In E-MapReduce (EMR) V3.27.0 and later, you can use Raft-RocksDB-Tablestore to store
the metadata managed by Namespace Service of JindoFS. When you create an EMR JindoFS
cluster, create three master nodes and deploy a Raft instance on the master nodes.
Each peer node of the Raft instance uses the local Raft-RocksDB to store metadata.
Prerequisites
- A Tablestore instance is created. We recommend that you use a high-performance instance.
For more information, see Create instances.
Note You must enable the transaction feature.
- An EMR cluster that has three master nodes is created. For more information, see Create a cluster.
Background information
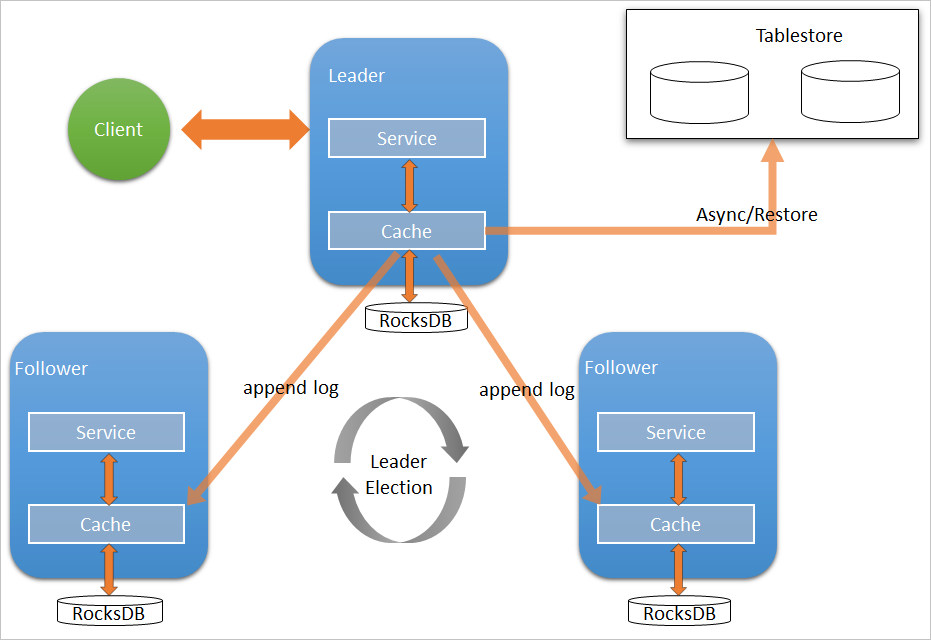
RocksDB supports data replication among three nodes based on the Raft protocol. You
can bind an EMR cluster to a Tablestore instance and use the Tablestore instance as
an additional storage medium for Namespace Service of JindoFS. EMR asynchronously
uploads metadata from the local RocksDB to the Tablestore instance in real time.
The following figure shows the architecture of high-availability Raft-RocksDB-Tablestore
for Namespace Service.
Configure a Raft instance as the local storage backend
- Suspend all the SmartData components of an EMR cluster.
- Log on to the Alibaba Cloud EMR console.
- In the top navigation bar, select the region where your cluster resides and select a resource group based on your business requirements.
- Click the Cluster Management tab.
- On the Cluster Management page, find your cluster and click Details in the Actions column.
- In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
- Select Stop All Components from the drop-down list in the upper-right corner.
- Configure Namespace Service parameters based on your business requirements.
- Go to the bigboot tab for the SmartData service.
- In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
- Click the Configure tab.
- In the Service Configuration section, click the bigboot tab.
- Configure the parameters described in the following table on the bigboot tab.
| Parameter |
Description |
Example |
| namespace.backend.type |
The backend storage type of Namespace Service.
Default value: rocksdb. Set this parameter to raft.
|
raft |
| namespace.backend.raft.initial-conf |
The addresses of the three master nodes where the Raft instance is deployed. The value
is fixed.
|
emr-header-1:8103:0,emr-header-2:8103:0,emr-header-3:8103:0 |
| jfs.namespace.server.rpc-address |
The addresses of the three master nodes that are used for the client to access the
Raft instance. The value is fixed.
|
emr-header-1:8101,emr-header-2:8101,emr-header-3:8101 |
Note If you do not need to use Tablestore for remote storage, skip
Step 5.
- Optional:Configure a Tablestore instance as the remote asynchronous storage backend.
On the
bigboot tab for the SmartData service, configure the parameters described in the following
table.
| Parameter |
Description |
Example |
| namespace.ots.instance |
The name of the Tablestore instance. |
emr-jfs |
| namespace.ots.accessKey |
The AccessKey ID that is used to access the Tablestore instance. |
kkkkkk |
| namespace.ots.accessSecret |
The AccessKey secret that is used to access the Tablestore instance. |
XXXXXX |
| namespace.ots.endpoint |
The endpoint of the Tablestore instance. We recommend that you use a VPC endpoint. |
http://emr-jfs.cn-hangzhou.vpc.tablestore.aliyuncs.com |
| namespace.backend.raft.async.ots.enabled |
Specifies whether to enable asynchronous upload to Tablestore. Valid values:
Set this parameter to true. Make sure that the initialization of the SmartData service
is not completed.
