MaxCompute lets you create Object Storage Service (OSS) external tables in a project to map to directories in OSS. You can use OSS external tables to access unstructured data from files in an OSS directory or write data from a MaxCompute project to an OSS directory. This topic describes the syntax and parameters for creating, reading from, and writing to OSS external tables.
Scope
OSS external tables do not support the cluster property.
The size of a single file cannot exceed 2 GB. You must split files that are larger than 2 GB.
MaxCompute and OSS must be in the same region.
Access methods
You can use the following platforms to create OSS external tables and to read from or write to them.
Method | Platform |
MaxCompute SQL | |
Visualization |
Prerequisites
You have created a MaxCompute project.
Prepare an OSS bucket and directory. For more information, see Create a bucket and Manage directories.
MaxCompute can automatically create directories in OSS. If an SQL statement includes external tables and User-Defined Functions (UDFs), you can use a single SQL statement to read from and write to the external table and run the UDF. The original method of manually creating directories is also supported.
Because MaxCompute is deployed only in some regions, cross-region network connectivity can be an issue. Keep your bucket in the same region as your MaxCompute project.
Authorization
Obtain permissions to access OSS. An Alibaba Cloud account, a RAM user, or a RAM role can be used to access OSS external tables. For authorization information, see STS authorization for OSS.
Obtain the CreateTable permission in your MaxCompute project. For more information about table operation permissions, see MaxCompute permissions.
Create an OSS external table
Partitioned and non-partitioned tables: OSS external tables can be partitioned or non-partitioned. The type depends on the storage path of the data files in OSS. If the data files are stored in a partitioned path, create a partitioned table. Otherwise, create a non-partitioned table.
Network domain name: Use the classic network domain name for OSS. MaxCompute does not guarantee network connectivity for public network domain names.
An OSS external table only records the mapping to an OSS directory. Deleting an OSS external table does not delete the data files in the mapped OSS directory.
If an OSS data file is an archived object, you must first restore the object.
The statements to create OSS external tables have different parameter settings for data files of different formats. Create an external table that meets your business needs based on the syntax and parameter descriptions. Otherwise, operations to read data from or write data to OSS will fail.
Syntax
Create an external table using the built-in text data parser
Syntax | Data file format | Example |
| Supported data file formats for reading from or writing to OSS:
|
Create an external table using a built-in open source data parser
Syntax | Data file format | Example |
| Supported data file formats for reading from or writing to OSS:
|
Create an external table using a custom parser
Syntax | Data file format | Example |
| Supported data file formats for reading from or writing to OSS: Data files in formats other than those listed above. |
Parameters
The following are common parameters for external tables of various formats. For unique parameters, see the documentation for each specific external table format.
Basic syntax parameters
Parameter
Required
Description
mc_oss_extable_name
Yes
The name of the OSS external table to create.
Table names are not case-sensitive. You do not need to distinguish between uppercase and lowercase letters when querying the external table, and you cannot force case conversion.
col_name
Yes
The name of a column in the OSS external table.
When reading data from OSS, the schema of the created OSS external table must be the same as the schema of the OSS data file. Otherwise, the data cannot be read.
data_type
Yes
The data type of a column in the OSS external table.
When reading data from OSS, the data type of each column in the OSS external table must be the same as the data type of the corresponding column in the OSS data file. Otherwise, the data cannot be read.
table_comment
No
The comment for the table. The comment must be a valid string of no more than 1,024 bytes. Otherwise, an error is reported.
partitioned by (col_name data_type, ...)
No
If the data files in OSS are stored in a partitioned path, include this parameter to create a partitioned table.
col_name: The name of the partition key column.
data_type: The data type of the partition key column.
'<(tb)property_name>'='<(tb)property_value>'
Yes
The extended properties of the OSS external table. For more information about the parameters, see the documentation for the unique parameters of each format.
oss_location
Yes
The OSS path where the data files are located. By default, all data files in this path are read.
The format is
oss://<oss_endpoint>/<Bucket name>/<OSS directory name>/.oss_endpoint:
The OSS domain name. You must use the classic network endpoint provided by OSS, which contains
-internal.Example:
oss://oss-cn-beijing-internal.aliyuncs.com/xxx.For more information about OSS classic network domain names, see Regions and endpoints.
Keep the OSS region where the data files are stored the same as the region of your MaxCompute project. If they are in different regions, network connectivity issues may occur.
If you do not specify an endpoint, the system uses the endpoint of the region where the current project is located.
This method is not recommended because cross-region file storage may cause network connectivity issues.
Bucket name: The name of the OSS bucket. The bucket name must follow the
oss_endpoint.Example:
oss://oss-cn-beijing-internal.aliyuncs.com/your_bucket/path/.For more information about how to view bucket names, see List buckets.
Directory name: The name of the OSS directory. Do not specify a file name after the directory.
