Function Compute supports HTTP triggers, which allow you to invoke functions using HTTP requests. The function processes the HTTP request and returns a result. This topic describes how to configure an HTTP trigger in the Function Compute console and use it to invoke a function.
Prerequisites
Step 1: Create a trigger
Log on to the Function Compute console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Functions.
In the top navigation bar, select a region. On the Functions page, click the function that you want to manage.
On the function details page, on the Triggers tab, click Create Trigger.
In the Create Trigger panel, configure the parameters and click OK.
Configuration item
Operation
Example
Trigger Type
Select HTTP Trigger.
HTTP Trigger
Name
Enter a custom trigger name.
http-trigger
Version Or Alias
The default value is LATEST. To create a trigger for another version or alias, you must first select that version on the function details page from the Version Or Alias drop-down list. For an overview of versions and aliases, see Manage versions and Manage aliases.
LATEST
Request Methods
Specify the methods that can trigger this HTTP trigger.
GET, POST, PUT, DELETE
Disable Internet URL
By default, this option is disabled, which allows the trigger to be accessed from a public domain name.
If you enable this option, a default public domain name is not provided for the HTTP trigger. If you then call the function using a public domain name, an
access denied due to function internet URL is disableerror is reported. Access through a custom domain name is not affected.No
Authentication Method
Select the method that Function Compute uses to authenticate HTTP requests. The following values are available:
No Authentication: Identity authentication is not required for HTTP requests. Anonymous access is supported. Anyone can send an HTTP request to call your function.
Signature Authentication: Identity authentication is required for HTTP requests. For sample code for signature authentication, see Access an HTTP trigger URL using a signature.
Basic Authentication: Identity authentication is required for HTTP requests. For sample code for Basic authentication, see Configure Basic authentication for an HTTP trigger.
JWT Authentication: JWT authentication is required for HTTP requests. For more information, see Configure JWT authentication for an HTTP trigger.
Bearer Authentication: Bearer authentication is required for HTTP requests. For more information, see Enable Bearer authentication for an HTTP trigger.
No Authentication
After creating a trigger, you can modify its configuration items, such as Version or Alias, Request Methods, and Authentication Method.
Step 2: Write and deploy code
After you create the HTTP trigger, you can write the function code.
On the function details page, click the Code tab. In the code editor, write your code and then click Deploy Code. For sample code, see the handler documentation for different runtimes in the section of the Function Compute documentation.
Step 3: Test the function
Method 1: Use the console to test the function
On the Function Details page, click the Code tab.
Synchronous invocation
Click Test Function.
Asynchronous invocation
Click the
 icon next to Test Function and select Async Invocation. Then, click Test Function.
icon next to Test Function and select Async Invocation. Then, click Test Function.
After the execution completes, you can view the result on the Code tab.
Method 2: Use cURL to test the function
On the function details page, click the Triggers tab. In the Configuration Information column for the HTTP trigger, obtain the public endpoint.
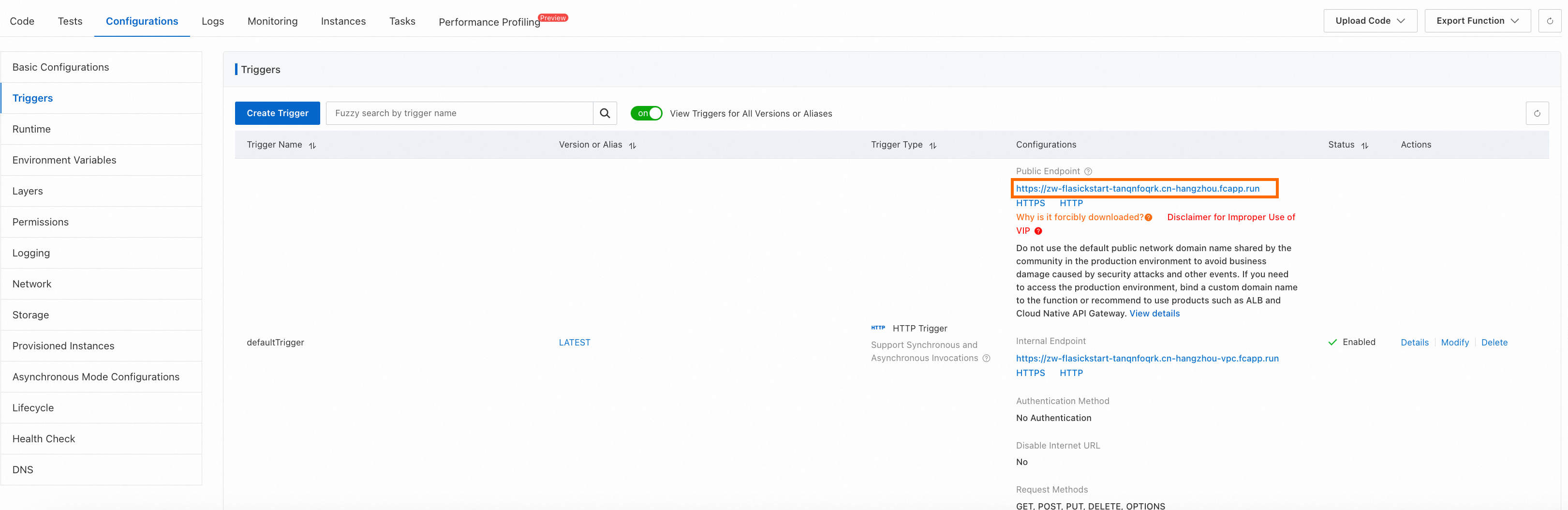
Run a cURL command on the command line to test the function.
