Remote authentication is an access control feature that protects your resources. This feature works by verifying user requests sent to Alibaba Cloud Content Delivery Network (CDN) edge nodes. Based on the verification result from your authentication server, CDN determines how to process each request. When you enable remote authentication, only authorized users can access your resources. This topic describes how remote authentication works, explains how to enable it in the console, and provides related API references.
How it works
ApsaraVideo VOD supports both URL signing and remote authentication to prevent unauthorized downloading or use of your resources. These two features differ in their technical implementation:
URL signing: You send the authentication rules for a domain name to the CDN edge nodes. The edge nodes then handle the entire authentication process. For more information, see URL signing.
Remote authentication: You must set up and manage your own authentication server. When a CDN edge node receives a user request that requires authentication, it forwards the request to your authentication server for verification.
The following figure shows how remote authentication works.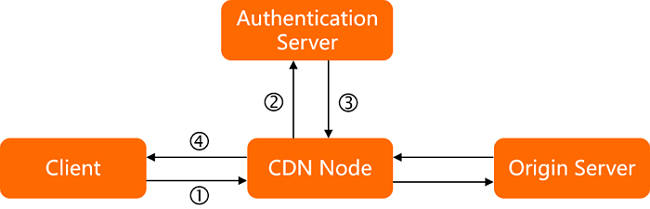
A user sends a resource access request to a CDN edge node. The request contains authentication parameters.
The CDN edge node receives the user request and forwards it to the authentication server.
The authentication server verifies the parameters in the request, determines the result, and sends the result back to the CDN edge node.
The CDN edge node processes the user request based on the authentication result. If authentication is successful, access is granted. If it fails, access is denied or restricted. For example:
Example 1: Authentication is successful. The CDN edge node serves the cached data to the user.
Example 2: Authentication fails. The CDN edge node returns an HTTP 403 status code to the user.
Example 3: Authentication fails. The CDN edge node throttles the user's access.
Example 4: Authentication times out. The CDN edge node performs the default action for timeouts, which is to allow the request.
Usage notes
After you enable remote authentication, all user requests are authenticated. If you expect a high volume of requests, consider the processing load and performance of your authentication server.
Procedure
Log on to the ApsaraVideo VOD console.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose Configuration Management.
Click CDN Configuration > Domain Names to go to the Domain Names page.
Find the domain name that you want to configure and click Configure.
Click Resource Access Control.
Click the Remote Authentication tab.
Turn on Remote Authentication and configure the parameters.
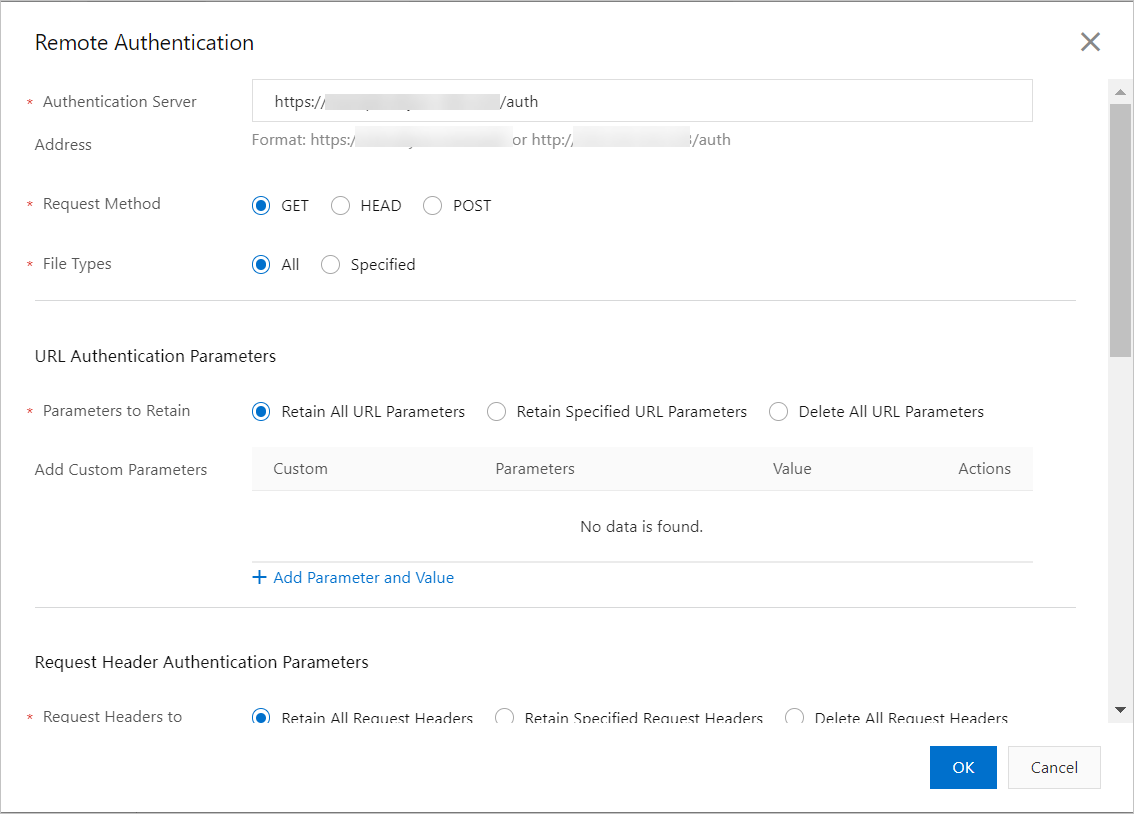
 The following table describes the parameters.
The following table describes the parameters.Parameter
Description
Authentication Server Address
The publicly accessible address of your authentication server. The system validates the format and value of the address you enter.
