This topic describes how to migrate data from BigQuery on Google Cloud Platform (GCP) to Alibaba Cloud MaxCompute over the Internet.
Prerequisites
Category | Platform | Requirement | Reference |
Environment and data | Google Cloud Platform |
| If you do not have the relevant environment and datasets, see the following references for preparation:
|
Alibaba Cloud |
| If you do not have the relevant environment, see the following references for preparation:
| |
Account | Google Cloud Platform | An Identity and Access Management (IAM) user is created and granted the permissions to access Google Cloud Storage. | |
Alibaba Cloud | A Resource Access Management (RAM) user and a RAM role are created. The RAM user is granted the read and write permissions on OSS buckets and the online migration permissions. | ||
Region | Google Cloud Platform | N/A | N/A |
Alibaba Cloud | The OSS bucket and the MaxCompute project are in the same region. | N/A |
Background information
The following figure shows the process to migrate datasets from BigQuery to Alibaba Cloud MaxCompute.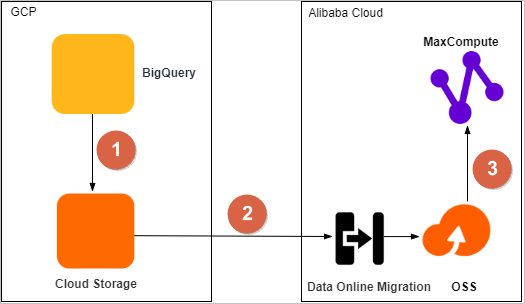
No. | Description |
1 | Export datasets from BigQuery to Google Cloud Storage. |
2 | Migrate data from Google Cloud Storage to an OSS bucket by using the Data Online Migration service of OSS. |
3 | Migrate data from the OSS bucket to a MaxCompute project in the same region, and then verify the integrity and accuracy of the migrated data. |
Step 1: Export datasets from BigQuery to Google Cloud Storage
Use the bq command-line tool to run the bq extract command to export datasets from BigQuery to Google Cloud Storage.
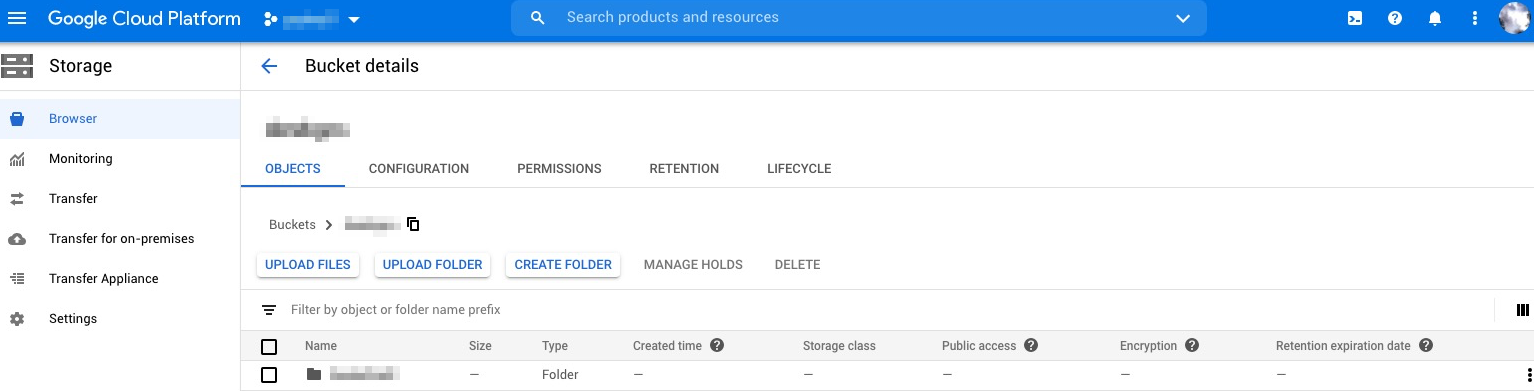
Log on to Google Cloud Platform, and create a bucket for the data you want to migrate. For more information, see Creating storage buckets.
Use the bq command-line tool to query the Data Definition Language (DDL) scripts of tables in the TPC-DS datasets and download the scripts to an on-premises device. For more information, see Getting table metadata using INFORMATION_SCHEMA.
