VPN Gateway is integrated with Network Intelligence Service (NIS). You can use NIS to diagnose VPN gateways and troubleshoot issues based on the solutions provided by NIS. This way, you can troubleshoot the issues that you encounter when you use SSL-VPN connections. The issues include SSL negotiation issues and issues that are related to the VPN gateway status. The diagnostic process does not affect your business.
Diagnostic items
The following table describes the diagnostic items of a VPN gateway.
Category | Diagnostic item | Description |
Configuration Diagnostics | Instance configurations | Checks whether a VPN gateway is being configured. If the VPN gateway is being configured, wait until the VPN gateway enters the Active state before you perform an operation on the VPN gateway. |
Version check | Checks whether the VPN gateway uses the latest version. We recommend that you upgrade your VPN gateway to the latest version. For more information, see Upgrade a VPN gateway. | |
VPN tunnel configurations | Checks whether the SSL server that is used to create SSL-VPN connections is configured on the VPN gateway. If the required parameters are not configured, configure the parameters based on your network communication requirements. For more information, see Create and manage an SSL server. | |
Unreliable SSL connections | Checks whether unreliable SSL-VPN connections exist on the VPN gateway. If unreliable SSL-VPN connections that use the UDP protocol exist on an SSL server, we recommend that you set the Protocol parameter of the SSL server to TCP to resolve this issue. The TCP protocol is more reliable than the UDP protocol. For more information, see Modify an SSL server. | |
CIDR block conflicts within a virtual private cloud (VPC) | Checks whether the Local Network and Client CIDR Block configured for an SSL server conflict with the CIDR block of a vSwitch in the VPC. If such conflicts exist, we recommend that you modify the CIDR block of the SSL server. For more information, see Modify an SSL server. | |
Insufficient IP addresses | Checks whether the Client CIDR Block configured for an SSL server contains sufficient IP addresses to meet the requirements of SSL-VPN connections. If the IP addresses are insufficient, modify the client CIDR block. For more information, see Modify an SSL server. Make sure that the number of IP addresses in the client CIDR block is at least four times the number of SSL-VPN connections on the VPN gateway. For example, if you specify 192.168.0.0/24 as the client CIDR block, the system first divides a subnet CIDR block with a subnet mask of 30 from 192.168.0.0/24, such as 192.168.0.4/30. This subnet provides up to four IP addresses. Then, the system allocates an IP address from 192.168.0.4/30 to the client and uses the other three IP addresses to ensure network communication. In this case, one client consumes four IP addresses. Therefore, to ensure that an IP address can be allocated to your client, you must make sure that the number of IP addresses in the client CIDR block is at least four times the maximum number of SSL-VPN connections supported by the associated VPN gateway. | |
Public CIDR block conflicts | Checks whether the public CIDR block that is configured as the Client CIDR Block of an SSL server is specified as the user CIDR block of the VPC. If the client CIDR block of the SSL server is a public CIDR block, you must specify the public CIDR block as the user CIDR block of the VPC. For more information, see the What is a user CIDR block? and How do I configure a user CIDR block? sections of the "VPC FAQ" topic. | |
Quota Limit Diagnostics | VPN gateway bandwidth usage | Checks whether the bandwidth usage of the VPN gateway reaches 80% of the upper limit. If the bandwidth usage of the VPN gateway reaches 80% of the upper limit, you can upgrade the bandwidth of the VPN gateway based on your network requirements. For more information, see Upgrade or downgrade a VPN gateway. |
VPN connections | Checks whether the number of SSL-VPN connections on the VPN gateway reaches 80% of the upper limit. If the number of SSL-VPN connections on the VPN gateway reaches 80% of the upper limit, you can request a quota increase based on your network requirements. For more information, see Modify the maximum number of concurrent SSL connections. | |
Certificate Diagnostics | SSL client certificate expiration | Checks whether the SSL client certificate has expired. By default, the validity period of the SSL client certificate is three years. If the SSL client certificate has expired, delete the SSL client certificate, create a new SSL client certificate, and then install the new certificate on the client. For more information, see Create and manage an SSL client certificate and the Step 4: Configure the client section of the "Connect a client to a VPC" topic. |
SSL client certificate pre-expiration | Checks whether the SSL client certificate expires within 60 days. If the SSL client certificate expires within 60 days, we recommend that you delete the SSL client certificate, create a new SSL client certificate, and then install the new certificate on the client. For more information, see Create and manage an SSL client certificate and the Step 4: Configure the client section of the "Connect a client to a VPC" topic. | |
Cost Diagnostics | Overdue payments | Checks whether the VPN gateway has overdue payments. If the VPN gateway has overdue payments, add funds to your account. |
VPN gateway expiration | Checks whether the VPN gateway expires within seven days. |
Start a diagnostics
Log on to the VPN Gateway console.
