Naive Bayes is a probabilistic classification algorithm based on Bayes' theorem. This algorithm assumes that all features in the input data are independent of each other. You can use the Naive Bayes component of Machine Learning Designer to effectively handle various classification problems. This topic describes how to configure the Naive Bayes component.
Usage notes
The Naive Bayes component requires MaxCompute computing resources.
Configure the component
You can use one of the following methods to configure the Naive Bayes component.
Method 1: Use the Platform for AI (PAI) console
To configure the Naive Bayes component in the PAI console, perform the following steps: Log on to the PAI console, go to the Visualized Modeling (Designer) page, and open a pipeline. On the pipeline page, drag the Naive Bayes component to the canvas and configure the parameters in the right-side pane. The following table describes the parameters.
Tab | Parameter | Description |
Fields Setting | Feature Column | The feature columns. Default value: all columns in the input table except the column specified in the Label Column parameter. Columns of the DOUBLE, STRING, and BIGINT types are supported. |
Excluded Columns | The columns that are excluded for training. You cannot configure this parameter and the Feature Column parameter at the same time. | |
Forced Conversion Column | The columns that require forced data type conversion. If you leave this parameter empty, the following conversion rules apply:
Note If you want to convert a column of the BIGINT type into a column of the CATEGORICAL type, you must configure this parameter. | |
Label Column | The label column. You cannot use the label column as a feature column. The label column must be of the DOUBLE, STRING, or BIGINT types. | |
Input Sparse Format Data | Specifies whether the input data is sparse. Sparse data is in the key-value pair format. | |
Separator between K:V when input is sparse | The delimiter that is used to separate key-value pairs. By default, commas (,) are used. | |
The separator of key and value when the input is sparse | The delimiter that is used to separate the key and the value in a key-value pair. By default, colons (:) are used. | |
Whether To Generate PMML | Specifies whether to generate a Predictive Model Markup Language (PMML) model. If you did not configure a storage path for the pipeline and you select the checkbox for this parameter, click Create Now to configure the storage path for the pipeline. | |
Tuning | Number of cores | By default, the system automatically configures this parameter. |
Memory Size of Core(MB) | By default, the system automatically configures this parameter. |
Method 2: Use PAI commands
To configure the Naive Bayes component by using PAI commands, run the commands in the SQL Script component. For more information, see SQL Script.
PAI -name NaiveBayes -project algo_public
-DinputTablePartitions="pt=20150501"
-DmodelName="xlab_m_NaiveBayes_23772"
-DlabelColName="poutcome"
-DfeatureColNames="age,previous,cons_conf_idx,euribor3m"
-DinputTableName="bank_data_partition";Parameter | Required | Description | Default value |
inputTableName | Yes | The name of the input table. | No default value |
inputTablePartitions | No | The partitions that are selected from the input table for training. | All partitions |
modelName | Yes | The name of the output model. | No default value |
labelColName | Yes | The name of the label column. | No default value |
featureColNames | No | The names of the feature columns that are selected from the input table for training. | All columns except the label column |
excludedColNames | No | The names of the columns that are excluded for training. You cannot configure this parameter and the featureColNames parameter at the same time. | No default value |
forceCategorical | No | The columns that require forced data type conversion. If you leave this parameter empty, the following conversion rules apply:
Note If you want to convert a column of the BIGINT type into a column of the CATEGORICAL type, you must configure this parameter. | INT is a continuous type. |
coreNum | No | The number of CPU cores that are used for computing. | Automatically configured by the system |
memSizePerCore | No | The memory size of each CPU core. Valid values: 1 to 65536. Unit: MB. | Automatically configured by the system |
Example
Prepare training data and test data.
Use the MaxCompute client to create tables named train_data and test_data. The train_data table is used to store training data and the test_data table is used to store test data. In the tables, set the column name and type to
id bigint, y bigint, f0 double, f1 double, f2 double, f3 double, f4 double, f5 double, f6 double, f7 double. For information about how to install and configure the MaxCompute client, see MaxCompute client (odpscmd). For information about how to create a table, see Create tables.Import the following training data to the train_data table and test data to the test_data table. For information about how to import data, see Import data to tables.