Example:
oss://oss-cn-beijing-internal.aliyuncs.com/oss-mc-test/Demo1/.Incorrect examples:
-- HTTP connections are not supported. http://oss-cn-shanghai-internal.aliyuncs.com/oss-mc-test/Demo1/ -- HTTPS connections are not supported. https://oss-cn-shanghai-internal.aliyuncs.com/oss-mc-test/Demo1/ -- Incorrect connection address. oss://oss-cn-shanghai-internal.aliyuncs.com/Demo1 -- Do not specify a file name. oss://oss-cn-shanghai-internal.aliyuncs.com/oss-mc-test/Demo1/vehicle.csvPermission specification (RamRole):
Explicitly specify (Recommended): Create a custom role, attach an access policy, and use the ARN of the custom role. For more information, see STS authorization.
Use Default (Not recommended): Use the ARN of the
aliyunodpsdefaultrolerole.
WITH serdeproperties attributes
property_name
Scenario
property_value
Default value
odps.properties.rolearn
Add this property when using STS authorization.
Specify the ARN of the RAM role that has permissions to access OSS.
Obtain the ARN from the role details in the RAM console. Example:
acs:ram::xxxxxx:role/aliyunodpsdefaultrole.If the owners of MaxCompute and OSS are the same account:
If you do not specify
odps.properties.rolearnin the table creation statement, the ARN of thealiyunodpsdefaultrolerole is used by default. You must first create thealiyunodpsdefaultrolerole using STS authorization.To use the ARN of a custom role, you must first create the custom role. For more information, see STS authorization for OSS (custom authorization).
If the owners of MaxCompute and OSS are different accounts, you must specify the ARN of a custom role. For more information, see STS authorization for OSS (custom authorization).
Populate partitions for an OSS external table
If you create a partitioned OSS external table, you must perform an additional operation to import partition data.
Method 1 (Recommended): Automatically parse the OSS directory structure to identify and add partitions to the OSS external table.
This method is suitable for scenarios where you need to add all missing historical partitions at once. MaxCompute automatically populates the partitions of the OSS external table based on the partition directory that you specified when you created the table. You do not need to add them one by one by partition column name and value.
MSCK REPAIR TABLE <mc_oss_extable_name> ADD PARTITIONS [ WITH properties (key:VALUE, key: VALUE ...)];This method is not suitable for adding incremental data, especially when the OSS directory contains many partitions, such as more than 1,000. If the number of new partitions is much smaller than the number of existing partitions, frequently running the
msckcommand causes many repeated scans of the OSS directory and metadata updates. This reduces the command's execution efficiency. For scenarios that require you to update incremental partitions, use Method 2.Method 2: Manually run a command to add partition information to the OSS external table.
This method is suitable for scenarios where historical partitions have been created and you need to frequently and periodically append new partitions. You must create the partition before the data writing task is executed. Even if new data is written to OSS, you do not need to refresh the corresponding partition. The external table can read the latest data from the OSS directory.
ALTER TABLE <mc_oss_extable_name> ADD PARTITION (<col_name>=<col_value>)[ ADD PARTITION (<col_name>=<col_value>)...][location URL];The values of col_name and col_value must align with the directory name where the partition data file is located.
Assume the OSS directory structure for the partition data file is as shown in the following figure. col_name corresponds to
direction, and col_value corresponds toN, NE, S, SW, W. Oneadd partitionclause corresponds to one subdirectory. For multiple OSS subdirectories, you must use multipleadd partitionclauses.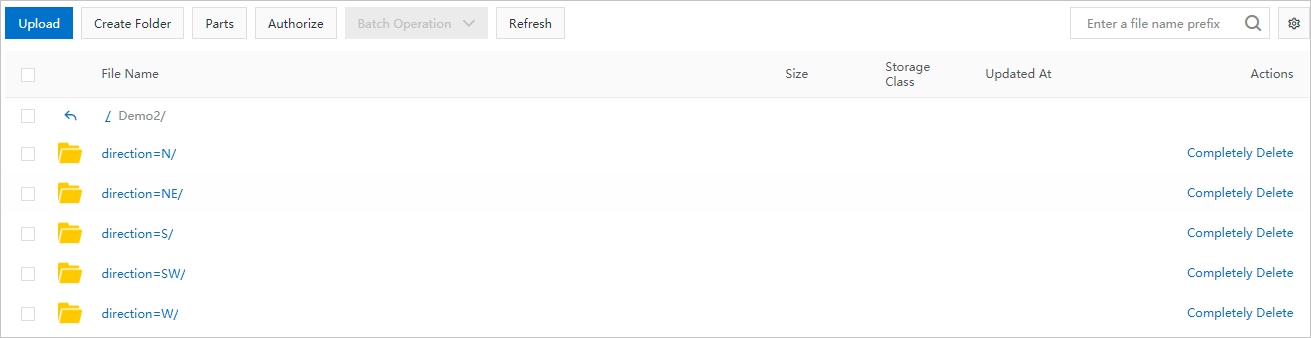
Read data from OSS
Notes
After you create an OSS external table, you can read data from OSS through the external table. For information about supported OSS data file types and the syntax for creating OSS external tables, see Syntax.