BigQuery does not support commands such as
show create tableto query DDL scripts of tables. BigQuery allows you to use built-in user-defined functions (UDFs) to query the DDL scripts of the tables in a dataset. The following code shows examples of DDL scripts.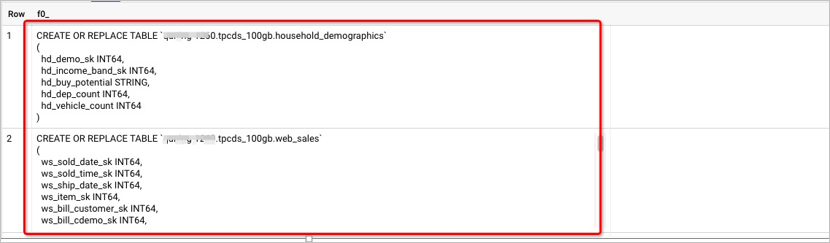
Use the bq command-line tool to run the
bq extractcommand to export tables in BigQuery datasets to the destination bucket of Google Cloud Storage. For more information about the operations, formats of exported data, and compression types, see Exporting table data.The following code shows a sample export command:
bq extract --destination_format AVRO --compression SNAPPY tpcds_100gb.web_site gs://bucket_name/web_site/web_site-*.avro.snappy;View the bucket and check the data export result.
Step 2: Migrate the exported data from Google Cloud Storage to OSS
You can use the Data Online Migration service to migrate data from Google Cloud Storage to OSS. For more information, see Migrate data from Google Cloud Platform to OSS. The Data Online Migration service is in public preview. Before you use the service, you must contact the Customer Service to activate the service.
Estimate the size and the number of files that you want to migrate. You can query the data size in the bucket of Google Cloud Storage by using the gsutil tool or checking the storage logs. For more information, see Getting bucket information.
Optional:If you do not have a bucket in OSS, log on to the OSS console and create a bucket to store the migrated data. For more information, see Create buckets.
Optional:If you do not have a RAM user, create a RAM user and grant relevant permissions to the RAM user.
Log on to the RAM console and create a RAM user. For more information, see Create a RAM user.
Find the newly created RAM user, and click Add Permissions in the Actions column. On the page that appears, select AliyunOSSFullAccess and AliyunMGWFullAccess, and click . Once the permission granting process is complete, click Close. The AliyunOSSFullAccess permission authorizes the RAM user to read and write OSS buckets. The AliyunMGWFullAccess permission authorizes the RAM user to perform online migration jobs.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Overview. In the Basic Information section of the Overview page, click the Login URL link, and use the credentials of the RAM user to log on to the Alibaba Cloud Management Console.
On Google Cloud Platform, create a user who uses the programmatic access method to access Google Cloud Storage. For more information, see IAM permissions for JSON methods.
Log on to the IAM & Admin console, and find a user who has permissions to access BigQuery. In the Actions column, click .
In the dialog box that appears, select JSON, and click CREATE. Save the JSON file to an on-premises device and click CLOSE.
In the Create service account wizard, click Select a role, and choose to authorize the IAM user to access Google Cloud Storage.
Create a source data address and a destination data address for online migration.
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud Data Transport console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Data Online Migration> Data Address.
On the Data Address page, click Create Data Address. In the Create Data Address panel, set the required parameters and click OK. For more information about the required parameters, see Migrate data.
Data source
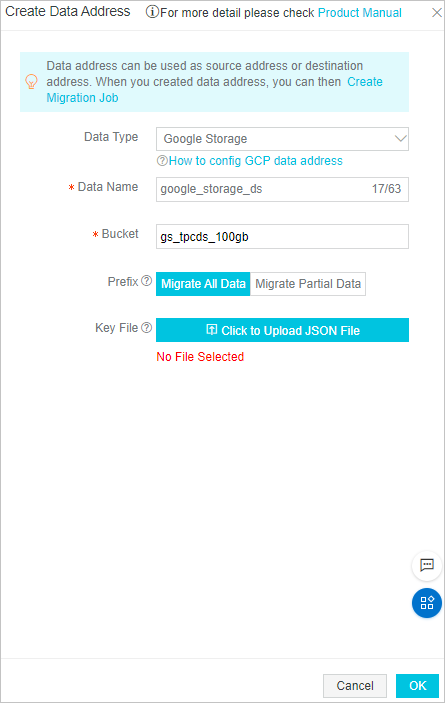 Note
NoteFor the Key File field, upload the JSON file that is downloaded in Step 4.
