Application Load Balancer (ALB) provides higher Layer 7 load balancing capabilities and more advanced routing features than Classic Load Balancer (CLB). ALB can balance large volumes of network traffic at the application layer and is interfaced with Web Application Firewall (WAF). Traffic forwarding and protection are decoupled for ALB. ALB supports more advanced features, which improve user experience. This topic describes how to migrate Layer 7 listeners from CLB to ALB by using a wizard.
Limits
CLB instances that the migration wizard supports
Internal-facing IPv4 CLB instances that are deployed in virtual private clouds (VPCs) and for which Layer 7 HTTP or HTTPS listeners are configured
Internet-facing IPv4 CLB instances for which Layer 7 HTTP or HTTPS listeners are configured
CLB instances that the migration wizard does not support
The migration wizard does not support the following types of CLB instances. We recommend that you manually migrate the CLB instances. For more information, see Guide for manually migrating layer 7 listeners from CLB to ALB.
CLB instances for which no HTTP or HTTPS listeners are configured
Internal-facing CLB instances that are deployed on the classic network
IPv6 CLB instances
Usage notes
You cannot use the migration wizard in a region that is not supported by ALB. For more information about the regions that are supported by ALB, see Supported regions and zones.
The configurations of WAF cannot be migrated. If WAF is enabled for a CLB instance, you must manually enable WAF for the destination ALB instance after the migration is complete. We recommend that you enable WAF 3.0 for a new ALB instance. For more information, see Enable WAF protection for an ALB instance.
The threshold-triggered alert rules that are configured for a CLB instance cannot be migrated. After the migration is complete, you can configure the alert rules for the destination ALB instance by using the CloudMonitor console, calling API operations, or using SDKs. For more information, see Configure alert rules for ALB metrics.
Anti-DDoS is enabled by default. The configurations that are used to increase the Anti-DDoS protection threshold cannot be migrated. After the migration is complete, you can manually increase the Anti-DDoS protection threshold in the Traffic Security console.
Access control configurations cannot be migrated. You can configure access control for the destination ALB instance after the migration is complete. For more information, see Network ACLs.
You must manually specify a server certificate and a certificate authority (CA) certificate for an HTTPS listener.
Configurations of the primary and secondary server groups of a CLB instance cannot be migrated to an ALB instance.
The backend servers of an internal-facing CLB instance can be directly migrated to an ALB instance. The backend servers of an Internet-facing CLB instance cannot be migrated to an ALB instance. The system creates a server group in the VPC in which the ALB instance resides during the migration. You must manually add backend servers to the server group. The backend servers must reside in the same VPC as the ALB instance.
Billing
You can use the migration wizard free of charge. However, you are charged for the ALB instance that is created during the migration based on the ALB billing rules.
Prerequisites
A Layer 7 HTTP or HTTPS listener is configured for the CLB instance to be migrated.
Relevant Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances are created. In this example, four ECS instances are used.
ECS instances that host business applications: ECS01 and ECS02 that are used as backend servers
ECS instances that are used for testing: ECS03 that is used to perform traffic tests before the migration and ECS04 that is used to verify the access traffic during the migration
If you have existing ECS instances for testing, you do not need to create ECS03 or ECS04.
Step 1: Use the migration wizard in the console
Use one of the following methods to go to the migration wizard.
Method 1: Go to the migration wizard in the CLB console
Log on to the CLB console.
In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the CLB instance resides.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose CLB > Instances. On the Instances page, find the CLB instance that you want to migrate and click the ID of the instance.
On the instance details page, click the Migration Wizard tab, read the confirm message, then in the Migrate from CLB to ALB card, click Enable.
Method 2: Go to the migration wizard in the ALB console
NoteIf you don't have any ALB instances in the region where the CLB instance to be migrated resides, this feature is not available. Use method 1 instead.
Log on to the ALB console.
In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the CLB instance resides.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose ALB > Instances. On the Instances page, click Migrate from CLB to ALB.
In the Migrate from CLB to ALB dialog box, read the confirm message, select the CLB instance that you want to migrate, and then click Open Migration Wizard.
In the Review Configurations step, confirm the basic information of the CLB instance and the predefined configurations of the ALB instance, configure the items marked with
 for all listeners, select the check box for Confirm system-modified configurations, and then click Next.
for all listeners, select the check box for Confirm system-modified configurations, and then click Next.  : the item that you need to manually configure.
: the item that you need to manually configure.  : the item that is automatically modified by the system.