If an SQL statement involves complex data types, add the
set odps.sql.type.system.odps2=true;command before the SQL statement and submit them together. For more information about data types, see Data type versions.For OSS external tables that map to open source data, set
set odps.sql.hive.compatible=true;at the session level before reading data from OSS. Otherwise, an error is reported.OSS provides limited bandwidth resources. If the data read and write traffic exceeds the instance bandwidth limit in a short period, the data read and write speed of the OSS external table is directly affected. For more information about OSS bandwidth, see Limits and performance metrics.
Syntax
<select_statement> FROM <from_statement>;select_statement: The
SELECTclause, which queries the data to be inserted into the target table from the source table.from_statement: The
FROMclause, which specifies the data source, such as the name of the external table.
Non-partitioned data
After you create a non-partitioned OSS external table, you can read data from OSS in the following ways:
Method 1 (Recommended): Import the open source format data from OSS into a MaxCompute internal table, and then read the data.
This method is suitable for scenarios that require repeated calculations or have high requirements for computing performance. By creating an internal table in the MaxCompute project with the same schema as the OSS external table, you can import OSS data into this internal table and then execute complex queries. This approach takes full advantage of MaxCompute's optimization mechanisms for internal storage to improve computing performance. The following is a sample command:
CREATE TABLE <table_internal> LIKE <mc_oss_extable_name>; INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE <table_internal> SELECT * FROM <mc_oss_extable_name>;Method 2: Read data directly from OSS, similar to operations on MaxCompute internal tables.
This method is suitable for scenarios with low requirements for computing performance. Unlike reading from an internal table, each data read operation directly retrieves the corresponding data from OSS.
Partitioned data
After an OSS external table is created, MaxCompute performs a full scan of all data in the OSS directory, including data files in subdirectories. If the data volume is large, a full directory scan can cause unnecessary I/O consumption and increase data processing time. You can solve this problem in two ways.
Method 1 (Recommended): Store data on OSS using a standard partitioned path or a custom partitioned path.
When you create an OSS external table, you must specify the partition and oss_location information in the table creation statement. We recommend that you store OSS data using a standard partitioned path.
Method 2: Plan multiple data storage paths.
You can create multiple OSS external tables to read data from each path. This means each OSS external table points to a subset of the OSS data. This method is cumbersome and not effective for data management, so we do not recommend it.
Standard partitioned path format
oss://<oss_endpoint>/<Bucket name>/<directory name>/<partitionKey1=value1>/<partitionKey2=value2>/...Example: A company stores daily log files in CSV format on OSS and processes the data daily using MaxCompute. The standard partitioned path for storing OSS data should be set as follows.
oss://oss-odps-test/log_data/year=2016/month=06/day=01/logfile
oss://oss-odps-test/log_data/year=2016/month=06/day=02/logfile
oss://oss-odps-test/log_data/year=2016/month=07/day=10/logfile
oss://oss-odps-test/log_data/year=2016/month=08/day=08/logfile
...Custom partitioned path format
A custom partitioned path format contains only partition column values, not partition column names. Example:
oss://oss-odps-test/log_data_customized/2016/06/01/logfile
oss://oss-odps-test/log_data_customized/2016/06/02/logfile
oss://oss-odps-test/log_data_customized/2016/07/10/logfile
oss://oss-odps-test/log_data_customized/2016/08/08/logfile
...If the data in OSS is stored in a partitioned manner but the path is not in the standard partitioned path format, MaxCompute lets you bind different subdirectories to different partitions to access the subdirectory data.
Solution: After you create the OSS external table, use the alter table ... add partition ... location ... command to specify subdirectories and bind different subdirectories to different partitions. The following is a sample command.
ALTER TABLE log_table_external ADD PARTITION (year = '2016', month = '06', day = '01')
location 'oss://oss-cn-hangzhou-internal.aliyuncs.com/bucket_name/oss-odps-test/log_data_customized/2016/06/01/';
ALTER TABLE log_table_external ADD PARTITION (year = '2016', month = '06', day = '02')
location 'oss://oss-cn-hangzhou-internal.aliyuncs.com/bucket_name/oss-odps-test/log_data_customized/2016/06/02/';
ALTER TABLE log_table_external ADD PARTITION (year = '2016', month = '07', day = '10')
location 'oss://oss-cn-hangzhou-internal.aliyuncs.com/bucket_name/oss-odps-test/log_data_customized/2016/07/10/';
ALTER TABLE log_table_external ADD PARTITION (year = '2016', month = '08', day = '08')
location 'oss://oss-cn-hangzhou-internal.aliyuncs.com/bucket_name/oss-odps-test/log_data_customized/2016/08/08/';Query optimization
Dynamic statistics collection
Because data is stored in an external data lake and lacks pre-existing statistics, the query optimizer uses a conservative strategy, which results in low query efficiency. The dynamic statistics collection feature allows the optimizer to temporarily collect table statistics during query execution to identify small tables. It then actively uses methods such as Hash Join, optimizing the join order, reducing shuffles, and shortening the execution pipeline to achieve query optimization.