Destination data address
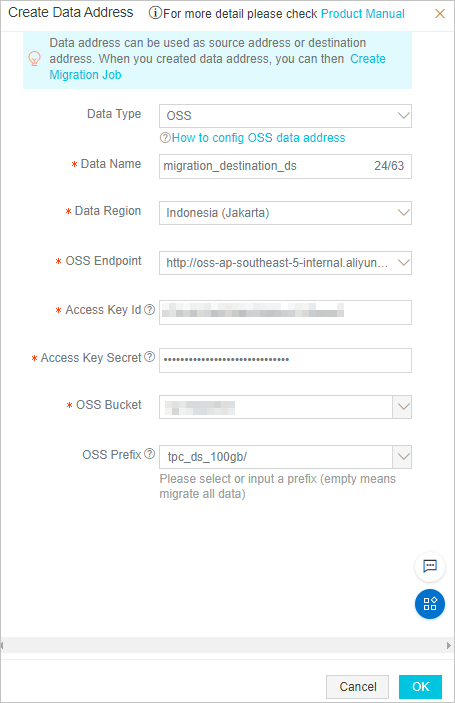 Note
NoteIn the Access Key Id and Access Key Secret fields, enter the AccessKey ID and the AccessKey secret of the RAM user.
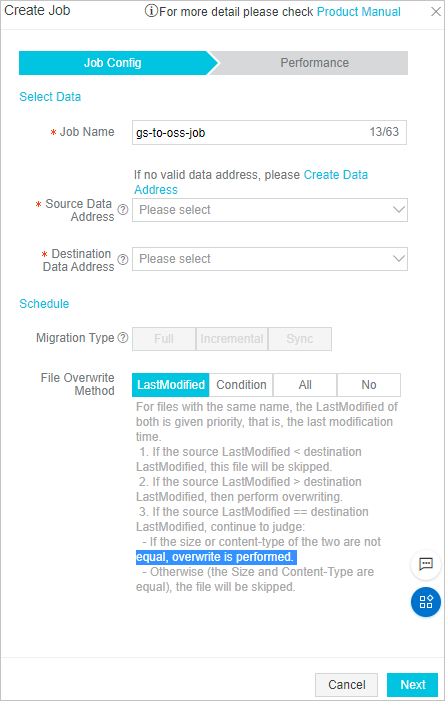
Create an online migration job.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Migration Jobs.
On the File Sync Management page, click Create Job. In the Create Job wizard, set the required parameters and click Create. For more information about the required parameters, see Migrate data.
Job Config
Performance tuning
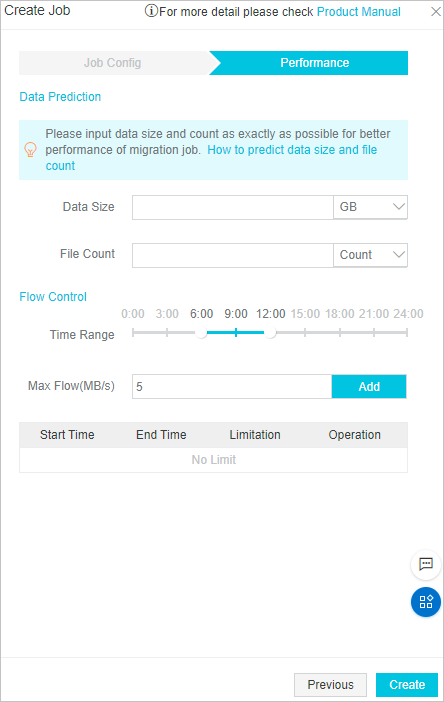 Note
NoteIn the Data Size and File Count fields, enter the size and the number of files that were migrated from Google Cloud Platform.
The migration job that you created is automatically run. If Finished is displayed in the Job Status column, the migration job is complete.
In the Operation column of the migration job, click Manage to view the migration report and confirm that all the data is migrated.
Log on to the OSS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Buckets. On the Buckets page, click the created bucket. In the left-side navigation pane of the bucket details page, choose Files > Files to view the migration results.
Step 3: Migrate data from the OSS bucket to the MaxCompute project in the same region
You can execute the LOAD statement of MaxCompute to migrate data from an OSS bucket to a MaxCompute project in the same region.
The LOAD statement supports Security Token Service (STS) and AccessKey for authentication. If you use AccessKey for authentication, you must provide the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret of your account in plaintext. STS authentication is highly secure because it does not expose the AccessKey information. In this section, STS authentication is used as an example to show how to migrate data.
On the Ad-Hoc Query tab of DataWorks or the MaxCompute client odpscmd, modify the DDL scripts of the tables in the BigQuery datasets, specify the MaxCompute data types, and create a destination table that stores the migrated data in MaxCompute.
