This topic describes how to use SQL to quickly read and write data with an Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) or extract, transform, and load (ETL) resource group in Lindorm Compute Engine.
Prerequisites
LindormTable has been activated. For more information, see Create an instance.
You have activated Lindorm Compute Engine. For more information, see Activate the service.
You have added the client IP address to the Lindorm whitelist. For more information, see Set a whitelist.
Use an OLAP resource group
The OLAP resource group in the compute engine provides a MySQL-compatible access interface. It is designed for query analysis scenarios and delivers high-concurrency and low-latency query responses. After you create an OLAP resource group, dedicated compute resources are allocated to ensure fast query responses.
Step 1: Create an OLAP resource group
Log on to the Lindorm console. In the upper-left corner of the page, select the region of the instance. On the Instances page, click the ID of the target instance or click View Instance Details in the Actions column for the instance.
On the Instance Details page, go to the Configurations section and click Resource Groups in the Compute Engine column.
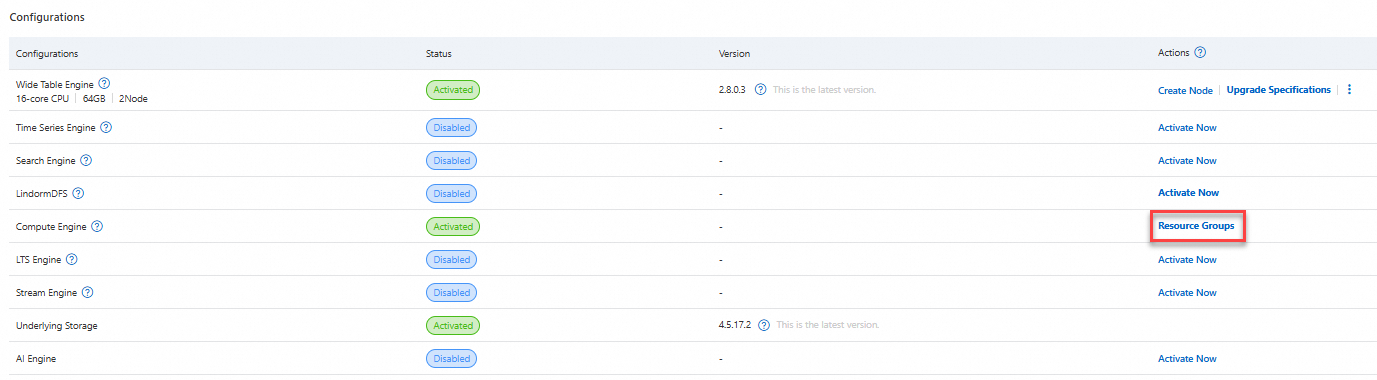
On the Resource Group Details page, click Create Resource Group and configure the following:
Parameter
Description
Resource Group Type
Select OLAP.
Resource Group Name
The name of the resource group. The name can contain only lowercase letters and digits. The name can be up to 63 characters in length. Example:
cg0.Node Specifications
Select the node specifications.
Working Nodes in Job
The value must be in the range of [4, 1024]. The default value is
4.Click OK to create the resource group.
NoteThe creation process takes about 20 minutes.
On the Resource Group Details page, when the status of the newly created resource group is Running under Status and Description, you can hover over the OLAP resource group name to obtain its VPC internal endpoint, such as
jdbc:mysql://ld-bp1dv48fk0yg0****-olap-proxy-ldps.lindorm.aliyuncs.com:9030.After you configure the MySQL client, use JDBC to connect to the VPC endpoint of the OLAP resource group. Log on using the username and password for LindormTable. You can then execute SQL queries.
mysql -hld-bp1dv48fk0yg0****-olap-proxy-ldps.lindorm.aliyuncs.com -P9030 -uroot -p
Step 2: Access data
Access column store data
Column store is a data lake that uses columnar storage and is compatible with the Iceberg ecosystem. Data is stored in the file engine of the Lindorm instance. You can use the OLAP resource group to write and query the data.
Column store data is stored in the lindorm_columnar catalog. Catalogs are used to identify different data sources. This catalog is accessed by default when you connect using the MySQL protocol. You can also run the SET CATALOG lindorm_columnar; command to explicitly switch to the column store data catalog.
Create and use a database.
-- Create a database. CREATE DATABASE olapdemo; -- Use the database. USE olapdemo;Create a table and write data to it.