Training data
id
y
f0
f1
f2
f3
f4
f5
f6
f7
1
-1
-0.294118
0.487437
0.180328
-0.292929
-1
0.00149028
-0.53117
-0.0333333
2
+1
-0.882353
-0.145729
0.0819672
-0.414141
-1
-0.207153
-0.766866
-0.666667
3
-1
-0.0588235
0.839196
0.0491803
-1
-1
-0.305514
-0.492741
-0.633333
4
+1
-0.882353
-0.105528
0.0819672
-0.535354
-0.777778
-0.162444
-0.923997
-1
5
-1
-1
0.376884
-0.344262
-0.292929
-0.602837
0.28465
0.887276
-0.6
6
+1
-0.411765
0.165829
0.213115
-1
-1
-0.23696
-0.894962
-0.7
7
-1
-0.647059
-0.21608
-0.180328
-0.353535
-0.791962
-0.0760059
-0.854825
-0.833333
8
+1
0.176471
0.155779
-1
-1
-1
0.052161
-0.952178
-0.733333
9
-1
-0.764706
0.979899
0.147541
-0.0909091
0.283688
-0.0909091
-0.931682
0.0666667
10
-1
-0.0588235
0.256281
0.57377
-1
-1
-1
-0.868488
0.1
Test data
id
y
f0
f1
f2
f3
f4
f5
f6
f7
1
+1
-0.882353
0.0854271
0.442623
-0.616162
-1
-0.19225
-0.725021
-0.9
2
+1
-0.294118
-0.0351759
-1
-1
-1
-0.293592
-0.904355
-0.766667
3
+1
-0.882353
0.246231
0.213115
-0.272727
-1
-0.171386
-0.981213
-0.7
4
-1
-0.176471
0.507538
0.278689
-0.414141
-0.702128
0.0491804
-0.475662
0.1
5
-1
-0.529412
0.839196
-1
-1
-1
-0.153502
-0.885568
-0.5
6
+1
-0.882353
0.246231
-0.0163934
-0.353535
-1
0.0670641
-0.627669
-1
7
-1
-0.882353
0.819095
0.278689
-0.151515
-0.307329
0.19225
0.00768574
-0.966667
8
+1
-0.882353
-0.0753769
0.0163934
-0.494949
-0.903073
-0.418778
-0.654996
-0.866667
9
+1
-1
0.527638
0.344262
-0.212121
-0.356974
0.23696
-0.836038
-0.8
10
+1
-0.882353
0.115578
0.0163934
-0.737374
-0.56974
-0.28465
-0.948762
-0.933333
Create a pipeline as shown in the following figure and then run the pipeline. For information about how to create a pipeline, see Algorithm modeling.
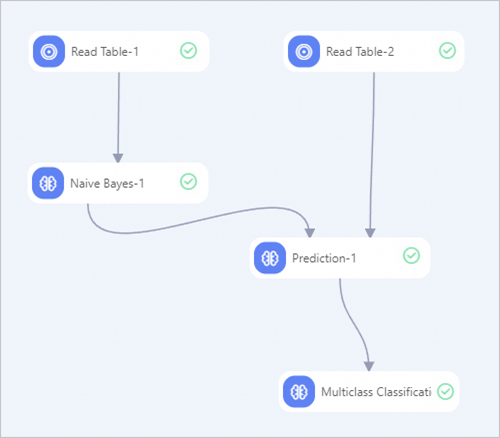
In the left-side pane of the pipeline page, search for and drag two Read Table components, one Naive Bayes component, one Prediction component, and one Multiclass Classification Evaluation component to the canvas.
Connect the components into a pipeline based on the preceding figure.
Configure the component parameters.
Click the Read Table-1 component on the canvas. On the Select Table tab in the right-side pane, set the Table Name parameter to train_data.
Click the Read Table-2 component on the canvas. On the Select Table tab in the right-side pane, set the Table Name parameter to test_data.
Click the Naive Bayes-1 component on the canvas and configure the parameters in the right-side pane. The following table describes the parameters that you must configure. Retain the default values for other parameters.
Tab
Parameter
Description
Fields Setting
Feature Column
Select the f0, f1, f2, f3, f4, f5, f6, and f7 columns from the training table.
Label Column
Select the y column from the training table.
Click the Prediction -1 component on the canvas. On the Fields Settings tab in the right-side pane, set the Reserved Columns parameter to id and y. Retain the default values for other parameters.
Click the Multiclass Classification Evaluation-1 component on the canvas. On the Fields Settings tab in the right-side pane, set the Original Classification Result Column parameter to y. Retain the default values for other parameters.
Click the
 button to run the pipeline.
button to run the pipeline.
After the pipeline run is completed, right-click the Prediction-1 component and choose to view the prediction results.
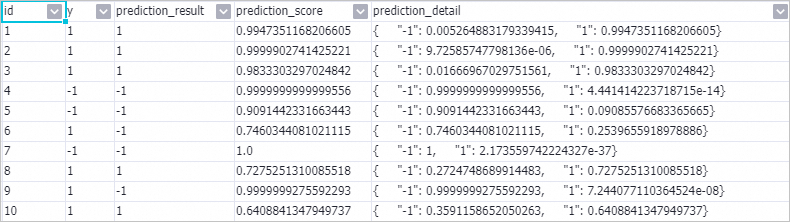
References
After you run the Naive Bayes component to generate a PMML model, you can deploy the model as an online service. For more information, see Deploy a model as an online service.
For information about Machine Learning Designer, see Overview of Machine Learning Designer.
Machine Learning Designer provides multiple preset algorithm components. You can select a component based on your business requirements. For more information, see Component reference: Overview of all components.