Synchronous call
The following is an example. Replace
https://example.cn-shenzhen.fcapp.runwith the public endpoint of the HTTP trigger that you obtained in the previous step. Replace$pathwith the name of the API operation that you want to call.curl -v https://example.cn-shenzhen.fcapp.run/$pathNoteCall a web function: For a Flask application, if a Python function's route is defined as
@app.route('/test'), replace$pathwithtest. If the route is defined as@app.route('/'), call the public endpoint of the HTTP trigger directly.Call an event function: Call the public endpoint of the HTTP trigger directly.
After the command is executed, Function Compute returns the code's execution result.
Asynchronous invocation
The following is an example. Replace
https://example.cn-shenzhen.fcapp.runwith the public endpoint of your HTTP trigger. Replace$pathwith the name of the API operation that you want to call.curl -v -H "X-Fc-Invocation-Type: Async" https://example.cn-shenzhen.fcapp.run/$pathNoteCall a web function: For a Flask application, if a Python function's route is defined as
@app.route('/test'), replace$pathwithtest. If the route is defined as@app.route('/'), call the public endpoint of the HTTP trigger directly.Call an event function: Call the public endpoint of the HTTP trigger directly.
After the command is executed, Function Compute returns the result of receiving the request. A
202status code indicates that the request was successfully submitted. Other status codes indicate that an error occurred during the invocation. For more information about the causes of error codes, see FAQ (Troubleshooting).
Method 3: (Not recommended) Use a browser to test the function
On the function details page, click the Triggers tab. In the Configuration Information column of the target HTTP trigger, obtain the public endpoint. Enter this endpoint into the address bar of your browser and press Enter.
After the execution is complete, the browser returns a file with the execution result.
(Optional) Use API Gateway to protect the function
Function Compute supports anonymous access for HTTP requests. This means that anyone can send an HTTP request to invoke your function. To prevent unauthorized users from accessing your function and causing unnecessary resource consumption or security risks, you can enable identity authentication and integrate your HTTP function with API Gateway. You can use API Gateway plug-ins, such as the IP access control plug-in, JWT authentication plug-in, or BasicAuth plug-in, to protect your HTTP function.
In the Function Compute console, find the target function. On the function details page, click the Triggers tab. In the Actions column of the target HTTP trigger, click Edit.
In the Edit Trigger panel, turn on the Disable Internet URL switch.
Log on to the API Gateway console and switch to the region where the HTTP function resides.
Create a group and an API.
You can create an API to allow external applications to call the internal function service in a specified way. You can use an API group to organize and manage multiple related API operations. This makes it easier to implement unified security policies and traffic shaping measures.
In the API Gateway console, in the navigation pane on the left, choose API Management > Group Management. Click Create Group.
In the Create Group dialog box, select an Instance. Set Group Name to
FC-Groupand BasePath to/. Then, click OK.In the Actions column of the target group, click API Management. Then, click Create API. On the Basic Information tab, configure the following information and click Next.

On the Define API Request tab, set Request Path to
/, keep the default values for the other parameters, and click Next.