For more information about ad hoc queries, see Use the ad-hoc query feature to execute SQL statements (optional). The following code shows a configuration example:
CREATE OR REPLACE TABLE `****.tpcds_100gb.web_site` ( web_site_sk INT64, web_site_id STRING, web_rec_start_date STRING, web_rec_end_date STRING, web_name STRING, web_open_date_sk INT64, web_close_date_sk INT64, web_class STRING, web_manager STRING, web_mkt_id INT64, web_mkt_class STRING, web_mkt_desc STRING, web_market_manager STRING, web_company_id INT64, web_company_name STRING, web_street_number STRING, web_street_name STRING, web_street_type STRING, web_suite_number STRING, web_city STRING, web_county STRING, web_state STRING, web_zip STRING, web_country STRING, web_gmt_offset FLOAT64, web_tax_percentage FLOAT64 ) Modify the INT64 and FLOAT64 fields to obtain the following DDL script: CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS <your_maxcompute_project>.web_site_load ( web_site_sk BIGINT, web_site_id STRING, web_rec_start_date STRING, web_rec_end_date STRING, web_name STRING, web_open_date_sk BIGINT, web_close_date_sk BIGINT, web_class STRING, web_manager STRING, web_mkt_id BIGINT, web_mkt_class STRING, web_mkt_desc STRING, web_market_manager STRING, web_company_id BIGINT, web_company_name STRING, web_street_number STRING, web_street_name STRING,` web_street_type STRING, web_suite_number STRING, web_city STRING, web_county STRING, web_state STRING, web_zip STRING, web_country STRING, web_gmt_offset DOUBLE, web_tax_percentage DOUBLE );The following table describes the mapping between BigQuery data types and MaxCompute data types.
BigQuery data type
MaxCompute data type
INT64
BIGINT
FLOAT64
DOUBLE
NUMERIC
DECIMAL and DOUBLE
BOOL
BOOLEAN
STRING
STRING
BYTES
VARCHAR
DATE
DATE
DATETIME
DATETIME
TIME
DATETIME
TIMESTAMP
TIMESTAMP
STRUCT
STRUCT
GEOGRAPHY
STRING
Optional:If you do not have a RAM role, create a RAM role that has the OSS access permissions and assign the role to the RAM user. For more information, see STS authorization.
Execute the LOAD statement to load all data from the OSS bucket to the MaxCompute table, and execute the SELECT statement to query and verify the imported data. You can only load one table at a time. To load multiple tables, you must execute the LOAD statement multiple times. For more information about the LOAD statement, see LOAD.
LOAD OVERWRITE TABLE web_site FROM LOCATION 'oss://oss-<your_region_id>-internal.aliyuncs.com/bucket_name/tpc_ds_100gb/web_site/' --The endpoint of the OSS bucket ROW FORMAT SERDE 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.avro.AvroSerDe' WITH SERDEPROPERTIES ('odps.properties.rolearn'='<Your_RoleARN>','mcfed.parquet.compression'='SNAPPY') STORED AS AVRO;Execute the following statement to query and verify the imported data:
SELECT * FROM web_site;The following result is returned:
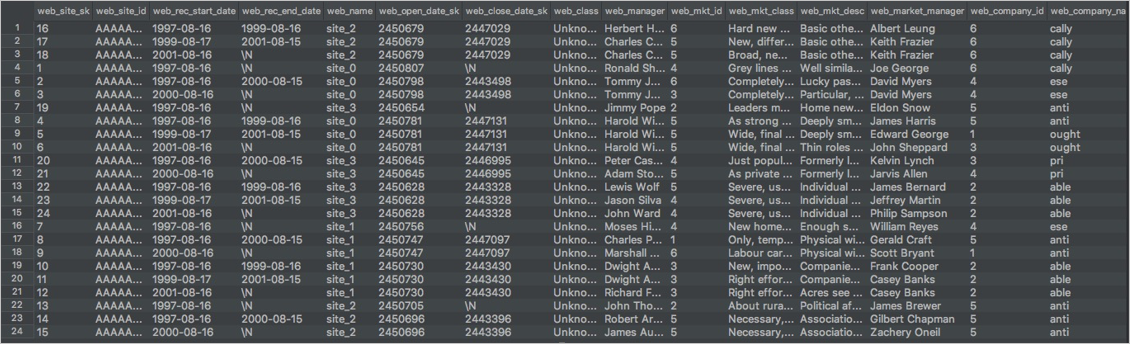
Verify that the data migrated to MaxCompute is the same as the data in BigQuery. This verification is based on the number of tables, the number of rows, and the query results of typical jobs.