Format requirements
The format must be one of the following:
http://example.com/auth
https://example.com/auth
http://192.0.2.1/auth
https://192.0.2.1/auth
Value requirements
The value cannot contain 127.0.0.1 or localhost, because these local addresses are invalid.
Request Method
The request methods that the authentication server supports. Valid values are GET, HEAD, and POST.
POST
Parameters are transmitted in the request body. The address bar remains unchanged.
Theoretically, there is no limit on the size of data transmission.
Requests are not cached or saved in the browser history.
Relatively high security.
GET
Parameters are transmitted in the request line. The address bar displays the submitted parameter values.
Due to browser limitations, the maximum data transmission size is 1024 bytes.
Requests can be cached and are saved in the browser history.
Relatively low security.
HEAD
The HEAD method is the same as the GET method, but the server does not return a request body in the response.
File Type for Authentication
All file types: All files are authenticated.
Specified file types: Only the specified file types are authenticated.
To specify multiple file types, separate them with a vertical bar (|). For example: mp4|flv.
File types are case-sensitive. For example, jpg and JPG are two different file types.
Parameter Retention Settings
Controls which parameters from the user's request URL are included in the authentication. You can select Retain all parameters, Retain specified parameters, or Delete all URL parameters.
To retain specified parameters, separate multiple parameters with a vertical bar (|). For example: user|token.
Parameters are case-sensitive. For example, key and KEY are two different parameters.
Add Custom Parameters
Adds custom parameters to the request URL that the CDN edge node forwards to the authentication server.
You can select Custom to set parameters and values, or select Select Parameter to use preset variables from the ApsaraVideo VOD console.
When you set custom parameters and values, note the following:
Separate multiple parameters with a vertical bar (|). For example: token=$arg_token|vendor=ali_cdn.
Parameters are case-sensitive. For example, key and KEY are two different parameters.
When you use preset variables, you can extract the variable values and add them to the request that CDN forwards to the authentication server.
For example, if you select the $http_host variable, host=$http_host is added to the user's request URL. Here, host represents the value of the host field in the user's request header. For a description of variable names and their meanings, see Variables.
Request Header Retention Settings
Controls which headers from the user's request are included in the authentication. You can select Retain all headers, Retain specified headers, or Delete all request headers.
To retain specified headers, separate multiple headers with a vertical bar (|). For example: user_agent|referer|cookies.
Parameters are not case-sensitive. For example, http_remote_addr and HTTP_Remote_Addr are the same parameter.
