If slow SQL queries occur in your ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance or the SQL statements that are executed affect the performance of your applications, you can optimize the SQL statements. Database Autonomy Service (DAS) provides the automatic SQL optimization feature. The feature can automatically diagnose slow SQL queries, generate index optimization suggestions, and create indexes without table locks.
Prerequisites
Your RDS instance runs one of the following MySQL versions and RDS editions:
MySQL 8.0 on RDS High-availability Edition, RDS Enterprise Edition, or RDS Cluster Edition
MySQL 5.7 on RDS High-availability Edition, RDS Enterprise Edition, or RDS Cluster Edition
MySQL 5.6 on RDS High-availability Edition
MySQL 5.5 on RDS High-availability Edition
After slow SQL queries are optimized, the overall performance of the RDS instance may degrade. To ensure that the automatic SQL optimization feature optimizes only abnormal SQL queries, we recommend that you enable the SQL Explorer and Audit feature. For more information, see Use the SQL Explorer and Audit feature.
Feature description
DAS uses online DDL statements that are supported by the native MySQL kernel to automatically create indexes. This prevents table locks that may be caused by the creation of regular indexes. For more information, see SQL optimization technology.
Limits
The automatic SQL optimization feature is not supported for SQL queries that involve tables using X-Engine.
Procedure
Go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the RDS instance resides. Then, find the RDS instance and click the ID of the instance.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, click the Autonomy Center tab. On the Autonomy Center tab, click Autonomy Service Settings.
On the Autonomous Function Settings tab, enable the autonomy service and select Automatic Index Creation and Deletion on the Optimization and Throttling tab.
SQL Diagnostics Only: DAS performs daily diagnostics on SQL statements and provides index optimization suggestions. However, DAS does not create indexes on your RDS instance.
SQL Diagnostics and Automatic Index Creation: DAS performs daily diagnostics on SQL statements, provides index optimization suggestions, and then creates indexes on your RDS instance based on the suggestions.
NoteDAS creates indexes within the maintenance window that you specify for your RDS instance.
Click OK.
Optional. In the Alert Configuration section, configure an alert template and subscribe to alert notifications. This helps you understand the status of an automatic SQL optimization task at the earliest opportunity.
The system recommends an alert template and adds alert rules for the required autonomy events in the alert template. You can configure the alert template as prompted.
NoteIf you have configured an alert template for your RDS instance, you must add alert rules for the required autonomy events to the alert template as prompted.
If you have not configured an alert template for your RDS instance but you want to configure one, you can configure the alert template by following the instructions provided in Configure alert templates and Configure alert rules.
In the Select Alert Contact Group step, select an alert contact group.
Click Add Contact to add an alert contact.
Click Create Contact Group to create an alert contact group.
Find the alert contact that you want to manage and click Edit or Remove in the Actions column to modify or delete information about the alert contact.
For more information, see Manage alert contacts.
Confirm the settings in the Associate with Resources step.
Click Submit Configuration. In the dialog box that appears, confirm the configuration.
What to do next
On the Autonomy Center tab, view the optimization events that occurred within a specified time range.
Find the event that you want to view and click Details. On the Root Cause Analysis and Suggestions tab of the Slow SQL Statements Diagnostics (Diagnostics and Optimization) event, view information about Problematic SQL Statements, SQL Statement Optimization, Index Recommendation, and Statement Optimization.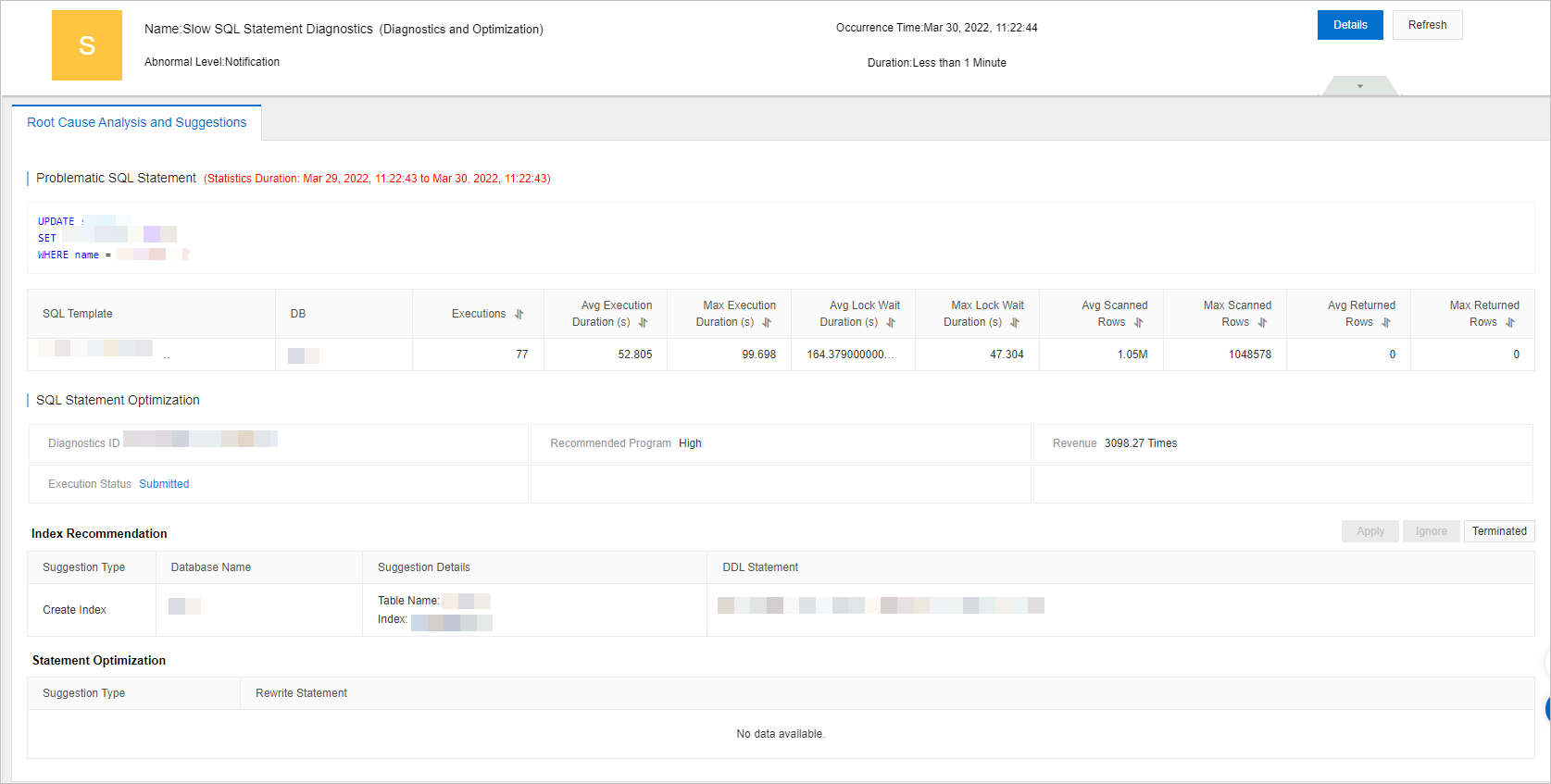
References
For more information about how to manually optimize an SQL statement, see SQL optimization.
Related operations
Operation | Description |
Enables, modifies, or disables the automatic SQL optimization feature for multiple database instances at a time. | |
Queries the SQL optimization suggestions that are generated by the SQL diagnostics feature of DAS. | |
Queries statistics on automatic SQL optimization events within a period of time, such as the total number of optimization events and the maximum improvement. |