-- Create a table. CREATE TABLE test (id INT, name STRING) ENGINE = iceberg; -- Insert data. INSERT INTO test VALUES (0, 'Jay'), (1, 'Edison');Query data.
Example 1:
SELECT id, name FROM test WHERE id != 0;The following result is returned:
+------+--------+ | id | name | +------+--------+ | 1 | Edison | +------+--------+Example 2:
SELECT count(distinct name) FROM test;The following is returned:
+----------------------+ | count(DISTINCT name) | +----------------------+ | 2 | +----------------------+Example 3:
SELECT * FROM (SELECT id, name FROM test WHERE id != 0) t0 JOIN (SELECT id, name FROM test WHERE id != 2) t1 ON t0.id=t1.id;+------+--------+------+--------+ | id | name | id | name | +------+--------+------+--------+ | 1 | Edison | 1 | Edison | +------+--------+------+--------+
Delete the table.
DROP TABLE test;Delete the database.
DROP DATABASE olapdemo;
Access wide table data
The OLAP resource group supports direct queries of data in LindormTable. You can use its computing power to efficiently run complex queries. The OLAP resource group supports only query operations. It does not support creating tables in or writing data to LindormTable.
LindormTable data is stored in the lindorm_table catalog. To access this data, you must switch to the catalog by running the SET CATALOG lindorm_table; command.
If you have a wide table, proceed to the next step. Otherwise, connect to LindormTable and run the following statements to create a wide table named tb.
-- Create a database.
CREATE DATABASE test;
-- Use the database.
USE test;
-- Create a data table and insert two rows of data.
CREATE TABLE tb (id varchar, name varchar, address varchar, primary key(id, name)) ;
UPSERT INTO tb (id, name, address) values ('001', 'Jack', 'hz');
UPSERT INTO tb (id, name, address) values ('002', 'Edison', 'bj'); In the MySQL command-line interface (CLI) that is connected to the OLAP resource group, run the following query statements to access the wide table data.
Explicitly switch the data source and use the database.
-- Explicitly switch the data source. SET CATALOG lindorm_table; -- Use the test database. USE test;Query the wide table data.
Example 1:
SELECT * FROM tb LIMIT 5;The following result is returned:
+------+--------+---------+ | id | name | address | +------+--------+---------+ | 001 | Jack | hz | | 002 | Edison | bj | +------+--------+---------+Example 2:
SELECT count(*) FROM tb;The following result is returned:
+----------+ | count(*) | +----------+ | 2 | +----------+
Use an ETL resource group
The ETL resource group in the compute engine provides serverless Spark SQL to run queries and write data. Resources are requested on demand and released automatically. This makes it ideal for infrequent queries or offline reporting.
Step 1: Activate the resource group
Log on to the Lindorm console. In the upper-left corner of the page, select the region of the instance. On the Instances page, click the ID of the target instance or click View Instance Details in the Actions column for the instance.
On the Instance Details page, go to the Configurations section and click Resource Groups in the Compute Engine column.

On the Resource Group Details page, click Create Resource Group and configure the following parameters:
Parameter
Description
Resource Group Type
Select ETL.
Resource Group Name
The name of the resource group. The name can contain only lowercase letters and digits, and must be no more than 63 characters in length. For example,
cg0.Daily Resource Quota
The maximum number of Capacity Units (CUs) that the resource group can consume per day. The unit is
CU*Hour. The default value is100000.ImportantIf the limit is exceeded, jobs are immediately deleted. For resource groups that require high stability, set this parameter to
0. A value of 0 indicates no limit.The maximum number of CPU cores in the resource group.
The maximum number of CPU cores for the resource group. Valid values: [100, 100000].
The maximum memory size in the resource group. Unit: GB.
The maximum memory size for the resource group. Valid values: [400 GB, 1000000 GB]. There is no default value.
Authorize Users
The default value is
*, which allows all users to access the resource group.Click OK to create the resource group.
Step 2: Prepare the environment
The following environments are deployed on an ECS instance in the same VPC as the Lindorm instance.
Install Java Development Kit (JDK) 1.8 or later.
Download the or Spark.
Decompress the Spark installation package.