The following parameters do not apply to Paimon, Hudi, or Delta Lake external tables.
SET odps.meta.exttable.stats.onlinecollect=true; SELECT * FROM <tablename>;Optimizing external table splits
You can optimize query efficiency by setting the split size parameter to adjust the amount of data processed by a single concurrent task. The split size setting has the following effects.
If the table data volume is very large and the amount of data read each time is too small, the number of splits is too high, which leads to excessive parallelism. The instance then spends most of its time waiting for resources.
If the table data volume is very small and the amount of data read each time is too large, the number of splits is too low, which results in insufficient concurrency. Most resources are then idle.
-- You can use either of the following parameters. -- Unit: MiB. Default value: 256 MiB. Applies to internal or external tables. SET odps.stage.mapper.split.size=<value>; SELECT * FROM <tablename>; -- Unit: MiB. Default value: 256 MiB. Applies only to external tables. SET odps.sql.unstructured.data.split.size=<value>; SELECT * FROM <tablename>;
Write data to OSS
Similar to reading data from OSS, MaxCompute lets you write data from internal tables or data processed from external tables to OSS. For more information about the limits, see Scope.
Write data to OSS using a built-in text or open source data parser: Built-in text data parser, Built-in open source data parser.
Write data to OSS using a custom parser: Example: Create an OSS external table using a custom parser.
Write data to OSS using the OSS multipart upload feature: Write data to OSS using the OSS multipart upload feature.
Syntax
INSERT {INTO|OVERWRITE} TABLE <table_name> PARTITION (<ptcol_name>[, <ptcol_name> ...])
<select_statement> FROM <from_statement>;Parameter | Required | Description |
table_name | Yes | The name of the external table to write to. |
select_statement | Yes | The |
from_statement | Yes | The |
To insert data into dynamic partitions, see Insert or overwrite data into dynamic partitions (DYNAMIC PARTITION).
Notes
If the
INSERT OVERWRITE ... SELECT ... FROM ...;operation allocates 1,000 mappers on the source table from_tablename, 1,000 TSV or CSV files are generated.You can control the number of generated files using configurations provided by MaxCompute.
If the outputter is in a mapper: Use
odps.stage.mapper.split.sizeto control the number of concurrent mappers, which adjusts the number of generated files.If the outputter is in a reducer or joiner: Use
odps.stage.reducer.numandodps.stage.joiner.numrespectively to adjust the number of generated files.
Risk of inconsistent writes: When you use an `INSERT OVERWRITE` statement on an OSS external table or use the `UNLOAD` command to export files to OSS, the data in the subdirectory of the specified OSS location or the location that corresponds to the partition is deleted before new data is written. If the location directory contains important data written directly to OSS by other external engines, that data is also deleted before the new data is written. Therefore, you must ensure that existing files in the location directory of the external table are backed up or that the `UNLOAD` directory is empty. For other risks of inconsistent writes, see Scope.
Write data to OSS using the OSS multipart upload feature
When you need to write data to OSS in an open source format, you can use an OSS external table created with an open source data parser and the OSS multipart upload feature to perform an INSERT operation to write data to OSS.
To enable the OSS multipart upload feature, set the following:
Scenario | Command |
Set at the project level | Takes effect for the entire project. |
Set at the session level | Takes effect only for the current task. |
The default value of the odps.sql.unstructured.oss.commit.mode property is false. The implementation principles for different values are as follows:
Value | Principle |
false | Data written by MaxCompute to an OSS external table is stored in the .odps folder under the LOCATION directory. The .odps folder contains a .meta file to ensure data consistency for MaxCompute. The content of .odps can only be correctly processed by MaxCompute. Other data processing engines may not be able to parse it correctly, which can cause errors. |
true | MaxCompute uses the multipart upload feature to be compatible with other data processing engines. It uses a |
Manage exported files
Parameters
When you need to add a prefix, suffix, or extension to the data files written to OSS, you can use the following parameters.