On the Define API Backend Service tab, set Trigger Path to the internal endpoint of the Function Compute trigger, such as
https://example.cn-hangzhou-vpc.fcapp.run. Configure the settings as shown in the figure and click Next.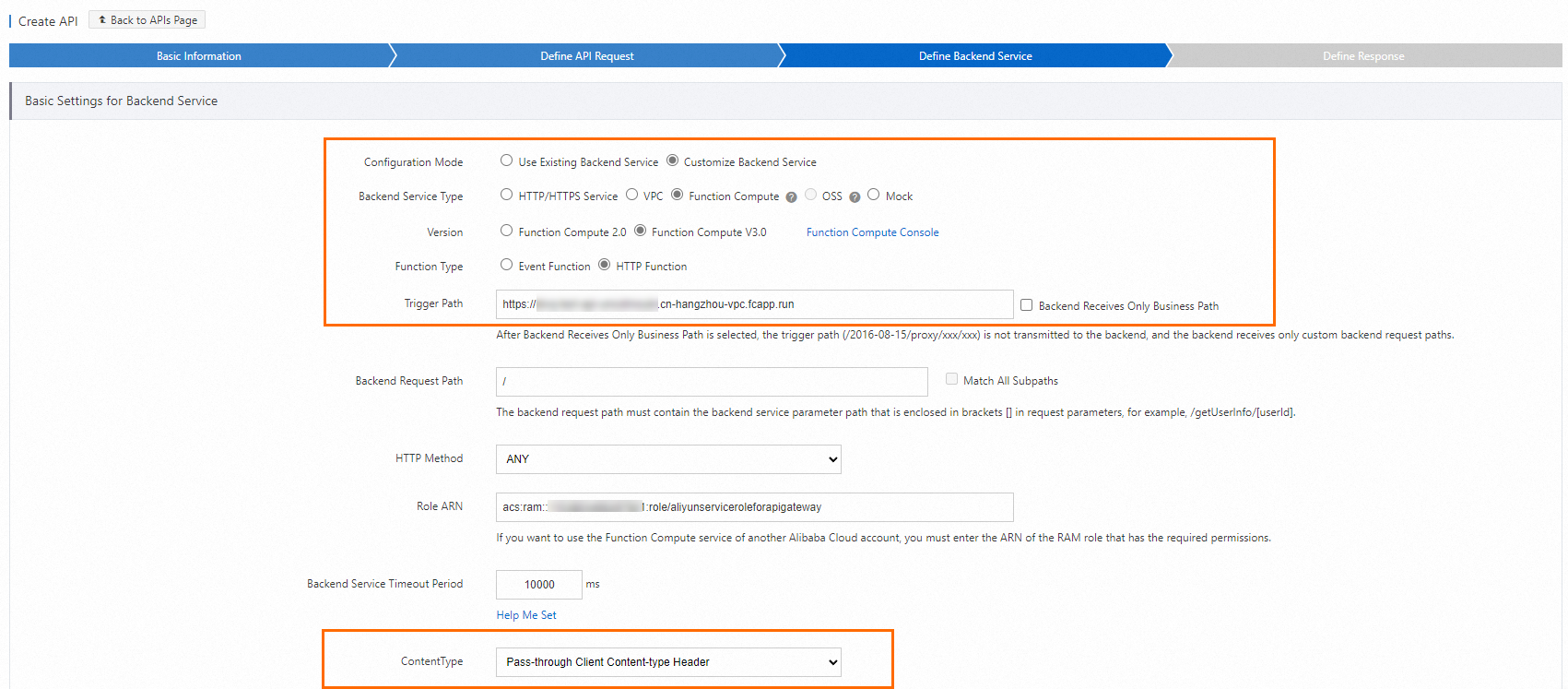
On the Define Response tab, keep the default configurations and click Create. After the API is created, click Publish in the Actions column of the API.
Debug the API. Before you publish the API, you can use the online debugging tool provided by API Gateway to test whether the API works as expected. This helps you find and resolve issues promptly. If the debugging is successful, API Gateway is connected to Function Compute.
In the API Gateway console, in the navigation pane on the left, choose API Calling > Debug.
On the Debug page, select the
FC-testAPI that you created and click Send Request. If the information shown in the following figure is displayed, the configuration is successful.
Create a plug-in of the Backend Signature type. Set
keyandsecretto theAccessKey IDandAccessKey Secretof your Alibaba Cloud account. Then, bind the plug-in to the API that you created. For more information, see Plug-in overview.
