This topic describes how to use Transaction Processing Performance Council Benchmark C (TCP-C) tests to measure the Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) capabilities of a PolarDB-X instance that runs the MySQL 5.7 or MySQL 8.0 database engine. You can follow the test procedures described in this topic to evaluate the performance of your database.
Background information
TPC-C is a benchmark that is widely used to evaluate the OLTP capabilities of databases. It is developed and released by the Transaction Processing Performance Council (TPC). TPC-C involves 10 tables of the following five transaction types: NewOrder for new order generation, Payment for order payments, OrderStatus for order status queries, Delivery for order deliveries, and StockLevel for inventory analysis. TPC-C uses transactions-per-minute-C (tpmC) to measure the maximum qualified throughput (MQTh) of a system. The measurement is based on the number of NewOrder transactions processed per minute.
The TPC-C performance tests described in this topic are implemented based on the TPC-C benchmark tests but cannot meet all requirements of the benchmark tests. Therefore, test results in this topic cannot be compared with the published results of the TPC-C benchmark tests.
Test design
Amount of test data
The test is performed based on 1,000 warehouses. The following list describes the amount of data in each major table:
The bmsql_order_line table contains 300 million rows of data.
The bmsql_stock table contains 100 million rows of data.
The bmsql_customer, bmsql_history, and bmsql_oorder tables each contain 30 million rows of data.
Instance specifications for the test
Instance specifications
Number of nodes
4C32G
2
4C32G
4
8C64G
2
8C64G
4
ECS instance type for stress testing
ecs.g6.8xlarge (32 vCPUs, 128 GB of memory)
Procedure
Create an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance for stress testing.
Create an ECS instance that is used to prepare data and perform stress testing. To prevent performance bottlenecks when you test PolarDB-X instances with high specifications, we recommend that you create an ECS instance with 32 vCPUs and 128 GB of memory.
NoteThe ECS instance must be deployed in a virtual private cloud (VPC). Record the name and ID of the VPC for subsequent use. You must deploy all database instances that are described in subsequent steps in the VPC.
Create a PolarDB-X instance for stress testing.
Create a PolarDB-X instance. Select the MySQL 5.7 or MySQL 8.0 database engine based on your business requirements. For information about how to create a PolarDB-X instance, see Create a PolarDB-X instance.
NoteMake sure that the ECS instance and the PolarDB-X instance are in the same VPC.
Create the database that you want to test in the PolarDB-X instance. In this example, a database named tpcc_1000 is created.
CREATE DATABASE tpcc_1000 MODE = 'auto';
Modify instance parameters.
NoteTo achieve optimal performance in stress testing, modify specific parameters of the compute nodes of the PolarDB-X instance.
Set the ENABLE_COROUTINE parameter to true and the XPROTO_MAX_DN_CONCURRENT and XPROTO_MAX_DN_WAIT_CONNECTION parameters to 4000. For more information, see Parameter settings.
Connect to the PolarDB-X instance by using a command-line client. Then, execute the following SQL statements in the same session to disable logging and CPU statistical sampling:
SET GLOBAL RECORD_SQL=false; SET GLOBAL MPP_METRIC_LEVEL=0; SET GLOBAL ENABLE_CPU_PROFILE=false; SET GLOBAL ENABLE_TRANS_LOG=false;
Prepare data for stress testing.
Prepare a stress testing tool.
Run the following command to download and decompress the stress testing tool package benchmarksql.tar.gz:
tar xzvf benchmarksql.tar.gzNoteBy default, BenchmarkSQL does not support the MySQL protocol. You must compile BenchmarkSQL to support the MySQL protocol. In this example, open source BenchmarkSQL 5.0 is used as a TPC-C testing tool. It requires JDK 8 or later and is compatible with MySQL 5.7 and MySQL 8.0.
Configure the stress test.
