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0. If unusual User-Agent strings are detected, block the requests.
- Abnormal referer field: If a request does not have a referer field or has a referer field that identifies the addresses of illegitimate websites, block the request. However, when a user visits your homepage or your website for the first time, the request may not contain the referer field. If a URL can only be accessed by using redirects, you can decide whether to block the URL based on the referer field.
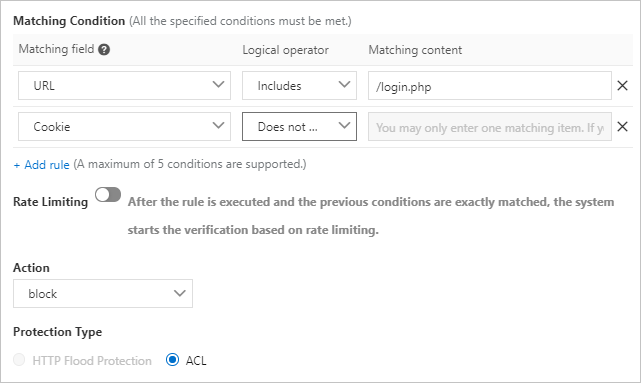
- Abnormal cookie: Similar to the referer field, a normal request contains cookies that identify the requested websites, unless it is the first time for the user to visit your website. Malicious requests in HTTP flood attacks typically do not contain any cookie information. You can block access requests without cookies.
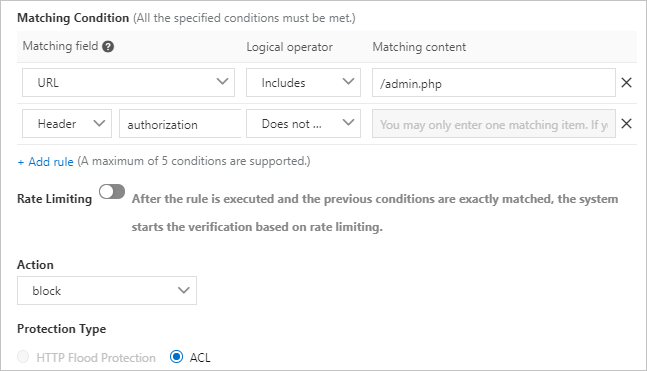
- Missing HTTP headers: Normal requests contain authorization headers while malicious requests do not.
- Incorrect request methods: If an API has only received POST requests before but is now overwhelmed by GET requests, you can block these GET requests.
You can analyze the features of requests and set Protection Type to ACL from the Custom Protection Policy page to block malicious requests. For more information, see Create a custom protection policy.
- Example 1: Block requests that do not contain cookies.
- Example 2: Block requests that do not contain authorization headers.
API abuse
We recommend that you use the data risk control function to protect important APIs from attacks. These APIs include logon, registration, voting, and SMS verification APIs.
Data risk control injects a JavaScript snippet into your website and collects information about user behaviors and environment variables to determine whether requests originate from a human or an automation script. Data risk control makes decisions based on CAPTCHA rather than the request rate or the source IP address. The function mitigates low-frequency attacks very effectively.
For more information, see Configure data risk control.
Malicious scans
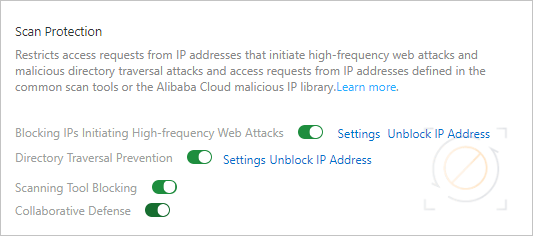
- Blocking IPs Initiating High-frequency Web Attacks: automatically blocks client IP addresses that initiate high-frequency web attacks.
- Directory Traversal Prevention: automatically blocks client IP addresses that initiate multiple directory traversal attacks in a short period of time.
- Scanning Tool Blocking: automatically blocks access requests from IP addresses defined in the common scan tools or the Alibaba Cloud malicious IP library.
- Collaborative Defense: automatically blocks access requests from IP addresses defined in the Alibaba Cloud malicious IP library.
For more information, see Configure scan protection.
App attacks
In addition to the preceding measures, you can also use SDK to enhance protection.
After you integrate the SDK with your app, all incoming requests are verified before they are sent to your server. The device information and request signature are combined to determine whether the requests are from legitimate apps. Requests that do not originate from official apps are automatically blocked. This ensures that only valid requests are served. You do not need to analyze the patterns of invalid requests.
To use the SDK, you must enable App Protection. For more information, see Configure application protection.
Malicious crawlers
For informational websites that offer services such as credit reports, apartment rentals, airline tickets, and e-book reading, malicious crawlers can significantly increase the bandwidth usage and server workload, and even cause data leaks. If the preceding measures cannot prevent against malicious crawlers, we recommend that you enable and use the Bot Management feature for more effective protection. For more information, see Configure a whitelist for Bot Management.