: the item that is automatically modified by the system.
You can click Modify Listener and Modify Certificate to modify the configurations of the ALB listeners. You can modify certificates only for HTTPS listeners.
In the Create Instance step, configure the VPC and vSwitch to which the ALB instance belongs, and click Next.
Parameter
Description
VPC
If you migrate an internal-facing CLB instance, the ALB instance is created in the same VPC as the CLB instance by default.
If you migrate an Internet-facing CLB instance, you need to manually configure a VPC for the ALB instance.
Zone
Select a zone and a vSwitch.
ALB supports multi-zone deployment. If the selected region supports two or more zones, select at least two zones to ensure the high availability of your service. ALB does not charge additional fees.
Select a vSwitch in each zone that you selected. If no vSwitch is available, create a vSwitch as prompted.
Optional: If you migrate an Internet-facing CLB instance, you must select an EIP in the selected zone.
If no EIP is available in the selected zone, you can select Purchase EIP. Then, the system automatically creates an EIP that uses the pay-as-you-go billing method and the pay-by-data-transfer metering method and associates the EIP with the ALB instance. The EIP uses BGP (Multi-ISP) lines and is protected by Anti-DDoS Origin Basic.
You can also associate an existing EIP with the ALB instance.
ImportantYou can associate only pay-as-you-go (pay-by-data-transfer) EIPs that are not associated with Internet Shared Bandwidth instances with an ALB instance.
The EIPs allocated to different zones of the same ALB instance must be of the same type.
In the Confirm Order step, confirm the configurations of the ALB instance, select the check boxes in the Pricing/Billing section, then click Start Migration.
In the Complete step, wait until the migration task is complete. Then, you can perform the following operations.
The migration task takes about 1 to 10 minutes to complete. Resource Orchestration Service (ROS) is used to perform the migration task. You can go to the ROS console to view the execution process of the task in the relevant stack.
Click View ALB Instance to go to the details page of the ALB instance.
Click CLB Instance List to go to the CLB instance list.
Click ALB Instance List to go to the ALB instance list.
After the migration task is complete, check whether the ALB instance has backend servers.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Instances page, find the ALB instance and click the ID of the instance.
On the instance details page, click the Listener tab. On the Listener tab, find the listener that you want to manage and click View Details in the Actions column.
On the Listener Details tab, click View/Modify Backend Server in the Server Group (Default Forwarding Rule) section. You are navigated to the Backend Servers tab. On the Backend Servers tab, check whether the ALB instance has backend servers.
If the ALB instance does not have backend servers, click Add Backend Server to add at least two backend servers to the ALB instance and deploy applications on each backend server. This ensures that the ALB instance can forward access requests from clients. In this example, ECS01 and ECS02 are added to the ALB instance as backend servers.
For more information about how to create an ECS instance, see Create an instance by using the wizard.
The following sample commands are used to deploy test applications on ECS01 and ECS02:
Step 2: Perform traffic tests
(Optional) Enable the access log feature
ALB and Simple Log Service provide the access log feature that allows you to monitor the loads of ALB instances and identify issues.
Log on to the ALB console.
In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the ALB instance resides.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose ALB > Instances. On the Instances page, find the ALB instance that you want to manage and click the ID of the instance.
On the instance details page, click the Access Logs tab. On the Access Logs tab, click Create Access Log.
In the Create Access Log dialog box, configure the Project and Logstore parameters, and click OK. In the message that appears, click OK.
Parameter
Description
Project
The Simple Log Service project that is used to isolate and manage resources. Valid values:
Select Project: Select a project from the drop-down list.
Create Project: Enter a project name in the field. A project is automatically created.
Logstore
The Logstore that is used to collect, store, and query logs in Simple Log Service. Valid values:
Select Logstore: Select a Logstore from the drop-down list.
Create Logstore: Enter a Logstore name in the field. A Logstore is automatically created. If you select Create Project, you must select Create Logstore.
Notes on Creating Service-linked Role
When you perform this operation, a service-linked role is automatically created.
Test traffic
Remotely log on to ECS03.
NoteIn this example, a public IP address is assigned to ECS03 when the instance is purchased.
Run the following command to open the hosts file:
sudo vi /etc/hostsAdd the EIP and domain name of the ALB instance to the hosts file. After the modification is complete, save and close the file.
118.XX.XX.113 www.example.netRun the following command to check whether the ALB instance can forward traffic as expected:
curl -v www.example.netThe following figure shows the test result.