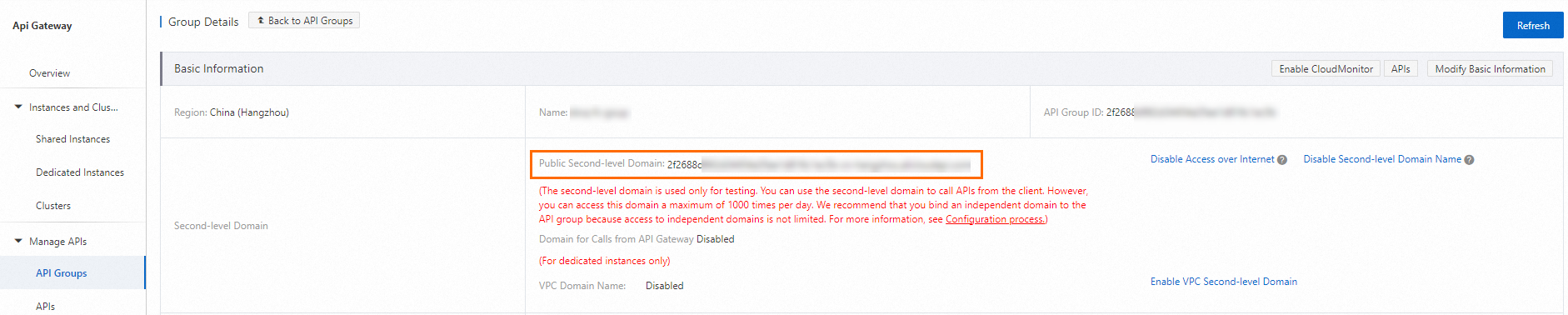
Resolve your domain name to the second-level domain provided by API Gateway using a CNAME record.
In the API Gateway console, in the navigation pane on the left, choose API Management > Group Management. Copy the public second-level domain.
Go to your domain name resolution management page. The Alibaba Cloud DNS console is available at https://dnsnext.console.alibabacloud.com. On the domain name list, find the domain name that you want to manage and click the domain name to go to the management page.
NoteIndependent domain names in the Chinese mainland regions must have an ICP filing from Alibaba Cloud or have their ICP filing transferred to Alibaba Cloud.
In the API Gateway console, in the navigation pane on the left, choose API Management > Group Management. Go to the Independent Domain section. In the lower-right corner of the page, click the button to bind a domain name. Enter your domain name and click OK. The domain name is bound.

After you complete these steps, you can access the HTTP function through your domain name. You can also create the following plug-ins and bind them to your API to protect your HTTP function.
Troubleshooting
Errors are divided into two main types:
Request errors occur when the sent request does not meet the required standards. A 4xx status code is returned in the response.
Function errors occur when there is a problem with the function code. A 5xx status code is returned.
The following table describes scenarios where request errors and function errors may occur to help you quickly troubleshoot issues.
Error type | HTTP status code | Cause analysis | Billed |
Request error | 400 | Your request exceeds the request limits. For more information, see HTTP trigger overview. | No |
400 | The request to call a function that requires identity authentication does not contain the Date or Authorization information. | No | |
403 | The signature of the request to call a function that requires identity authentication is invalid. This means the Authorization information is incorrect. The Date is part of the signature calculation, and the signature expires after 15 minutes. A common cause for this error is using an HTTP trigger that requires access authentication, but the Date in the request header is more than 15 minutes in the past. This makes the signature invalid. | No | |
403 | The request uses a method that is not configured in the HTTP trigger. For example, this error occurs if you send an HTTP request using the POST method, but only the GET method is configured in the HTTP trigger. | No | |
404 | An HTTP request is sent to a function that does not have an HTTP trigger configured. | No | |
User throttling | 429 | User traffic is throttled. Reduce the number of concurrent requests or contact the Function Compute developer team to increase the concurrency limit. | No |
Function error | 502 | The function's return value exceeds the response limits. For more information, see HTTP trigger overview. | Yes |
502 | The function code has a syntax error or an exception. | Yes | |
502 | An HTTP request is sent to a function that does not use an HTTP handler. | Yes | |
System error | 500 | A Function Compute system error occurred. Retry the operation. | No |
System throttling | 503 | Function Compute is experiencing system throttling. Retry with exponential backoff. | No |
If the issue persists, join the DingTalk user group (ID: 64970014484) to contact Function Compute engineers for assistance.