Data is a core asset for enterprises. As the business of enterprises grows, data increases exponentially. This requires business applications to be able to process data online and in real time. Database O&M personnel face great challenges in protecting the core data of enterprises because issues, such as accidental data deletion, system vulnerabilities and ransomware, hardware failures, and natural disasters, can cause data loss. Therefore, backup and restoration are important features of databases.
PolarDB supports data backups and redo log backups:
Data backup: Creates a backup set (snapshot) of the full data of a cluster at a specific point in time. This is a full backup.
Redo log backup: Records the incremental data generated after a backup set is created. This is an incremental backup.
A PolarDB cluster recovery restores data to the current cluster using a backup set (snapshot).
A PolarDB database or table recovery creates a new database or table in the current cluster to restore the data.
With a full data backup and subsequent redo log backups, you can restore an entire PolarDB cluster or specific databases and tables to any point in time.
Billing rules
You can use the backup and restoration feature free of charge. However, backup files consume storage space. For more information about billing rules, see Backup storage beyond the free quota.
For more information about how to view your bills, see Bills.
If you select to retain backup sets for a long time when you manually unsubscribe or release your cluster, the backup sets are automatically moved to the cluster recycle bin. In this case, level-1 backup files automatically become level-2 backup files and you are charged. For more information, see Cluster recycle bin.
Data backup
PSL4/PSL5
Level-1 backup
Level-1 backups use redirect-on-write (ROW) snapshots and are stored directly in the PolarDB distributed storage system. When a level-1 backup is created, data is not copied. When a data block is modified, the system retains a historical version of the block for the snapshot and generates a new block that is referenced by the source data. This is called a redirect. This method allows backups to finish in seconds, regardless of the database size.
PolarDB backup and recovery features use multi-threading parallel processing and other innovations to restore a new cluster from a backup set (snapshot) in about 10 minutes. The recovery time doubles if a Hot Standby Cluster is enabled. The actual time required depends on factors such as the amount of data in the database.
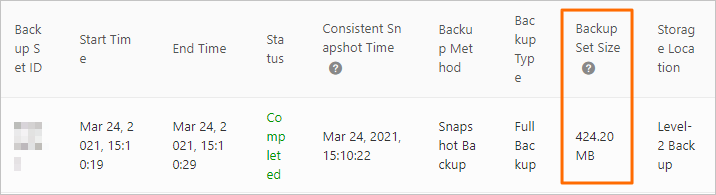
View level-1 backup size
Level-1 backup is enabled by default and cannot be disabled.
The retention period for level-1 backups is 3 to 14 days.
Level-2 backup
A level-2 backup is a compressed level-1 backup that is stored on a different offline storage medium. It has a lower storage cost, but restoring data from a level-2 backup is slower.
If a level-1 backup exceeds its specified retention period, it is automatically converted to a level-2 backup.
Level-2 backups support single-region and cross-region backups. For more information, see Single-region and cross-region backups.
View level-2 backup size
If the conversion of a level-1 backup is not complete before the next level-1 backup is scheduled for conversion, the next level-1 backup is deleted instead of being converted to a level-2 backup. For example, the backup time for level-1 backups of a PolarDB cluster is 01:00 every day, and the retention period is 24 hours. PolarDB generates level-1 backup A at 01:00 on January 1 and level-1 backup B at 01:00 on January 2. At 01:00 on January 2, backup A exceeds its retention period and its conversion to a level-2 backup begins. Because the backup file is large, the conversion takes a long time and is not complete by 01:00 on January 3. At this point, backup B expires at 01:00 on January 3 and is deleted instead of being converted to a level-2 backup.
Level-2 backup is disabled by default.
The retention period for level-2 backups is 30 to 7300 days.
enterprise SSD (ESSD)
Backups stored locally are called level-1 backups. Level-1 backups are snapshots stored on a distributed storage cluster. They offer the fastest backup and recovery speeds but at a higher cost. Long-term storage can slightly affect the write performance of the database. We recommend a retention period of no more than 2 weeks. A free quota for backup storage is provided. You are charged for usage that exceeds the free quota. You can change the backup cycle to control backup capacity.
Level-1 backup is enabled by default and cannot be disabled.
The retention period for level-1 backups is 3 to 14 days.
View level-1 backup size
Redo log backup
Log backups are created by uploading redo logs to OSS in parallel and in real time. Log backups support single-region and cross-region backups. The retention period is from 3 to 7300 days. You can also enable the Long-term Retention Before Cluster Deletion feature for long-term log retention.
Currently, only Enterprise Edition clusters support the Long-term Retention Before Cluster Deletion option.
Single-region backup for logs is enabled by default and cannot be disabled.
