You must encrypt sensitive data in your IT assets that are deployed on Alibaba Cloud. You can call cryptographic API operations of Key Management Service (KMS) to encrypt or decrypt data less than 6 KB. This topic describes how to call API operations of KMS to encrypt and decrypt the private keys of SSL certificates.
Background information
You can use a customer master key (CMK) to encrypt and decrypt data in but not limited to the following scenarios:
Encrypt configuration files.
Encrypt the private keys of SSL certificates.
Architecture
The data of the user is sent to the KMS server over a secure channel. The KMS server encrypts or decrypts the data and returns the result to the user over a secure channel. The following figure shows the entire procedure. 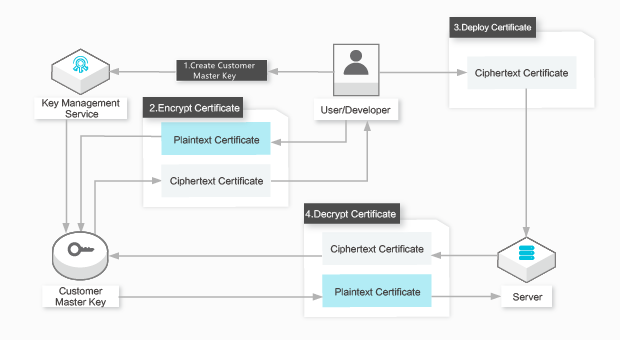 Procedure:
Procedure:
Create a CMK in the KMS console or by calling the CreateKey operation.
Call the Encrypt operation of KMS to encrypt the private key of an SSL certificate. The ciphertext private key is returned.
Deploy the SSL certificate by using the ciphertext private key to an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance.
Call the Decrypt operation of KMS to decrypt the ciphertext when the ECS instance starts and needs to use the SSL certificate.
Related API operations
You can call the following API operations to encrypt and decrypt data.
Operation | Description |
Creates a CMK. | |
Creates an alias for a CMK. | |
Encrypts data by using a CMK. | |
Decrypts data that is encrypted by KMS. You do not need to specify a CMK. |
Encrypt and decrypt the private key of an SSL certificate
The AccessKey pair of an Alibaba Cloud account has permissions on all API operations. Using the AccessKey pair to perform operations is a high-risk operation. We recommend that you use a RAM user to call API operations or perform routine O&M. We recommend that you do not save the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret in your project code. Otherwise, the AccessKey pair may be leaked and the security of all resources within your account may be compromised.
In this example, the AccessKey pair is saved in ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID and ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables to implement identity authentication. For more information about how to configure authentication information, see Instantiate a client and configure a credential.
Call the CreateKey operation to create a CMK.
aliyun kms CreateKeyExpected output:
{ "KeyMetadata": { "CreationDate": "2019-04-08T07:45:54Z", "Description": "", "KeyId": "1234abcd-12ab-34cd-56ef-12345678****", "KeyState": "Enabled", "KeyUsage": "ENCRYPT/DECRYPT", "DeleteDate": "", "Creator": "151266687691****", "Arn": "acs:kms:cn-hangzhou:151266687691****:key/1234abcd-12ab-34cd-56ef-12345678****", "Origin": "Aliyun_KMS", "MaterialExpireTime": "" }, "RequestId": "2a37b168-9fa0-4d71-aba4-2077dd9e80df" }(Optional) Create an alias for the CMK. We recommend that you perform this step.
Aliases are optionally used to identify CMKs. If a CMK does not have an alias, you can use the ID of the CMK to identify the CMK.
aliyun kms CreateAlias --AliasName alias/Apollo/WorkKey --KeyId 1234abcd-12ab-34cd-56ef-12345678****NoteIn this example, the alias
Apollo/WorkKeyis created for the CMK in the Apollo project. This alias is used in the subsequent sample code. You can usealias/Apollo/WorkKeyto reference the CMK when you call the Encrypt operation.Call the Encrypt operation to encrypt the private key of an SSL certificate. Then, KMS encrypts the private key.
In the following sample code:
alias/Apollo/WorkKeyis the alias of the CMK../certs/key.pem is the plaintext private key.
./certs/key.pem.cipher is the ciphertext private key.
#!/usr/bin/env python #coding=utf-8 import json from aliyunsdkcore import client from aliyunsdkkms.request.v20160120 import EncryptRequest from aliyunsdkkms.request.v20160120 import DecryptRequest def KmsEncrypt(client, plaintext, key_alias): request = EncryptRequest.EncryptRequest() request.set_accept_format('JSON') request.set_KeyId(key_alias) request.set_Plaintext(plaintext) response = json.loads(client.do_action(request)) return response.get("CiphertextBlob") def ReadTextFile(in_file): file = open(in_file, 'r') content = file.read() file.close() return content def WriteTextFile(out_file, content): file = open(out_file, 'w') file.write(content) file.close() clt = client.AcsClient(os.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID"),os.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET"),'<Region-Id>') key_alias = 'alias/Apollo/WorkKey' in_file = './certs/key.pem' out_file = './certs/key.pem.cipher' # Read private key file in text mode in_content = ReadTextFile(in_file) # Encrypt ciphertext = KmsEncrypt(clt, in_content, key_alias) # Write encrypted key file in text mode WriteTextFile(out_file, ciphertext)Call the Decrypt operation to decrypt the ciphertext private key. Then, KMS decrypts the private key that you have deployed to your ECS instance.
In the following sample code:
./certs/key.pem.cipher is the ciphertext private key.
./certs/decrypted_key.pem is the plaintext private key.
#!/usr/bin/env python #coding=utf-8 import json from aliyunsdkcore import client from aliyunsdkkms.request.v20160120 import EncryptRequest from aliyunsdkkms.request.v20160120 import DecryptRequest def KmsDecrypt(client, ciphertext): request = DecryptRequest.DecryptRequest() request.set_accept_format('JSON') request.set_CiphertextBlob(ciphertext) response = json.loads(client.do_action(request)) return response.get("Plaintext") def ReadTextFile(in_file): file = open(in_file, 'r') content = file.read() file.close() return content def WriteTextFile(out_file, content): file = open(out_file, 'w') file.write(content) file.close() clt = client.AcsClient(os.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID"),os.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET"),'<Region-Id>') in_file = './certs/key.pem.cipher' out_file = './certs/decrypted_key.pem' # Read encrypted key file in text mode in_content = ReadTextFile(in_file) # Decrypt ciphertext = KmsDecrypt(clt, in_content) # Write Decrypted key file in text mode WriteTextFile(out_file, ciphertext)