MaxCompute provides the Storage API to improve integration with the big data ecosystem and allow external engines to access data in MaxCompute. Mainstream third-party compute engines can call the Storage API to directly access the underlying storage of MaxCompute. This significantly improves the efficiency of data access and interaction.
Open Storage overview
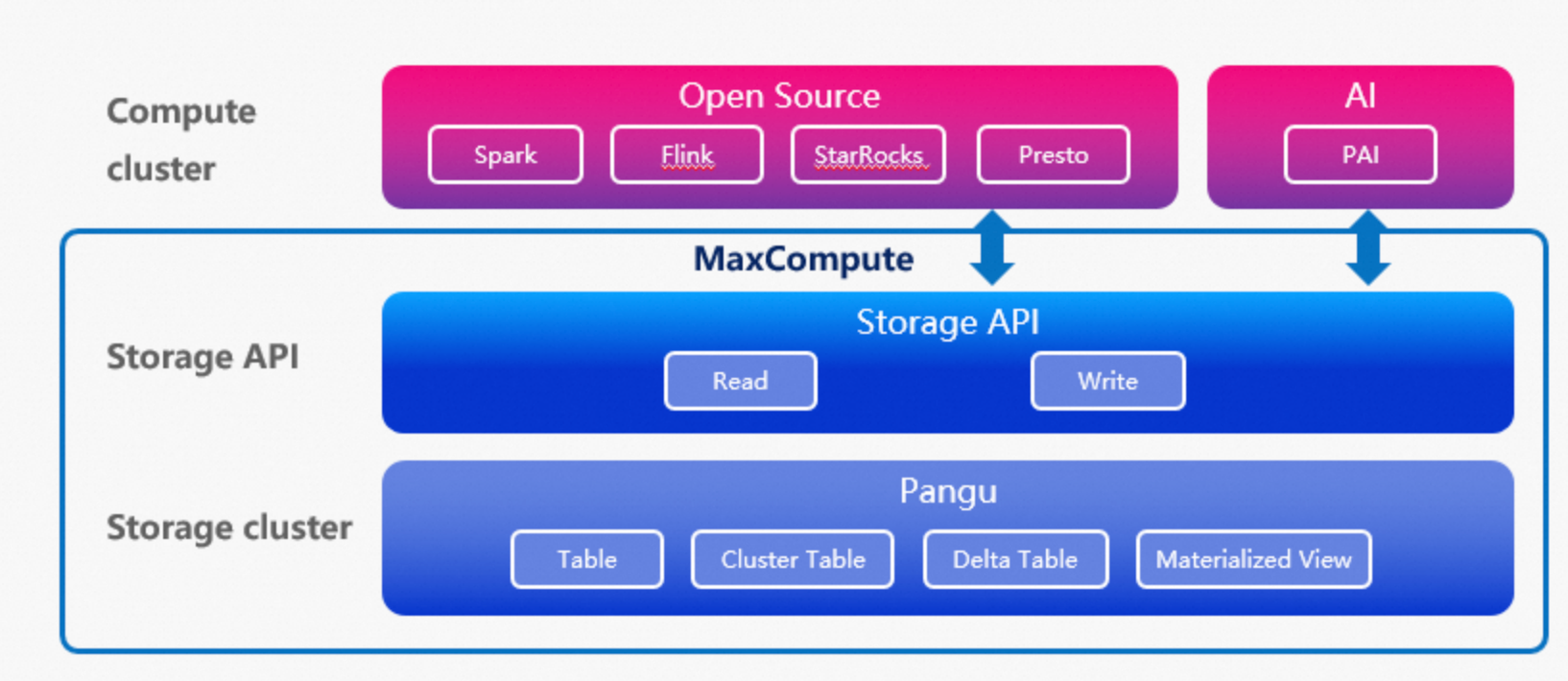
The Storage API is a data service interface that provides an efficient, low-latency, and secure method for data access. It allows mainstream third-party compute engines to access the MaxCompute storage system. This improves the integration and data processing efficiency between MaxCompute and open source compute engines or machine learning engines. Compute engines such as Spark, StarRocks, Presto, and Flink can use a connector to directly access data stored in MaxCompute. This simplifies the data usage process and improves data access performance. The following figure shows the architecture.