In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the VPN gateway is deployed.
On the VPN Gateways page, find the VPN gateway that you want to diagnose and choose in the Diagnose column.
In the Instance Diagnostics panel, view the diagnostic details.
NoteIf NIS is not activated, select Terms of Service for Standard Edition NIS and click Activate NIS free of charge to diagnose instances.
If you activate NIS as a RAM user and a message appears indicating that you do not have the permission, grant the AliyunNISFullAccess permission to the RAM user by using your Alibaba Cloud account. For more information, see Grant permissions to a RAM user.
If this is the first time that you perform a diagnostics, the system automatically creates the service-linked role AliyunServiceRoleForNis. For more information, see Service-linked roles.
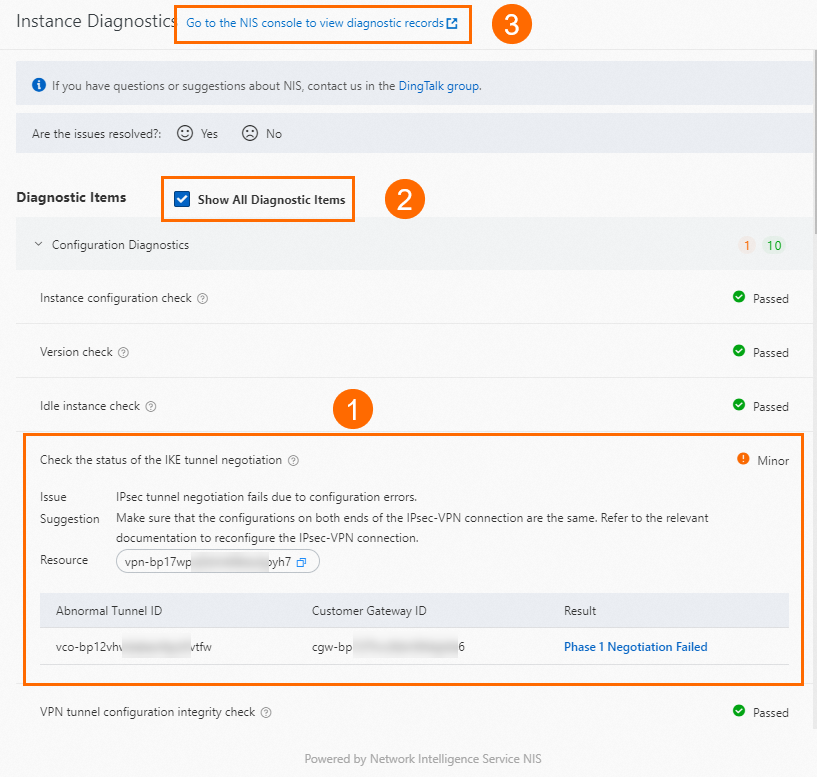
Section
Description
①
Anomalies are displayed in the Instance Diagnostics panel. You can view the diagnosis description, relevant resources, and suggestions.
②
You can select Show All Diagnostic Items in the Diagnostic Items section to view all diagnostic items of the VPN gateway.
③
You can go to the Overview page of the NIS console by clicking Go to the NIS console to view diagnostic records in the upper part of the Instance Diagnostics panel to view historical diagnostic reports about the VPN gateway. For more information, see Use features on the Overview page.
Diagnostics examples
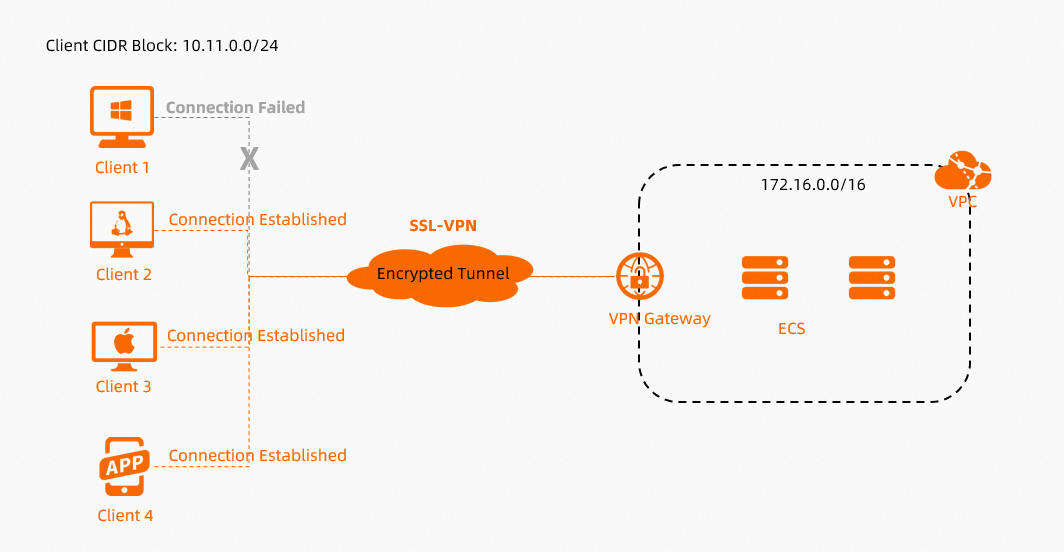
In scenarios in which you access VPC resources by using SSL-VPN connections, if issues such as client connection failures occur, you can diagnose the VPN gateway for troubleshooting.