property_name | Scenario | Description | property_value | Default value |
odps.external.data.output.prefix (Compatible with odps.external.data.prefix) | Add this property when you need to add a custom prefix to the output files. |
| A combination of allowed characters, such as 'mc_' | None |
odps.external.data.enable.extension | Add this property when you need to display the extension of the output files. | True indicates that the extension of the output file is displayed. False indicates that it is not displayed. |
| False |
odps.external.data.output.suffix | Add this property when you need to add a custom suffix to the output files. | Contains only digits, letters, and underscores (a-z, A-Z, 0-9, _). | A combination of allowed characters, such as '_hangzhou' | None |
odps.external.data.output.explicit.extension | Add this property when you need to add a custom extension to the output files. |
| A combination of allowed characters, such as "jsonl" | None |
Examples
Set the custom prefix of the output OSS file to
test06_. The DDL statement is as follows:CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE <mc_oss_extable_name> ( vehicleId INT, recordId INT, patientId INT, calls INT, locationLatitute DOUBLE, locationLongitude DOUBLE, recordTime STRING, direction STRING ) ROW FORMAT SERDE 'org.apache.hive.hcatalog.data.JsonSerDe' WITH serdeproperties ( 'odps.properties.rolearn'='acs:ram::<uid>:role/aliyunodpsdefaultrole' ) STORED AS textfile LOCATION 'oss://oss-cn-beijing-internal.aliyuncs.com/***/' TBLPROPERTIES ( -- Set a custom prefix. 'odps.external.data.output.prefix'='test06_') ; -- Write data to the external table. INSERT INTO <mc_oss_extable_name> VALUES (1,32,76,1,63.32106,-92.08174,'9/14/2014 0:10','NW');The following figure shows the generated file.

Set the custom suffix of the output OSS file to
_beijing. The DDL statement is as follows:CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE <mc_oss_extable_name> ( vehicleId INT, recordId INT, patientId INT, calls INT, locationLatitute DOUBLE, locationLongitude DOUBLE, recordTime STRING, direction STRING ) ROW FORMAT SERDE 'org.apache.hive.hcatalog.data.JsonSerDe' WITH serdeproperties ( 'odps.properties.rolearn'='acs:ram::<uid>:role/aliyunodpsdefaultrole' ) STORED AS textfile LOCATION 'oss://oss-cn-beijing-internal.aliyuncs.com/***/' TBLPROPERTIES ( -- Set a custom suffix. 'odps.external.data.output.suffix'='_beijing') ; -- Write data to the external table. INSERT INTO <mc_oss_extable_name> VALUES (1,32,76,1,63.32106,-92.08174,'9/14/2014 0:10','NW');The following figure shows the generated file.

An extension is automatically generated for the output OSS file. The DDL statement is as follows:
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE <mc_oss_extable_name> ( vehicleId INT, recordId INT, patientId INT, calls INT, locationLatitute DOUBLE, locationLongitude DOUBLE, recordTime STRING, direction STRING ) ROW FORMAT SERDE 'org.apache.hive.hcatalog.data.JsonSerDe' WITH serdeproperties ( 'odps.properties.rolearn'='acs:ram::<uid>:role/aliyunodpsdefaultrole' ) STORED AS textfile LOCATION 'oss://oss-cn-beijing-internal.aliyuncs.com/***/' TBLPROPERTIES ( -- Automatically generate an extension. 'odps.external.data.enable.extension'='true') ; -- Write data to the external table. INSERT INTO <mc_oss_extable_name> VALUES (1,32,76,1,63.32106,-92.08174,'9/14/2014 0:10','NW');The following figure shows the generated file:
Set the custom extension of the output OSS file to
jsonl. The DDL statement is as follows:CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE <mc_oss_extable_name> ( vehicleId INT, recordId INT, patientId INT, calls INT, locationLatitute DOUBLE, locationLongitude DOUBLE, recordTime STRING, direction STRING ) ROW FORMAT SERDE 'org.apache.hive.hcatalog.data.JsonSerDe' WITH serdeproperties ( 'odps.properties.rolearn'='acs:ram::<uid>:role/aliyunodpsdefaultrole' ) STORED AS textfile LOCATION 'oss://oss-cn-beijing-internal.aliyuncs.com/***/' TBLPROPERTIES ( -- Set a custom extension. 'odps.external.data.output.explicit.extension'='jsonl') ; -- Write data to the external table. INSERT INTO <mc_oss_extable_name> VALUES (1,32,76,1,63.32106,-92.08174,'9/14/2014 0:10','NW');The following figure shows the generated file.

Set the prefix of the output OSS file to
mc_, the suffix to_beijing, and the extension tojsonl. The DDL statement is as follows:CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE <mc_oss_extable_name> ( vehicleId INT, recordId INT, patientId INT, calls INT, locationLatitute DOUBLE, locationLongitude DOUBLE, recordTime STRING, direction STRING ) ROW FORMAT SERDE 'org.apache.hive.hcatalog.data.JsonSerDe' WITH serdeproperties ( 'odps.properties.rolearn'='acs:ram::<uid>:role/aliyunodpsdefaultrole' ) STORED AS textfile LOCATION 'oss://oss-cn-beijing-internal.aliyuncs.com/***/' TBLPROPERTIES ( -- Set a custom prefix. 'odps.external.data.output.prefix'='mc_', -- Set a custom suffix. 'odps.external.data.output.suffix'='_beijing', -- Set a custom extension. 'odps.external.data.output.explicit.extension'='jsonl') ; -- Write data to the external table. INSERT INTO <mc_oss_extable_name> VALUES (1,32,76,1,63.32106,-92.08174,'9/14/2014 0:10','NW');The following figure shows the generated file.