Run the following commands on the ECS instance to specify the connection information of the PolarDB-X instance in the props.mysql configuration file.
cd benchmarksql/run vi props.mysqlThe following example shows the content of the configuration file. The parameters in the configuration file are described in this section after the example.
db=mysql driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver conn=jdbc:mysql://{HOST}:{PORT}/tpcc?readOnlyPropagatesToServer=false&rewriteBatchedStatements=true&failOverReadOnly=false&connectTimeout=3000&socketTimeout=90000&allowMultiQueries=true&clobberStreamingResults=true&characterEncoding=utf8&netTimeoutForStreamingResults=0&autoReconnect=true user={USER} password={PASSWORD} warehouses=1000 loadWorkers=100 terminals=128 //To run specified transactions per terminal- runMins must equal zero runTxnsPerTerminal=0 //To run for specified minutes- runTxnsPerTerminal must equal zero runMins=5 //Number of total transactions per minute limitTxnsPerMin=0 //Set to true to run in 4.x compatible mode. Set to false to use the //entire configured database evenly. terminalWarehouseFixed=true //The following five values must add up to 100 //The default percentages of 45, 43, 4, 4 & 4 match the TPC-C spec newOrderWeight=45 paymentWeight=43 orderStatusWeight=4 deliveryWeight=4 stockLevelWeight=4 // Directory name to create for collecting detailed result data. // Comment this out to suppress. resultDirectory=my_result_%tY-%tm-%td_%tH%tM%tS // osCollectorScript=./misc/os_collector_linux.py // osCollectorInterval=1 // osCollectorSSHAddr=user@dbhost // osCollectorDevices=net_eth0 blk_sdaconn: the connection string used to connect to the PolarDB-X instance. You must specify values for the {HOST} and {PORT} fields.
user: the username used to log on to the PolarDB-X instance.
password: the password of the username used to log on to the PolarDB-X instance.
warehouses: the number of warehouses.
loadWorkers: the number of concurrent loadWorkers that are used to import data.
terminals: the number of concurrent terminals in the TPC-C stress test.
runMins: the duration of the stress test. Unit: minutes.
Import the stress testing data.
Run the following commands on the ECS instance to import the stress testing data:
cd benchmarksql/run/sql.common cp tableCreates.sql.auto tableCreates.sql cd .. nohup ./runDatabaseBuild.sh props.mysql &NoteBy default, 100 concurrent loadWorkers are used to import more than 500 million rows of data. Data import requires several hours. We recommend that you use nohup to run the import task in the background to prevent the task from being interrupted due to SSH disconnections.
Verify data integrity
Connect to the PolarDB-X instance by using a command-line client and execute the following SQL statements. If the returned result sets are empty, the test data is complete.
SELECT a.* FROM (SELECT w_id, w_ytd FROM bmsql_warehouse) a LEFT JOIN (SELECT d_w_id, SUM(d_ytd) AS d_ytd_sum FROM bmsql_district GROUP BY d_w_id) b ON a.w_id = b.d_w_id AND a.w_ytd = b.d_ytd_sum WHERE b.d_w_id IS NULL; SELECT a.* FROM (SELECT d_w_id, d_id, D_NEXT_O_ID - 1 AS d_n_o_id FROM bmsql_district) a LEFT JOIN (SELECT o_w_id, o_d_id, MAX(o_id) AS o_id_max FROM bmsql_oorder GROUP BY o_w_id, o_d_id) b ON a.d_w_id = b.o_w_id AND a.d_id = b.o_d_id AND a.d_n_o_id = b.o_id_max WHERE b.o_w_id IS NULL; SELECT a.* FROM (Select d_w_id, d_id, D_NEXT_O_ID - 1 AS d_n_o_id FROM bmsql_district) a LEFT JOIN (SELECT no_w_id, no_d_id, MAX(no_o_id) AS no_id_max FROM bmsql_new_order GROUP BY no_w_id, no_d_id) b ON a.d_w_id = b.no_w_id AND a.d_id = b.no_d_id AND a.d_n_o_id = b.no_id_max WHERE b.no_id_max IS NULL; SELECT * FROM (SELECT (COUNT(no_o_id)-(MAX(no_o_id)-MIN(no_o_id)+1)) AS diff FROM bmsql_new_order GROUP BY no_w_id, no_d_id) a WHERE diff != 0; SELECT a.* FROM (SELECT o_w_id, o_d_id, SUM(o_ol_cnt) AS o_ol_cnt_cnt FROM bmsql_oorder GROUP BY o_w_id, o_d_id) a LEFT JOIN (SELECT ol_w_id, ol_d_id, COUNT(ol_o_id) AS ol_o_id_cnt FROM bmsql_order_line GROUP BY ol_w_id, ol_d_id) b ON a.o_w_id = b.ol_w_id AND a.o_d_id = b.ol_d_id AND a.o_ol_cnt_cnt = b.ol_o_id_cnt WHERE b.ol_w_id IS NULL; SELECT a.* FROM (SELECT d_w_id, SUM(d_ytd) AS d_ytd_sum FROM bmsql_district GROUP BY d_w_id) a LEFT JOIN (Select w_id, w_ytd FROM bmsql_warehouse) b ON a.d_w_id = b.w_id AND a.d_ytd_sum = b.w_ytd WHERE b.w_id IS NULL;
Perform stress testing.