Start a diagnostics. For more information, see the Start a diagnostics section of this topic.
In the Instance Diagnostics panel, view the diagnostic details.
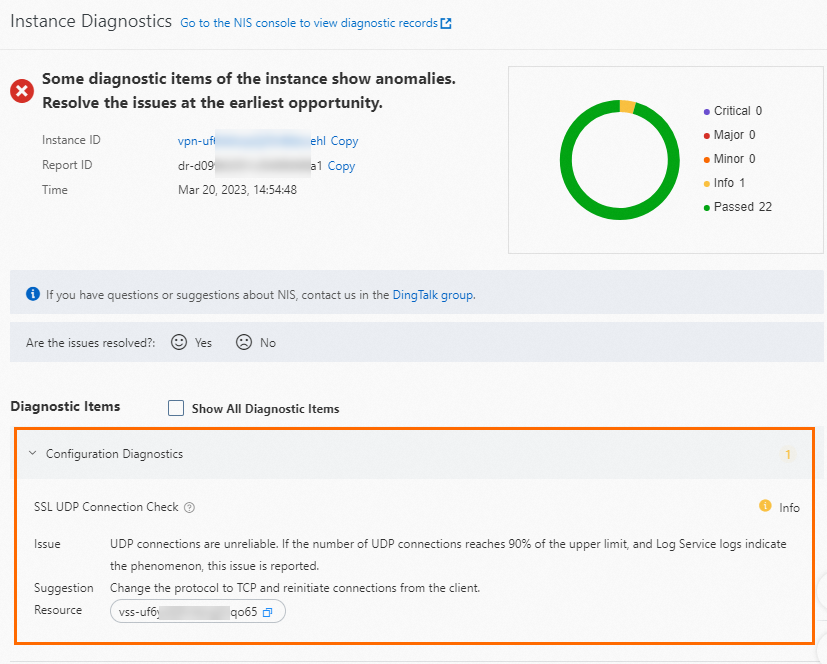
The preceding figure shows an example of a VPN gateway that fails the diagnostics due to failed client connections. The client connections fail because the SSL server uses UDP to establish SSL-VPN connections. We recommend that you change the protocol of the SSL server to TCP to prevent this issue.
After you resolve the issue, diagnose the VPN gateway again. Make sure that the VPN gateway passes the diagnostics.
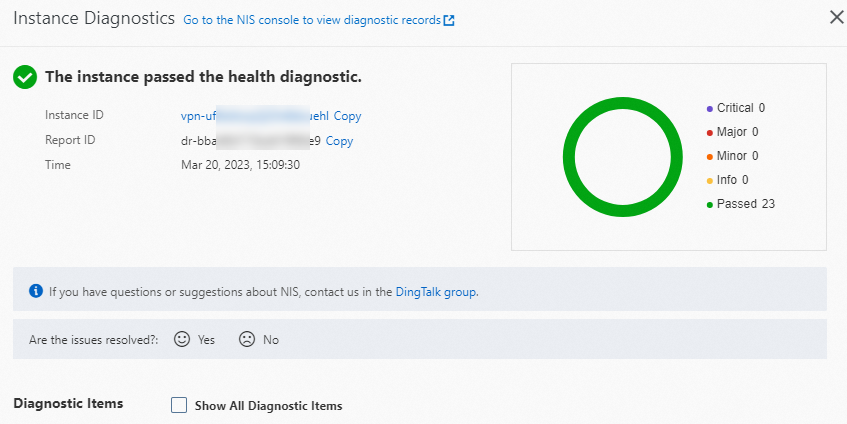
If the VPN gateway passes the diagnostics but issues occur when you use the SSL-VPN connection, such as communication failures between the data center and the VPC, view the logs of the SSL-VPN connection and refer to the FAQ topics of VPN Gateway for troubleshooting. For more information, see Troubleshoot SSL-VPN connection issues and FAQ about SSL-VPN connections.