Serverless workflow provides the service integration feature to simplify the interaction between users and cloud services. In this topic, the Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) queues are used with callback to orchestrate tasks that do not involve functions in Function Compute.
Overview
Serverless workflow not only allows you to orchestrate functions that are deployed in Function Compute in Function as a Service (FaaS) mode into flows, but also allows you to orchestrate other computing tasks into flows. The topic Perform callbacks on asynchronous tasks under Best Practices describes how to use functions in Function Compute to send messages to Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) queues. In custom environments, after a task executor (worker) receives a message, it notifies Serverless workflow of the task execution result based on the callback. This topic describes how to use Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) queues, a new feature of Serverless workflow. Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) queues further simplify the orchestration of custom task types. Serverless workflow allows you to directly send messages to Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) queues. In this way, you do not need to develop, test, and maintain the function that is deployed in Function Compute for sending the messages, improving the availability and reducing the latency. Compared with sending messages to Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) topics by using functions in Function Compute, using the integrated Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) service to send messages to specified Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) queues has the following benefits:
You do not need to develop a function in Function Compute to send messages. This reduces the cost of development, testing, and maintenance.
The message delivery delay is reduced, a remote access process is eliminated, and the cold start of Function Compute is avoided.
Service dependency is removed and fault tolerance is improved.
Serverless workflow will support more cloud services in the future to make it easier to orchestrate flows that consist of different types of tasks.
Service integration
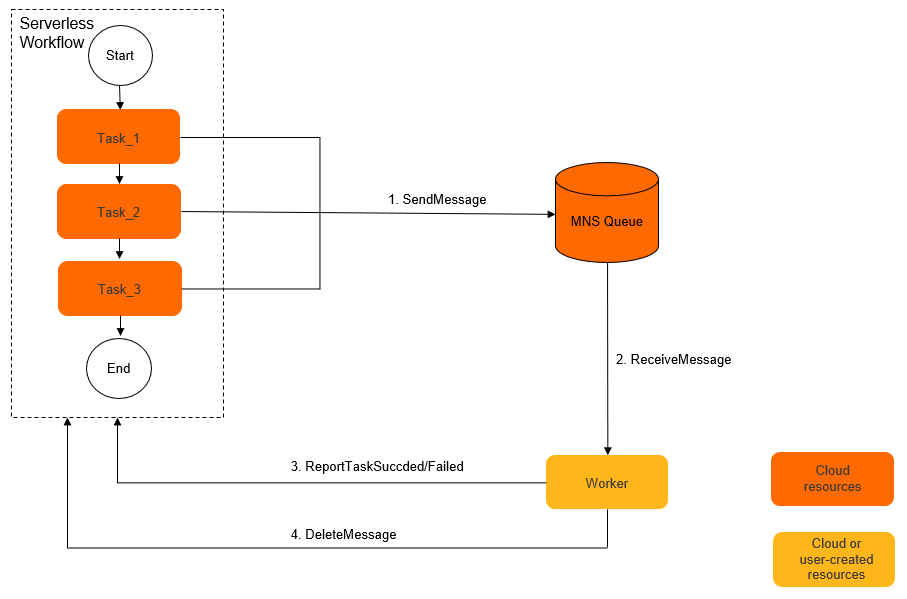
In the following figure, the three serial tasks are sent by Serverless workflow to the specified Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) queue in sequence. After the messages are sent, Serverless workflow waits for the callback in this step. You can call the ReceiveMessage operation of Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) to pull messages in the worker in a custom environment, such as an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance, a container, or a server in an on-premises data center. After the worker receives the messages, it executes the corresponding task based on the message content. After the task ends, the worker calls the ReportTaskSucceeded/Failed operation of Serverless workflow. Serverless workflow continues the step after receiving the task result. After the worker reports the success result, the message is deleted from the Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) queue.