Scenarios
The Storage API is ideal for scenarios that require data accessibility and multi-engine computing. If enterprises or developers need to flexibly switch between computing frameworks or use specific engine features to process data in MaxCompute, the Storage API acts as a bridge to facilitate data exchange and enable diverse data processing.
Key features
High throughput: The Storage API supports efficient columnar data reads, predicate pushdown for data filtering before transmission, and the Arrow data format.
Secure and user-friendly: Offers direct readaccess to the underlying storage with table semantics. This abstracts away storage complexities while adhering to security policies such as project isolation, access control, and data encryption.
Ecosystem integration: Spark on EMR and StarRocks can use a connector to directly access data in MaxCompute. This simplifies compute engine integration.
Scope
Third-party engines that access MaxCompute can read standard tables, partitioned tables, clustered tables, Delta Tables, and materialized views. However, they cannot read external tables or logical views in MaxCompute.
Reading data of the JSON type is not supported.
For the pay-as-you-go Storage API, the number of concurrent requests is limited to 1,000 per tenant, and the transmission rate is limited to 10 MB/s per concurrent request.
Data transmission resources
When a third-party engine uses the MaxCompute Storage API for data transmission tasks, you can use either exclusive resource groups for Data Transmission Service (subscription) resources. The following table describes the resources.
Resource group name | Billing description | Supported regions | Usage instructions |
This resource group is based on the subscription billing method. You are charged based on the number of concurrent instances that you purchase. |
| Purchase and use an exclusive resource group for Data Transmission Service |
On the Resource Observation page, you can view usage details for exclusive resource groups for Data Transmission Service (subscription). For more information, see Resource Observation.
Usage examples
Access MaxCompute using a connector. For more information, see the following topics:
Access MaxCompute using an SDK. For more information, see the following topics:
Arrow data type mapping
The MaxCompute Storage API uses Apache Arrow data types to ensure an efficient and structured representation of data during storage and transmission. When you write data using the MaxCompute Storage API, the data is not computed or processed. For example, duplicate keys are not removed from Map data. The original data structure is retained unless the storage engine has specific restrictions.
The following table describes the mappings between MaxCompute and Apache Arrow data types.
MaxCompute data type | Arrow data type |
TINYINT | Int8Type |
SMALLINT | Int16Type |
INT | Int32Type |
BIGINT | Int64Type |
FLOAT | FloatType |
DOUBLE | DoubleType |
BOOLEAN | BooleanType |
DECIMAL | Decimal128Type Note The precision of the MaxCompute DECIMAL type is higher than that of the Storage API Decimal128Type.
|
DECIMAL(precision, scale) | Decimal128Type |
STRING | StringType |
BINARY | BinaryType |
VARCHAR | StringType |
CHAR | StringType |
DATETIME | TimestampType[1] The time unit is milliseconds, and the timezone is UTC. |
TIMESTAMP | TimestampType[2] The time unit is nanoseconds, and the timezone is UTC. Note The TIMESTAMP type supports a wider value range. If you use the Storage API to read or write TIMESTAMP data that is beyond the precision range of TimestampType, the high-precision part of the value is truncated. This causes a loss of precision. |
DATE | Date32Type |
INTERVAL_DAY_TIME | DayTimeIntervalType Note The INTERVAL_DAY_TIME type is accurate to nanoseconds. The Storage API DayTimeIntervalType type is accurate to milliseconds. If you use the Storage API to read or write INTERVAL_DAY_TIME data, the nanosecond part is truncated. This causes a loss of precision. |
INTERVAL_YEAR_MONTH | MonthIntervalType |
ARRAY | ListType |
MAP | MapType Note If a MAP contains duplicate keys:
For example, if you write the raw data |
STRUCT | StructType |
JSON | StringType |