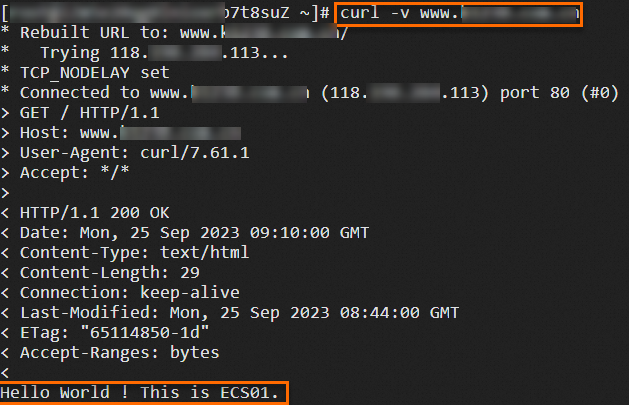
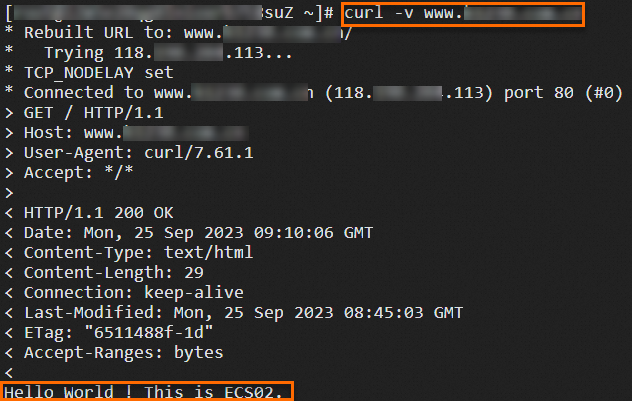
Optional. Return to the ALB console, go to the Access Logs tab on the details page of the ALB instance, and then click the link on the right side of the Simple Log Service to view the access logs.
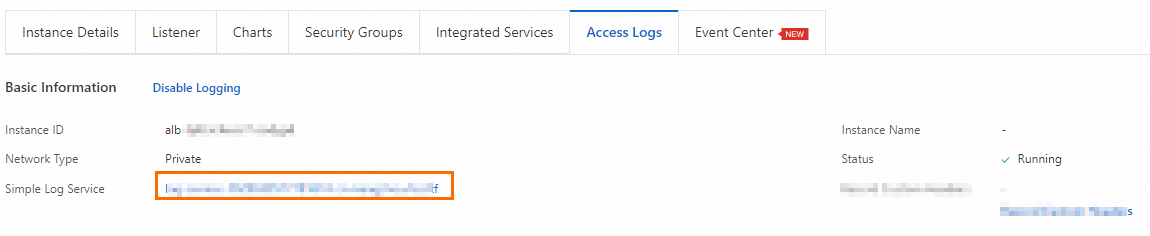 In the Simple Log Service console, you can view the run logs of the domain name- or URL-based forwarding rules of the ALB instance based on fields such as request_uri, http_host, upstream_addr, and status.
In the Simple Log Service console, you can view the run logs of the domain name- or URL-based forwarding rules of the ALB instance based on fields such as request_uri, http_host, upstream_addr, and status.
Step 3: Migrate traffic to the ALB instance
Due to semantic differences in how CLB and ALB forwarding rules handle domains and URLs, we strongly recommend that you carefully compare your CLB and ALB configurations before migrating traffic. To ensure functionally equivalent behavior, you may need to adjust the forwarding rules in ALB to account for these differences. Furthermore, all configurations must undergo thorough testing and validation to prevent any unexpected impact on your services during the migration process.
We recommend that you migrate traffic from the CLB instance during off-peak hours.
In this example, an A record is configured for the CLB instance. The service domain name is resolved to the IP address of the CLB instance based on the A record. After you verify the configurations of the ALB instance, migrate traffic from the CLB instance to the ALB instance. In this example, Alibaba Cloud DNS is used. You can perform the following steps to migrate traffic from the CLB instance to the ALB instance. For more information about Alibaba Cloud DNS, see Public Authoritative DNS Resolution.


Step 1: Configure a temporary domain name and add a CNAME record for the CLB instance
We recommend that you add a CNAME record for the ALB instance. To meet the conditions for configuring weights for DNS records, you must add a CNAME record for the temporary domain name and point the temporary domain name to the IP address of the CLB instance. In this example, the service domain name for the CLB instance is www.example.net.