Run the following commands to perform the TPC-C test:
cd benchmarksql/run ./runBenchmark.sh props.mysqlDuring stress testing, you can view the real-time tpmC values. After the test is complete, the average tpmC value is displayed. The following example shows the stress testing results.
[2024/07/16 16:32:20.369] Average tpmC: 286806.15 Current tpmC: 290244.00 Memory Usage: 510MB / 3584MB [2024/07/16 16:32:25.369] Average tpmC: 286821.77 Current tpmC: 287712.00 Memory Usage: 209MB / 3584MB [2024/07/16 16:32:30.369] Average tpmC: 286855.77 Current tpmC: 288828.00 Memory Usage: 984MB / 3584MB [2024/07/16 16:32:35.370] Average tpmC: 286852.69 Current tpmC: 286682.66 Memory Usage: 653MB / 3584MB 16:32:35,487 [Thread-714] INFO jTPCC : Term-00, 16:32:35,487 [Thread-714] INFO jTPCC : Term-00, Measured tpmC (NewOrders) = 286841.81 16:32:35,487 [Thread-714] INFO jTPCC : Term-00, Measured tpmTOTAL = 637027.51 16:32:35,487 [Thread-714] INFO jTPCC : Term-00, 16:32:35,487 [Thread-714] INFO jTPCC : Term-00, Session Start = 2024-07-16 16:27:35 16:32:35,487 [Thread-714] INFO jTPCC : Term-00, Session End = 2024-07-16 16:32:35 16:32:35,487 [Thread-714] INFO jTPCC : Term-00, Transaction Count = 3186400
Test results
MySQL 5.7
Version: polardb-2.4.0_5.4.19-20240610_xcluster5.4.19-20240527. For more information, see Release notes.