Write large files using dynamic partitions
Business scenario
You can export the calculation results of an ancestor table to OSS in the form of partitions and write them as a large file (for example, 4 GB). You can achieve this by configuring the odps.adaptive.shuffle.desired.partition.size parameter (in MB) in a dynamic partition format.
Advantage: You can control the desired output file size by configuring the parameter value.
Disadvantage: The overall execution time is longer because writing large files reduces the degree of parallelism, which in turn increases the execution time.
Metric descriptions
-- The service.mode must be turned off.
SET odps.service.mode=off;
-- The dynamic partition capability must be enabled.
SET odps.sql.reshuffle.dynamicpt=true;
-- Set the desired data consumption for each reducer. Assume you want each file to be 4 GB.
SET odps.adaptive.shuffle.desired.partition.size=4096; Example
Write a JSON file of about 4 GB to OSS.
Prepare the test data. Use the public dataset table
bigdata_public_dataset.tpcds_1t.web_sales, which is about 30 GB. The data is stored in a compressed format on MaxCompute, so the size increases after export.Create a JSON external table.
-- Sample table name: json_ext_web_sales CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE json_ext_web_sales( c_int INT , c_string STRING ) PARTITIONED BY (pt STRING) ROW FORMAT SERDE 'org.apache.hive.hcatalog.data.JsonSerDe' WITH serdeproperties ( 'odps.properties.rolearn'='acs:ram::<uid>:role/aliyunodpsdefaultrole' ) STORED AS textfile LOCATION 'oss://oss-cn-hangzhou-internal.aliyuncs.com/oss-mc-test/demo-test/';Without setting any parameters, write the test table to the JSON external table in a dynamic partition format.
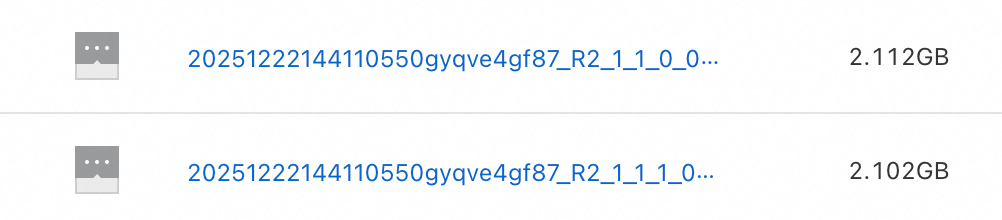
-- The service.mode must be turned off. set odps.service.mode=off; -- Enable the Layer 3 syntax switch. SET odps.namespace.schema=true; -- Write to the JSON external table in a dynamic partition format. INSERT OVERWRITE json_ext_web_sales PARTITION(pt) SELECT CAST(ws_item_sk AS INT) AS c_int, CAST(ws_bill_customer_sk AS string) AS c_string , COALESCE(CONCAT(ws_bill_addr_sk %2, '_', ws_promo_sk %3),'null_pt') AS pt FROM bigdata_public_dataset.tpcds_1t.web_sales;The files stored on OSS are shown in the following figure:
Add the parameter
odps.adaptive.shuffle.desired.partition.sizefor large file output and write the test table to the JSON external table in a dynamic partition format.-- The service.mode must be turned off. SET odps.service.mode=off; -- Enable the Layer 3 syntax switch. SET odps.namespace.schema=true; -- The dynamic partition capability must be enabled. SET odps.sql.reshuffle.dynamicpt=true; -- Set the desired data consumption for each reducer. Assume you want each file to be 4 GB. SET odps.adaptive.shuffle.desired.partition.size=4096; -- Write to the JSON external table in a dynamic partition format. INSERT OVERWRITE json_ext_web_sales PARTITION(pt) SELECT CAST(ws_item_sk AS INT) AS c_int, CAST(ws_bill_customer_sk AS string) AS c_string , COALESCE(CONCAT(ws_bill_addr_sk %2, '_', ws_promo_sk %3),'null_pt') AS pt FROM bigdata_public_dataset.tpcds_1t.web_sales;The files stored on OSS are shown in the following figure:

Import from or export to OSS
LOAD command: Imports data from external storage, such as OSS, into a MaxCompute table or partition.
UNLOAD command: Exports data from a MaxCompute project to external storage, such as OSS, for use by other compute engines.
Appendix: Prepare sample data
Prepare OSS directories
The provided sample data information is as follows:
oss_endpoint:
oss-cn-hangzhou-internal.aliyuncs.com, which is China (Hangzhou).Bucket name:
oss-mc-test.Directory names:
Demo1/,Demo2/,Demo3/, andSampleData/.