NoteIf you select Retain all headers, CDN POPs delete the HOST header by default. To keep the HOST header, use Retain specified headers or Add Custom Parameters. The HOST header is deleted by default because the HOST header forwarded to the authentication server contains the accelerated domain name. This may prevent the authentication server from recognizing the request, leading to a 404 error or authentication failure.
Add Custom Parameters
Adds custom parameters to the request header that the CDN edge node forwards to the authentication server.
You can select Custom to set parameters and values, or select Select Parameter to use preset variables from the ApsaraVideo VOD console.
When you set custom parameters and values, note the following:
Separate multiple request headers with a vertical bar (|). For example: User-Agent=$http_user_agent|vendor=ali_cdn.
Parameters are not case-sensitive. For example, http_remote_addr and HTTP_Remote_Addr are the same parameter.
When you use preset variables, you can extract the variable values and add them to the request that CDN forwards to the authentication server.
For example, if you select the $http_host variable, host=$http_host is added to the user's request URL. Here, host represents the value of the host field in the user's request header. For a description of variable names and their meanings, see Variables.
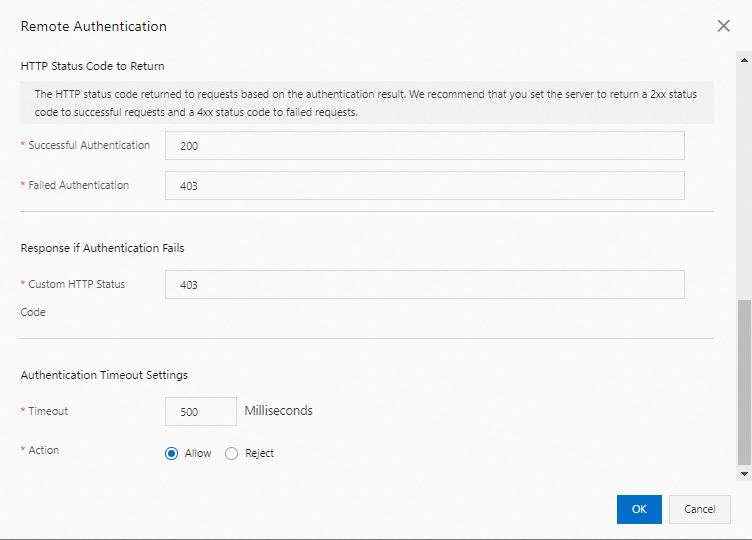
Success Status Code
The HTTP status code that the authentication server returns for a successful authentication. We recommend setting this to a 2xx status code.
For example, if you set this to 200, a response of 200 from the authentication server means success. If the server returns a status code that is not a success or failure code, the request times out.
Status Codes for Authentication Failure
The HTTP status code that the authentication server returns for a failed authentication. We recommend setting this to a 4xx status code.
For example, if you set this to 403, a response of 403 from the authentication server means failure. If the server returns a status code that is not a success or failure code, the request times out.
Custom Response Status Code
The status code that the CDN edge node returns to the user when authentication fails.
For example, if you set this to 403, the CDN edge node returns 403 to the user when a request fails authentication.
Timeout Period
The time from when a CDN edge node sends an authentication request until it receives a response from the authentication server.
The unit is milliseconds. The maximum value is 3000 milliseconds.
Action on Timeout
The action that the CDN edge node takes on a user request if the interaction with the authentication server times out. Valid values:
Allow: The CDN POP allows the user request.
Deny: The CDN POP denies the request and returns the custom response status code that you configured.
Click OK to complete the configuration.
After you configure remote authentication, you can modify or disable it on the Remote Authentication tab.
Variables
When you add custom parameters, you can use the preset variables that are available in the ApsaraVideo VOD console. The following table describes these variables.
Variable name | Description |
$http_host | The value of the host field in the request header. |
$http_user_agent | The value of the user_agent field in the request header. |
$http_referer | The value of the referer field in the request header. |
$http_content_type | The value of the content_type field in the request header. |
$http_x_forward_for | The value of the x_forward_for field in the request header. |
$remote_addr | The client IP address of the request. |
$scheme | The protocol type of the request. |
$server_protocol | The protocol version of the request. |
$uri | The original URI of the request. |
$args | The query string of the request, without the question mark (?). |
$request_method | The request method. |
$request_uri | The content of uri + '?' + args. |