Set the SPARK_HOME environment variable to the path where you decompressed the package.
export SPARK_HOME=/path/to/spark/;Edit the
$SPARK_HOME/conf/beeline.confconfiguration file.endpoint: The JDBC URL of the Lindorm compute engine. For more information about how to retrieve the URL, see View endpoints.
user: The username to access LindormTable.
password: The password that corresponds to the username.
shareResource: Specifies whether to share compute resources across multiple sessions for the same user. The default value is
true.compute-group: The name of the ETL resource group used by the compute engine. If you do not set this parameter, the default value is
default.
Go to the
$SPARK_HOME/bindirectory and run the./beelinecommand. The command displays the following output:Welcome to Lindorm Distributed Processing System (LDPS) !!! Initializing environment. It might take minutes ... Environemnt prepared. You may visit your jdbc cluster by below url: http://alb-boqak6zfns5gzx****.cn-hangzhou.alb.aliyuncsslb.com/proxy/75ce76086b61470da7046bd4c2b7**** Please note -- you are sharing this JDBC cluster between SQL sessions from the same user. The cluster will be released by auto if idle for 4 hours. You may also kill it manually by visiting above web url and clicking 'kill' in tab of 'Query Engine' lindorm-beeline>In the interactive session, enter SQL statements to run write or query operations.
NoteUse the returned link,
http://alb-boqak6zfns5gzx****.cn-hangzhou.alb.aliyuncsslb.com/proxy/75ce76086b61470da7046bd4c2b7****, to access the Spark UI for the compute engine.
Step 3: Access data
Access column store data
Column store is a data lake that uses columnar storage and is compatible with the Iceberg ecosystem. Data is stored in the file engine of the Lindorm instance. You can use Spark SQL to write and query the data.
Column store data is stored in the lindorm_columnar catalog. Catalogs are used to identify different data sources. This catalog is accessed by default when you connect using the MySQL protocol. You can also run the SET CATALOG lindorm_columnar; command to explicitly switch to the column store data catalog.
Create and use a database.
-- Create a database CREATE DATABASE etldemo; -- Use the database USE etldemo;Create a data table and write data to it.
-- Create a table CREATE TABLE test (id INT, name STRING); -- Insert data INSERT INTO test VALUES (0, 'Jay'), (1, 'Edison');Query data.
Example 1:
SELECT id, name FROM test WHERE id != 0;The following result is returned:
+------+--------+ | id | name | +------+--------+ | 1 | Edison | +------+--------+Example 2:
SELECT count(distinct name) FROM test;The following is returned:
+----------------------+ | count(DISTINCT name) | +----------------------+ | 2 | +----------------------+Example 3:
SELECT * FROM (SELECT id, name FROM test WHERE id != 0) t0 JOIN (SELECT id, name FROM test WHERE id != 2) t1 ON t0.id=t1.id;+------+--------+------+--------+ | id | name | id | name | +------+--------+------+--------+ | 1 | Edison | 1 | Edison | +------+--------+------+--------+
Delete the table.
DROP TABLE test;Delete the database.
DROP DATABASE etldemo;
Access wide table data
You can use a Spark SQL connection in an ETL resource group to query data in LindormTable. You can use elastic compute resources to run complex queries and computations on wide table data. Spark SQL connections do not support Data Definition Language (DDL) statements, such as creating or deleting tables in LindormTable. However, you can use them to query data.
LindormTable data is stored in the lindorm_table catalog. To access this data, you must switch to the catalog by running the SET CATALOG lindorm_table; command.
If you have a wide table, proceed to the next step. Otherwise, connect to LindormTable and run the following statements to create a wide table named tb.
-- Create a database.
CREATE DATABASE test;
-- Use the database.
USE test;
-- Create a data table and insert two rows of data.
CREATE TABLE tb (id varchar, name varchar, address varchar, primary key(id, name)) ;
UPSERT INTO tb (id, name, address) values ('001', 'Jack', 'hz');
UPSERT INTO tb (id, name, address) values ('002', 'Edison', 'bj'); In the lindorm-beeline interactive session, run the following query statements to access the wide table data.
Explicitly switch the data source and use the database.
-- Explicitly switch the data source. SET CATALOG lindorm_table; -- Use the test database. USE test;Query the wide table data.
Example 1:
SELECT * FROM tb LIMIT 5;The following result is returned:
+------+--------+---------+ | id | name | address | +------+--------+---------+ | 001 | Jack | hz | | 002 | Edison | bj | +------+--------+---------+Example 2:
SELECT count(*) FROM tb;The following result is returned:
+-----------+ | count(1) | +-----------+ | 2 | +-----------+