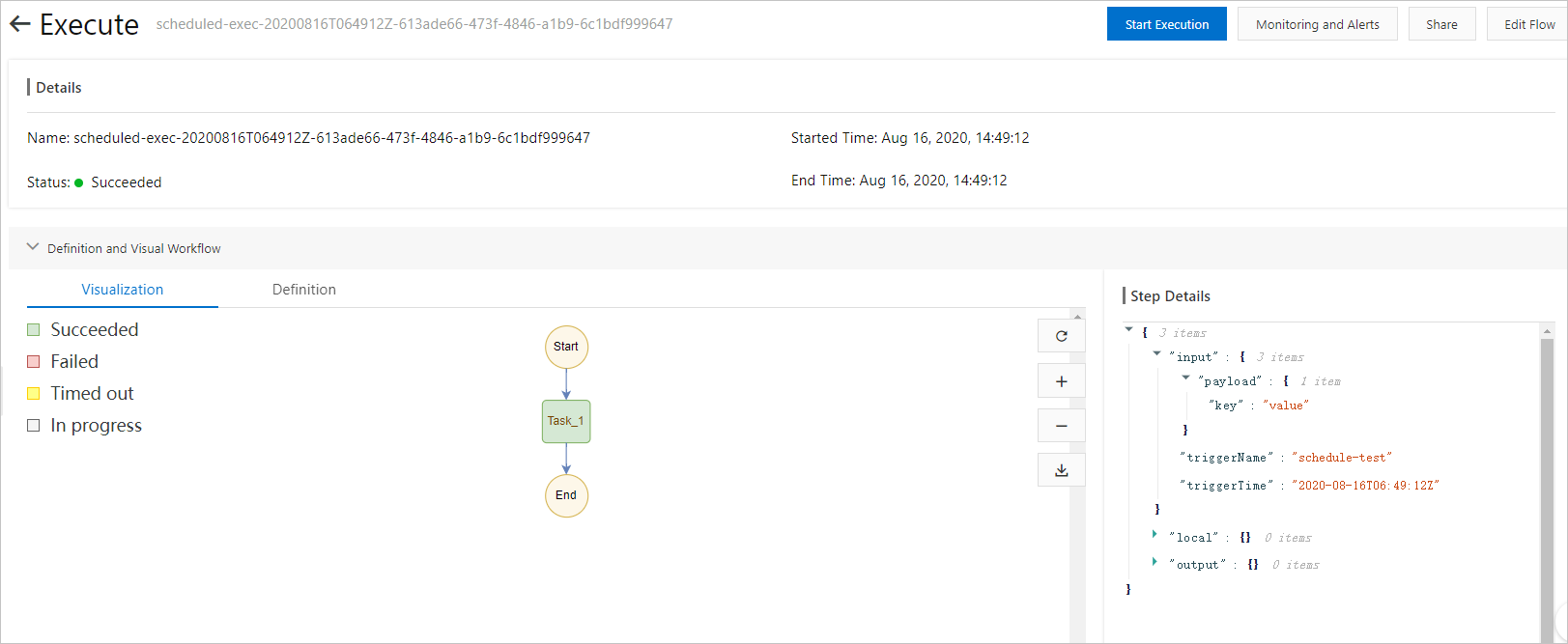
Procedure
Perform the following step to use this feature:
Step 1: Prepare for using this feature
In the Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) console, create an Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) queue. For more information, see Create a queue.
Serverless workflow assumes the Create execution roles (the role of the RAM user) that you specify in the flow to send messages to the Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) queue in your Alibaba Cloud account. Therefore, you must add Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) SendMessage policies for the role of the RAM user. The following example shows a fine-grained policy. If you do not need the fine-grained policy, you can log on to the Serverless workflow console, and add
AliyunMNSFullAccessin System Policy to Flow RAM Role.