To configure weights for different DNS records of the same domain name, make sure that the DNS records have the same type, hostname, and ISP line. The supported record types are A, CNAME, and AAAA.
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud DNS console.
On the Public Zone page, find and click the domain name
example.net. The domain name points to the CLB instance.On the Settings tab of the domain name details page, find the A record that points to the service address of the CLB instance and click Edit in the Actions column.
In the Edit Record dialog box, update Hostname, keep the values for the other parameters, and click OK. In this example, update Hostname to web0.
On the Settings tab, click Add Record. In the Add Record panel, set the following parameters and click OK.
Parameter
Description
Record Type
Select CNAME from the drop-down list.
Hostname
Enter the prefix of your domain name. In this example, www is entered.
Query Source
Select Default.
TTL
Specify a time to live (TTL) value for the CNAME record. The TTL determines the time period that the record is cached on the DNS server. The TTL is set to 5 seconds in this example.
Record Value
Enter a temporary domain name. In this example, web0.example.net is entered.
Step 2: Add a CNAME record for the ALB instance
On the Settings tab of the domain name details page, click Add Record. In the Add Record panel, set the following parameters and click OK.
Parameter
Description
Record Type
Select CNAME from the drop-down list.
Hostname
Enter the prefix of the domain name. In this example, www is entered.
Query Source
Select Default.
TTL
Specify a TTL value for the CNAME record. The TTL determines the time period that the record is cached on the DNS server. The TTL is set to 5 seconds in this example.
Record Value
Enter the domain name of the ALB instance.
Step 3: Configure weights to perform a canary release
On the Settings tab of the domain name details page, find the CNAME record created in Step 2, click the down arrow icon in the Actions column, and choose Edit Record Set.
In the Edit Record panel, in the Record Values section, set the weight of the record for the CLB instance to 100, and set the weight of the record for the ALB instance to 0. Click OK.

Check whether your service is affected. If no, gradually reduce the weight of the DNS record for the CLB instance and gradually increase the weight of the DNS record for the ALB instance.
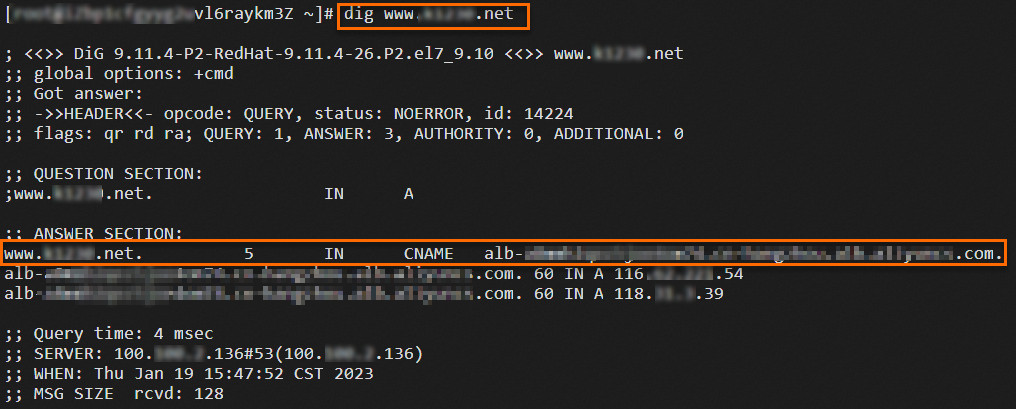
Log on to ECS04 that resides in the same VPC as the ALB instance and run the
digcommand multiple times to verify the traffic migration.NoteA public IP address is assigned to ECS04 and dig is installed on ECS04 by running the
yum install bind-utilscommand.dig www.example.netThe following figures show the results. The results show that requests are forwarded to the ALB and CLB instances based on the weights of the DNS records.
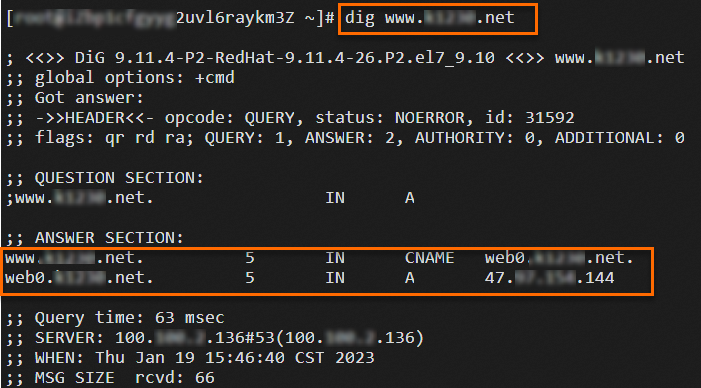
Step 4: Complete traffic migration
Based on the traffic test result, gradually reduce the weight of the DNS record for the CLB instance to 0 and gradually increase the weight of the DNS record for the ALB instance to 100. After you perform the preceding operations, traffic is migrated from the CLB instance to the ALB instance. When all persistent connections to the CLB instance are closed and no new traffic is sent to the CLB instance, you can monitor the CLB instance for a period of time and then release the CLB instance. For more information about how to release a CLB instance, see Create and manage a CLB instance.