Log backups enable consistent backups with point-in-time recovery (PITR). With a full data backup (snapshot) and subsequent log backups, you can restore a PolarDB cluster to any point in time. This ensures the security of recent data and prevents data loss from accidental operations. When you restore to a point in time, the speed of applying redo logs is approximately 20 to 70 seconds/GB. The total recovery time is the sum of the time required to restore from the backup set (snapshot) and the time required to apply the redo logs.
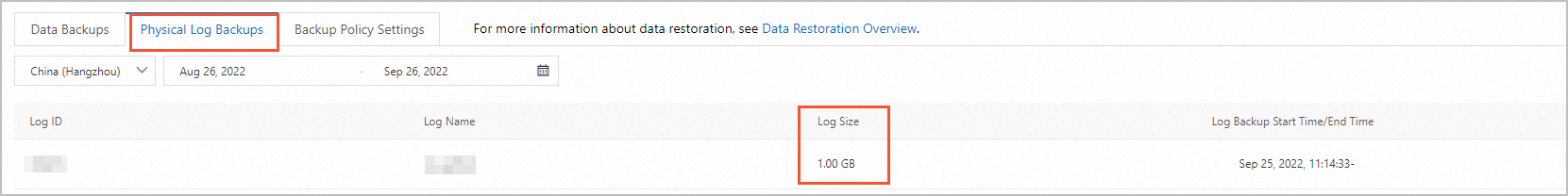
View backup size
The total size of log backups is the sum of the sizes of all individual log backup files. The following figure shows an example:
Threats
If the redo log generation rate of a PolarDB for MySQL cluster reaches 35 MB/s to 50 MB/s, redo logs may become stacked. This can increase your backup storage costs.
Single-region and cross-region backups
Notes on backups
Backup type
Description
Enabled by default
Scenarios
Benefits
Single-region backup
Backups are stored in a different zone within the same region.
Yes.
NoteWhen you enable level-2 backup, single-region backup is enabled by default.
Long-term archiving.
You can lower costs by dumping backups at a lower frequency as needed.
Cross-region backup
Backups are stored in a region other than the current region.
ImportantThis feature is available only for PolarDB for MySQL Enterprise Edition.
No. You must enable it manually.
Geo-redundancy and MLPS Level 3 compliance.
Low Recovery Point Objective (RPO). Suitable for secure, non-public network environments. You can lower costs with low-frequency dumps as needed.
NoteLow-frequency level-2 backup: The backup cycle of level-2 backups is set to a lower frequency than that of level-1 backups.
Supported regions for cross-region backup
Source region
Destination region
the Chinese mainland
the Chinese mainland
US (Silicon Valley), US (Virginia)
China (Hong Kong)
Singapore, Indonesia (Jakarta), Japan (Tokyo), Malaysia (Kuala Lumpur)
Germany (Frankfurt)
China (Hong Kong)
the Chinese mainland
US (Silicon Valley), US (Virginia)
Japan (Tokyo), Singapore, Malaysia (Kuala Lumpur), Indonesia (Jakarta)
Germany (Frankfurt)
Japan (Tokyo)
the Chinese mainland
US (Silicon Valley), US (Virginia)
China (Hong Kong)
Singapore, Malaysia (Kuala Lumpur), Indonesia (Jakarta)
Germany (Frankfurt)
US (Silicon Valley)
the Chinese mainland
US (Virginia)
China (Hong Kong)
Singapore, Malaysia (Kuala Lumpur), Indonesia (Jakarta)
Germany (Frankfurt)
US (Virginia)
the Chinese mainland
US (Silicon Valley)
China (Hong Kong)
Singapore, Malaysia (Kuala Lumpur), Indonesia (Jakarta)
Germany (Frankfurt)
Singapore
the Chinese mainland
US (Silicon Valley), US (Virginia)
China (Hong Kong)
Malaysia (Kuala Lumpur), Indonesia (Jakarta)
Germany (Frankfurt)
Malaysia (Kuala Lumpur)
the Chinese mainland
US (Silicon Valley), US (Virginia)
China (Hong Kong)
Singapore, Indonesia (Jakarta), Japan (Tokyo)
Germany (Frankfurt)
Indonesia (Jakarta)
the Chinese mainland
US (Silicon Valley), US (Virginia)
China (Hong Kong)
Singapore, Japan (Tokyo), Malaysia (Kuala Lumpur)
Germany (Frankfurt)
Germany (Frankfurt)
the Chinese mainland
US (Silicon Valley), US (Virginia)
China (Hong Kong)
Singapore, Indonesia (Jakarta), Japan (Tokyo), Malaysia (Kuala Lumpur)
China (Hangzhou) Finance Cloud
China (Shanghai) Finance Cloud, China (Shenzhen) Finance Cloud
China (Shanghai) Finance Cloud
China (Hangzhou) Finance Cloud, China (Shenzhen) Finance Cloud
China (Shenzhen) Finance Cloud
China (Hangzhou) Finance Cloud, China (Shanghai) Finance Cloud
FAQ
For answers to common questions about backup and recovery, see FAQ.