{
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"mns:SendMessage"
],
"Resource": [
"acs:mns:$region:$account_id:/queues/$queue_name/messages"
]
}
],
"Version": "1"
} Step 2: Define a flow
The following code in Flow Definition Language (FDL) defines a task step that can send messages to the Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) queue named fnf-demo and wait for the callback.
version: v1
type: flow
steps:
- type: task
name: Task_1
resourceArn: acs:mns:::/queues/fnf-demo/messages # This task step sends messages to the Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) queue fnf-demo that is under the same account in the same region.
pattern: waitForCallback # The task step suspends after the message is sent to the Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) queue and waits until it receives the callback.
inputMappings:
- target: task_token
source: $context.task.token # Serverless Workflow queries the task token from the context object.
- target: key
source: value
serviceParams: # The service integration parameters.
MessageBody: $ # The mapped input is used as the body of the message you want to send.
Priority: 1 # The priority of the Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) queue. Step 3: Define a worker
The following Python 2.7 code simulates a worker that executes a task. It can run in any environment that can access Serverless workflow and Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS). The worker calls the Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) ReceiveMessage operation for long polling. When it enters a task step with an Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) configuration, Serverless workflow sends a message to the fnf-demo queue. After the worker executes the task, it calls back the ReportTaskSucceeded/Failed operation of Serverless workflow. After Serverless workflow receives the task execution result, it continues the current task step. The worker deletes the message from the queue.
In a virtual environment, install Serverless Workflow, Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS), and Python SDK.
cd /tmp; mkdir -p fnf-demo-callback; cd fnf-demo-callback virtualenv env; source env/bin/activate pip install -t . aliyun-python-sdk-core -t . aliyun-python-sdk-fnf -t . aliyun-mnsCompile the code for the local task executor worker.py.
import json import os from aliyunsdkcore.client import AcsClient from aliyunsdkcore.acs_exception.exceptions import ServerException from aliyunsdkcore.client import AcsClient from aliyunsdkfnf.request.v20190315 import ReportTaskSucceededRequest from mns.account import Account # pip install aliyun-mns from mns.queue import * def main(): region = os.environ['REGION'] account_id = os.environ['ACCOUNT_ID'] ak_id = os.environ['AK_ID'] ak_secret = os.environ['AK_SECRET'] queue_name = "fnf-demo" fnf_client = AcsClient( ak_id, ak_secret, region ) mns_endpoint = "https://%s.mns.%s.aliyuncs.com" % (account_id, region) my_account = Account(mns_endpoint, ak_id, ak_secret) my_queue = my_account.get_queue("fnf-demo") my_queue.set_encoding(False) wait_seconds = 10 try: while True: try: print "Receiving messages" recv_msg = my_queue.receive_message(wait_seconds) print "Received message %s, body %s" % (recv_msg.message_id, recv_msg.message_body) body = json.loads(recv_msg.message_body) task_token = body["task_token"] output = "{\"key\": \"value\"}" request = ReportTaskSucceededRequest.ReportTaskSucceededRequest() request.set_Output(output) request.set_TaskToken(task_token) resp = fnf_client.do_action_with_exception(request) print "Report task succeeded finished" my_queue.delete_message(recv_msg.receipt_handle) print "Deleted message " + recv_msg.message_id except MNSExceptionBase as e: print(e) except ServerException as e: print(e) if e.error_code == 'TaskAlreadyCompleted': my_queue.delete_message(recv_msg.receipt_handle) print "Task already completed, deleted message " + recv_msg.message_id except ServerException as e: print(e) if __name__ == '__main__': main()Run the worker to long poll the fnf-demo queue. After the worker receives the message, it performs callback to report the result to Serverless workflow.
# Run the worker process. export REGION={your-region} export ACCOUNT_ID={your-account-id} export AK_ID={your-ak-id} export AK_SECRET={your-ak-secret} python worker.py
Step 4: Execute the flow and view the result
In the Serverless workflow console, execute the flow and run the worker. The result shows that the flow is successful.