Non-partitioned table data
The file uploaded to the
Demo1/directory is vehicle.csv, which contains the following data. TheDemo1/directory is used to map to a non-partitioned table that is created with the built-in text data parser.1,1,51,1,46.81006,-92.08174,9/14/2014 0:00,S 1,2,13,1,46.81006,-92.08174,9/14/2014 0:00,NE 1,3,48,1,46.81006,-92.08174,9/14/2014 0:00,NE 1,4,30,1,46.81006,-92.08174,9/14/2014 0:00,W 1,5,47,1,46.81006,-92.08174,9/14/2014 0:00,S 1,6,9,1,46.81006,-92.08174,9/15/2014 0:00,S 1,7,53,1,46.81006,-92.08174,9/15/2014 0:00,N 1,8,63,1,46.81006,-92.08174,9/15/2014 0:00,SW 1,9,4,1,46.81006,-92.08174,9/15/2014 0:00,NE 1,10,31,1,46.81006,-92.08174,9/15/2014 0:00,NPartitioned table data
The
Demo2/directory contains five subdirectories:direction=N/,direction=NE/,direction=S/,direction=SW/, anddirection=W/. The uploaded files are vehicle1.csv, vehicle2.csv, vehicle3.csv, vehicle4.csv, and vehicle5.csv, respectively. These files contain the following data. TheDemo2/directory is used to map to a partitioned table that is created with the built-in text data parser.--vehicle1.csv 1,7,53,1,46.81006,-92.08174,9/15/2014 0:00 1,10,31,1,46.81006,-92.08174,9/15/2014 0:00 --vehicle2.csv 1,2,13,1,46.81006,-92.08174,9/14/2014 0:00 1,3,48,1,46.81006,-92.08174,9/14/2014 0:00 1,9,4,1,46.81006,-92.08174,9/15/2014 0:00 --vehicle3.csv 1,6,9,1,46.81006,-92.08174,9/15/2014 0:00 1,5,47,1,46.81006,-92.08174,9/14/2014 0:00 1,6,9,1,46.81006,-92.08174,9/15/2014 0:00 --vehicle4.csv 1,8,63,1,46.81006,-92.08174,9/15/2014 0:00 --vehicle5.csv 1,4,30,1,46.81006,-92.08174,9/14/2014 0:00Compressed data
The file uploaded to the
Demo3/directory is vehicle.csv.gz. The file inside the compressed package is vehicle.csv, which has the same content as the file in theDemo1/directory. It is used to map to an OSS external table with compression properties.Custom parser data
The file uploaded to the
SampleData/directory is vehicle6.csv, which contains the following data. TheSampleData/directory is used to map to an OSS external table that is created with an open source data parser.1|1|51|1|46.81006|-92.08174|9/14/2014 0:00|S 1|2|13|1|46.81006|-92.08174|9/14/2014 0:00|NE 1|3|48|1|46.81006|-92.08174|9/14/2014 0:00|NE 1|4|30|1|46.81006|-92.08174|9/14/2014 0:00|W 1|5|47|1|46.81006|-92.08174|9/14/2014 0:00|S 1|6|9|1|46.81006|-92.08174|9/14/2014 0:00|S 1|7|53|1|46.81006|-92.08174|9/14/2014 0:00|N 1|8|63|1|46.81006|-92.08174|9/14/2014 0:00|SW 1|9|4|1|46.81006|-92.08174|9/14/2014 0:00|NE 1|10|31|1|46.81006|-92.08174|9/14/2014 0:00|N
FAQ
How do I resolve the "Inline data exceeds the maximum allowed size" error when processing OSS data using an external table?
Problem
When processing OSS data, the error
Inline data exceeds the maximum allowed sizeis reported.Cause
OSS Store has a size limit for each small file. An error is reported if a file exceeds 3 GB.
Solution
To resolve this issue, you can adjust the following two properties. The principle is to adjust the execution plan by changing the property values to control the size of data that is written by each reducer to the OSS external table. This ensures that the OSS Store file does not exceed the 3 GB limit.
set odps.sql.mapper.split.size=256; # Adjusts the size of data read by each mapper, in MB. set odps.stage.reducer.num=100; # Adjusts the number of workers in the reduce stage.
How do I resolve a memory overflow error that occurs after I upload a UDF to access an OSS external table on MaxCompute, even though the UDF passed local tests?
Problem
When accessing an OSS external table on MaxCompute, a UDF that passed local tests returns the following error after being uploaded.
FAILED: ODPS-0123131:User defined function exception - Traceback: java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap spaceAfter setting the following parameters, the running time increases, but the error persists.
set odps.stage.mapper.mem = 2048; set odps.stage.mapper.jvm.mem = 4096;Cause
There are too many object files in the external table, which causes excessive memory usage, and no partitions are set.
Solution
Use a smaller amount of data for the query.
Partition the object files to reduce memory usage.
How do I merge multiple small files into a single file using an OSS external table?