FAQ
How do I migrate the redirect rules and forwarding rules of a CLB instance?
During the migration, the system automatically configures redirect rules and domain name- and URL-based forwarding rules for the destination ALB instance.
Due to semantic differences in how CLB and ALB forwarding rules handle domains and URLs, we strongly recommend that you carefully compare your CLB and ALB configurations before migrating traffic. To ensure functionally equivalent behavior, you may need to adjust the forwarding rules in ALB to account for these differences.
What are the differences between CLB and ALB forwarding rules?
CLB and ALB forwarding rules have semantic differences in how they handle domain names and URL paths:
Domain name matching
CLB: Domain name-based forwarding rules support exact matches and wildcard matches. The matching priority is fixed to ensure the most specific rule is applied first:
Exact match
More specific wildcard (e.g.,
*.example.com)Less specific wildcard (e.g.,
*.com)
ALB: Domain name-based forwarding rules support exact matches, wildcard matches, and regex matches. The matching order is determined by a user-defined priority that you configure.
URL path matching
CLB: URL path-based forwarding rules are based on a longest prefix match algorithm.
ALB: URL path-based forwarding rules support exact matches, wildcard matches, and regex matches.
The table below illustrates how CLB and ALB URL path-based rules handle some special characters and patterns. You can use this as a reference when adapting your forwarding rules during a migration from CLB to ALB.
Configured URL path in rule
URL path in request
CLB match?
ALB match?
Explanation
??No
No
The
?character is ignored for path matching purposes in both CLB and ALB.Any valid character
No
Yes
ALB supports
?as a single-character wildcard. CLB does not recognize?as a wildcard.%%No
- (not allowed)
The URL-encoded character
%61is decoded toabefore the matching logic is applied.%61%61No
- (not allowed)
The URL-encoded character
%61is decoded toabefore the matching logic is applied.aNo
No
-
a%61Yes
Yes
The URL-encoded character
%61is decoded toabefore the matching logic is applied.ab,abc, and so onYes
No
CLB performs prefix matching by default. ALB requires an exact match unless a wildcard rule (e.g.,
/a*) is used.test/*test- (not supported)
No
ALB supports explicit wildcard syntax (
*). CLB's prefix matching does not use the*character in its rules.test/- (not supported)
Yes
test/a- (not supported)
Yes
How do I migrate the certificate of an HTTPS listener that is configured for a CLB instance?
You must manually specify the certificates during the migration. If no certificate is available, you can go to Certificate Management Service to purchase or upload certificates.
For more information about server certificates, see Purchase an SSL certificate and Upload, sync, and share SSL certificates.
For more information about CA certificates, see Purchase and enable a private CA
.
After the migration is complete, the system automatically configures the certificates for the ALB instance based on the specified server certificate, additional certificate, and CA certificate.
ALB can distribute traffic to multiple domain names. For more information, see Configure an ALB instance to serve multiple domain names over HTTPS.
ALB supports HTTPS one-way authentication and HTTPS mutual authentication. For more information, see End-to-end data transfer over HTTPS and Configure mutual authentication on an HTTPS listener.
How do I migrate backend servers if ECS instances in different VPCs are added to the same Internet-facing CLB instance as backend servers?
An ALB server group must be deployed in a VPC. During the migration, the system creates a server group in the VPC in which the ALB instance resides. You must manually add backend servers to the server group. The backend servers must reside in the same VPC as the ALB instance.
Server groups of the IP type allow you to add ECS instances to an ALB instance across VPCs as backend servers. If you want to add ECS instances to an ALB instance across VPCs, you can create a server group of the IP type for the ALB instance after the migration by using the migration wizard. Then, you can add ECS instances in different VPCs to the server group by specifying the IP addresses of the ECS instances. For more information, see Specify a backend server located in a VPC in a different region for ALB.