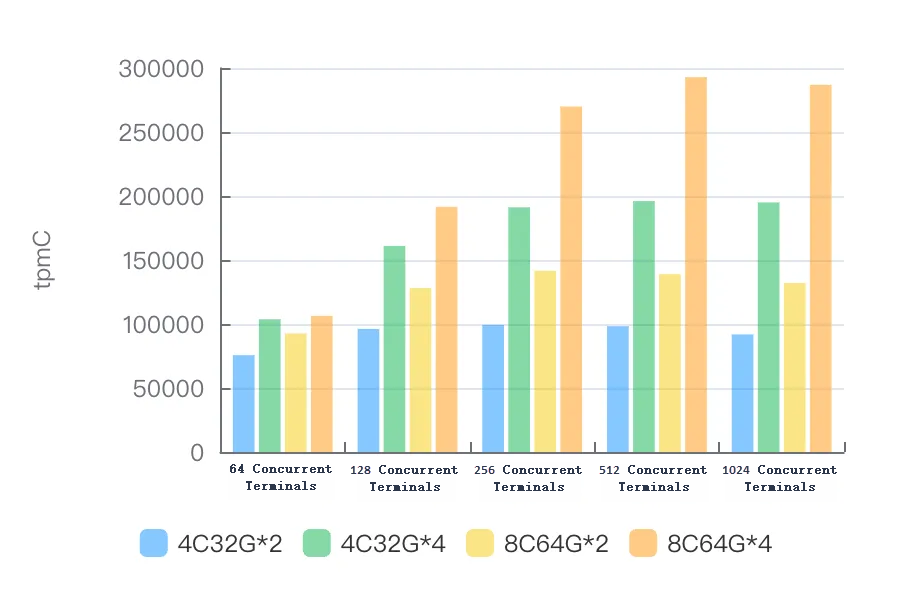
Instance specifications | tpmC for 64 concurrent terminals | tpmC for 128 concurrent terminals | tpmC for 256 concurrent terminals | tpmC for 512 concurrent terminals | tpmC for 1024 concurrent terminals |
4C32G*2 | 75655.51 | 96178.92 | 99315.74 | 98272.41 | 91849.33 |
4C32G*4 | 103698.48 | 160964.59 | 191213.08 | 196013.09 | 194955.2 |
8C64G*2 | 92608.23 | 128178.78 | 141578.84 | 138943.08 | 132062.62 |
8C64G*4 | 106394.6 | 191550.55 | 269927.62 | 292926.91 | 286841.81 |
MySQL 8.0
Version: polardb-2.4.0_5.4.19-20240610_xcluster8.4.19-20240523. For more information, see Release notes.
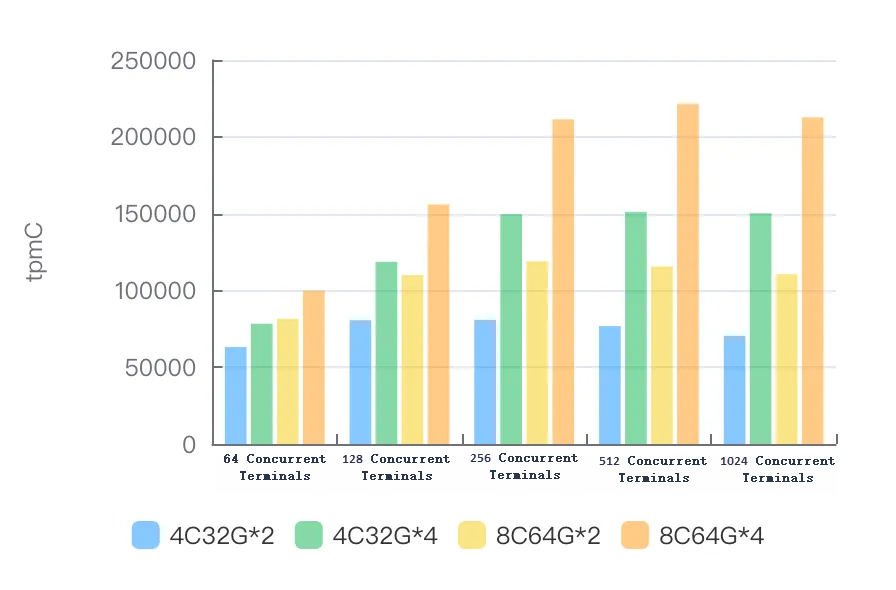
Instance specifications | tpmC for 64 concurrent terminals | tpmC for 128 concurrent terminals | tpmC for 256 concurrent terminals | tpmC for 512 concurrent terminals | tpmC for 1024 concurrent terminals |
4C32G*2 | 63102.89 | 80591.88 | 80843.53 | 76747.57 | 70397.38 |
4C32G*4 | 78316.27 | 118637.24 | 149567.59 | 151138.05 | 150177.41 |
8C64G*2 | 81533.11 | 109978.06 | 118902.41 | 115632.36 | 110539.75 |
8C64G*4 | 99772.56 | 155959.31 | 211403.16 | 221496.06 | 212633.02 |