Check the Logview log to see if the last stage in the SQL execution plan is a reducer or a joiner.
If it is a reducer, run the statement
set odps.stage.reducer.num=1;If it is a joiner, run the statement
set odps.stage.joiner.num=1;
How do I resolve the "Couldn't connect to server" error when reading from an OSS external table?
Problem
When reading data from an OSS external table, the error
ODPS-0123131:User defined function exception - common/io/oss/oss_client.cpp(95): OSSRequestException: req_id: , http status code: -998, error code: HttpIoError, message: Couldn't connect to serveris reported.Cause
Cause 1: When the OSS external table was created, a public endpoint was used for the
oss_endpointin the oss_location address, instead of an internal endpoint.Cause 2: When the OSS external table was created, the endpoint of another region was used for the
oss_endpointin the oss_location address.
Solution
For Cause 1:
Check whether the
oss_endpointin the oss_location parameter of the OSS external table creation statement is an internal endpoint. If it is a public endpoint, change it to an internal endpoint. For more information about the parameters, see Parameters.For example, if a user in the Indonesia (Jakarta) region used the address
oss://oss-ap-southeast-5.aliyuncs.com/<bucket>/....to create an external table, it should be changed to the corresponding internal addressoss://oss-ap-southeast-5-internal.aliyuncs.com/<bucket>/.....For Cause 2:
Check whether the
oss_endpointin the oss_location parameter of the OSS external table creation statement is the endpoint of the region that you want to access. For more information about OSS classic network domain names, see Regions and endpoints.
How do I resolve the "Network is unreachable (connect failed)" error when creating an OSS external table?
Problem
When creating an OSS external table, the error
ODPS-0130071:[1,1] Semantic analysis exception - external table checking failure, error message: Cannot connect to the endpoint 'oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com': Connect to bucket.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com:80 [bucket.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com] failed: Network is unreachable (connect failed)is reported.Cause
When the OSS external table was created, a public endpoint was used for the
oss_endpointin the oss_location address, instead of an internal endpoint.Solution
Check whether the
oss_endpointin the oss_location parameter of the OSS external table creation statement is an internal endpoint. If it is a public endpoint, change it to an internal endpoint. For more information about the parameters, see Parameters.For example, if a user in the China (Beijing) region used the address
oss://oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/<bucket>/....to create an external table, it should be changed to the corresponding internal addressoss://oss-cn-beijing-internal.aliyuncs.com/<bucket>/.....
How do I resolve slow SQL job execution on an OSS external table?
Slow reading of GZ compressed files in an OSS external table
Symptoms
A user created an OSS external table with a data source of a 200 GB GZ compressed file in OSS. The data reading process is slow.
Cause
The SQL processing speed is slow because too few mappers are executing the computation in the map stage.
Solution
For structured data, you can set the following parameter to adjust the amount of data read by a single mapper to speed up SQL execution.
set odps.sql.mapper.split.size=256; # Adjusts the size of table data read by each mapper, in MB.For unstructured data, check whether there is only one OSS file in the OSS external table path. If there is only one, only one mapper can be generated because unstructured data in a compressed format cannot be split. This results in slow processing speed. We recommend that you split the large OSS file into smaller files in the corresponding external table path on OSS. This increases the number of mappers that are generated when the external table is read and improves the reading speed.
Slow search of MaxCompute external table data using an SDK
Symptoms
Searching MaxCompute external table data using an SDK is slow.
Solution
External tables only support full table scans, which is slow. We recommend using a MaxCompute internal table instead.
How do I resolve the issue where old data is deleted but new data is not written when using the OSS multipart upload feature?
Problem
In an
insert overwritescenario, if the job fails in extreme cases, the result may be inconsistent with expectations. The old data is deleted, but the new data is not written.Cause
The newly written data fails to be written to the target table due to a very low probability of a hardware failure or metadata update failure. The delete operation in OSS does not support rollback, so the deleted old data cannot be recovered.
Solution
If you are overwriting an OSS external table based on its old data, for example,
insert overwrite table T select * from table T;, back up the OSS data in advance. If the job fails, you can then overwrite the OSS external table based on the backed-up old data.If the
insert overwritejob can be resubmitted, simply resubmit the job if it fails.
Solution for the "table not found" error when accessing an OSS external table from Spark
Problem
When using Spark to access an OSS external table, the task fails with a "table not found" error.
Solution
Add the following parameters:
Enable external table configuration:
spark.sql.catalog.odps.enableExternalTable=true;Configure the region where OSS is located:
spark.hadoop.odps.oss.region.default=cn-<region>
If the error persists after you add the above parameters, as shown below:

Recreate the OSS external table and then access it again.
References
Supported OSS external table formats:
Create an OSS external table and read from or write to OSS using a custom parser: Custom parsers.
Parse an OSS file into a dataset with a schema that supports column filtering and processing: Special feature: Schemaless Query.