Simple Log Service (SLS) automatically moves log data between hot, Infrequent Access (IA), and Archive storage tiers based on retention policies you configure. This reduces long-term storage costs by up to 91% while keeping all data queryable in real time -- no scripts, no manual retrieval, no application changes.
Storage tiers
SLS provides three storage tiers. Each tier balances query performance, concurrency, and cost differently. All three tiers support the same capabilities -- query, analysis, visualization, alerting, shipping, and transformation. Data in every tier is accessible in real time without retrieval fees.
| Tier | Best for | Latency (billions of records) | Concurrency per project (query / analysis) | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hot storage | High-frequency queries and real-time analysis | 10-100 ms | 100 / 2 | USD 0.002875/GB-day |
| IA storage | Low-frequency queries and problem backtracking | 100 ms-seconds | 10 / 2 | USD 0.000762/GB-day |
| Archive storage | Long-term retention for data audits | Minutes | 1 / 1 | USD 0.000259/GB-day |
IA storage was formerly known as cold storage.
How data moves between tiers
SLS manages data movement automatically based on the retention periods configured for each tier. Data progresses from hot to IA to Archive as it ages, and is deleted after the total retention period expires.

Forward movement (automatic)
Data moves forward when the retention period for a tier elapses:
| Movement | Minimum retention before move |
|---|---|
| Hot -> IA | 7 days in hot storage |
| Hot -> Archive | 30 days in hot storage |
| IA -> Archive | 30 days in IA storage |
The minimum retention period for Archive storage is 60 days.
Reverse movement (on-demand)
Move data back to a higher-performance tier by increasing the retention period for that tier.
| Direction | How to trigger |
|---|---|
| IA -> Hot | Increase the hot storage retention period |
| Archive -> IA | Increase the IA storage retention period |
| Archive -> Hot | Increase the hot storage retention period |
After a retention period change, SLS starts moving data within approximately 1 minute.
Retention period examples
The data retention period of a Logstore equals the sum of the retention periods for all configured tiers.
Example 1: 90-day retention with two tiers
Hot storage: 30 days, Archive storage: 60 days. Data moves from hot to Archive after 30 days and is deleted after 90 days total.
Example 2: 97-day retention with three tiers
Hot storage: 7 days, IA storage: 30 days, Archive storage: 60 days. Data moves from hot to IA after 7 days, from IA to Archive after 30 more days, and is deleted after 97 days total.
Example 3: Permanent retention
Set the data retention period to 3,650 days for permanent storage. Data that remains in the Archive tier after 3,650 days is not deleted -- it continues to be stored in the Archive tier indefinitely.


Configure tiered storage
Console
Log on to the Simple Log Service console.
In the Projects section, click the one you want.
On the tab, click the
 icon next to the Logstore and select Modify.
icon next to the Logstore and select Modify.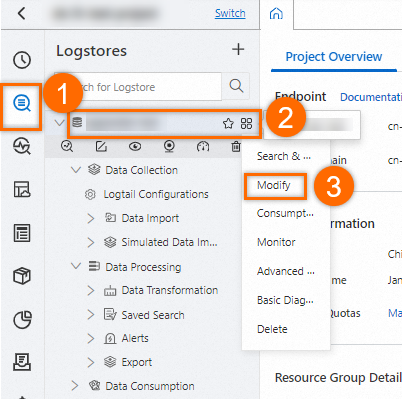
On the Logstore Attributes page, click Modify. Turn on Intelligent Tiered Storage, configure the storage policy, and click Save.

The following table describes the tiered storage parameters. For other Logstore parameters, see Create a basic logstore.
Parameter
Description
Data Retention Period
Set to Specified Days or Permanent Storage. The total retention period equals the sum of all tier retention periods.
Intelligent Tiered Storage
Turn on to enable tiered storage.
Storage Policy
Configure the retention period for each tier.
Data retention period for the hot storage tier
Set to 7-3,650 days for hot-to-IA movement, or 30-3,650 days for hot-to-Archive movement. Must be less than the total Data Retention Period.
Data retention period for the IA storage tier
Set to 30-3,650 days. Must be less than the total Data Retention Period.
Data retention period for the Archive storage tier
Set to 60-3,650 days. Data is automatically deleted when this period elapses. Must be less than the total Data Retention Period.
ImportantAfter you shorten the total data retention period, the change takes effect within 1 minute. For example, if you reduce the retention period from 5 days to 1 day, SLS deletes data from the previous 4 days. Actual deletion may be delayed by up to 7 days, but delayed data does not incur charges or count toward storage capacity.
After you change the retention period for the hot or IA storage tier, SLS starts moving data based on the new setting within approximately 1 minute.
API
Use the following API operations to configure tiered storage programmatically:
Create a Logstore with tiered storage: Call CreateLogStore and set the
ttl,hot_ttl, andinfrequentAccessTTLparameters.Update tiered storage for an existing Logstore: Call UpdateLogStore and modify the
ttl,hot_ttl, andinfrequentAccessTTLparameters.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
ttl | Total data retention period of the Logstore (days) |
hot_ttl | Data retention period for the hot storage tier (days) |
infrequentAccessTTL | Data retention period for the IA storage tier (days) |
Billing
Storage tiers differ only in storage cost per GB-day. Data movement between tiers is free.
| Billing model | Details |
|---|---|
| Pay-by-feature | Standard tiered storage charges apply based on the tier and retention period. |
| Pay-by-ingested-data | Hot storage is free for 30 days after data ingestion. After 30 days, charges apply. If intelligent tiered storage is enabled, charges are based on the tier and retention period. |
For detailed billing information, see Billing overview and Billing examples.
References
Manage a Logstore -- Create, modify, or delete a Logstore
Set the data retention period and delete logs -- Configure permanent storage (3,650 days)
Pay-as-you-go -- Compare pay-by-feature and pay-by-ingested-data billing modes
Storage redundancy -- SLS supports locally redundant storage (LRS) and zone-redundant storage (ZRS)