Note If the initialization is completed, the setting does not take effect because metadata
has been generated in the local RocksDB.
|
true |
- Save the configurations.
- In the upper-right corner of the Service Configuration section, click Save.
- In the Confirm Changes dialog box, specify Description and turn on Auto-update Configuration.
- Click OK.
- Select Start All Components from the drop-down list in the upper-right corner.
Recover metadata from a Tablestore instance
If you have configured a Tablestore instance as the remote asynchronous storage backend
for your EMR cluster, a complete replica of JindoFS metadata is stored in the Tablestore
instance. After you stop or release the EMR cluster, you can recover JindoFS metadata
from the Tablestore instance to a new EMR cluster. This way, you can access the original
files from the new EMR cluster.
- Optional:Prepare for the recovery.
- Optional:Collect the metadata statistics of the original EMR cluster. The metadata statistics
indicate the numbers of files and folders.
hadoop fs -count jfs://test/
1596 1482809 25 jfs://test/
(Number of folders) (Number of files)
- Stop the jobs that are running on the original EMR cluster. You may need to wait for
30 to 120 seconds for EMR to synchronize all metadata of the cluster to the Tablestore
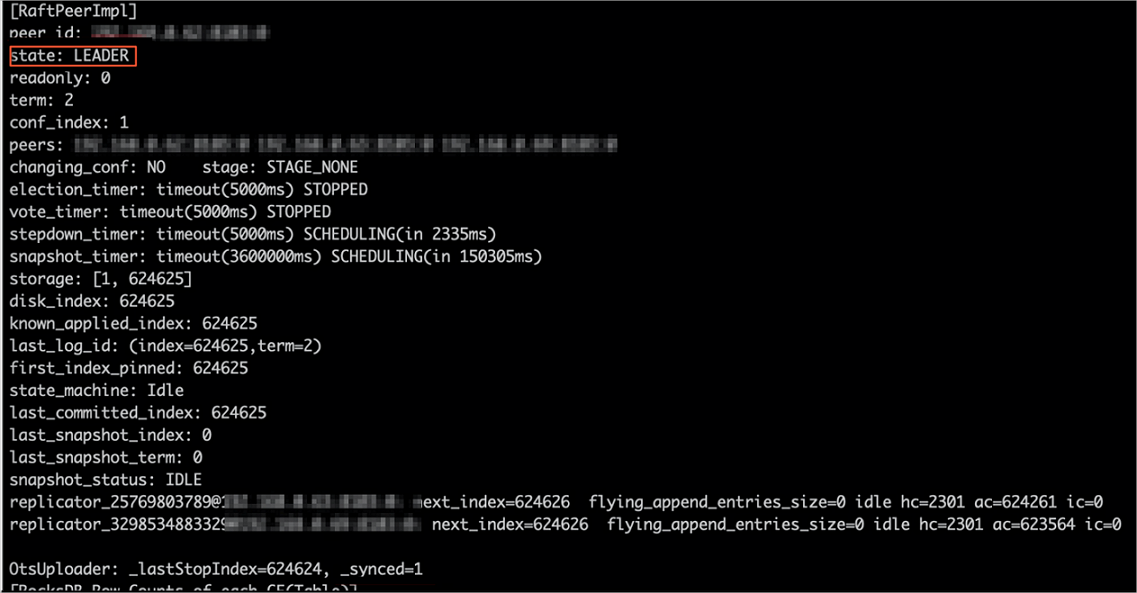
instance. Run the following command to view the metadata status. If the command output
contains
_synced=1 for the LEADER node, the latest metadata is synchronized to the Tablestore instance.jindo jfs -metaStatus -detail
- Stop or release the original EMR cluster and make sure that no clusters are accessing
the Tablestore instance.
- Create an EMR cluster.
- Configure parameters for metadata recovery.
On the
bigboot tab for the SmartData service, configure the parameters described in the following
table.
| Parameter |
Description |
Required value |
| namespace.backend.raft.async.ots.enabled |
Specifies whether to enable asynchronous upload to Tablestore. Valid values:
|
false |
| namespace.backend.raft.recovery.mode |
Specifies whether to enable metadata recovery from Tablestore. Valid values:
|
true |
- Save the configurations.
- In the upper-right corner of the Service Configuration section, click Save.
- In the Confirm Changes dialog box, specify Description and turn on Auto-update Configuration.
- Click OK.
- Select Start All Components from the drop-down list in the upper-right corner.
- After the SmartData service of the new EMR cluster is activated, EMR automatically
recovers metadata from the Tablestore instance to the local Raft-RocksDB. You can
run the following command to view the recovery progress:
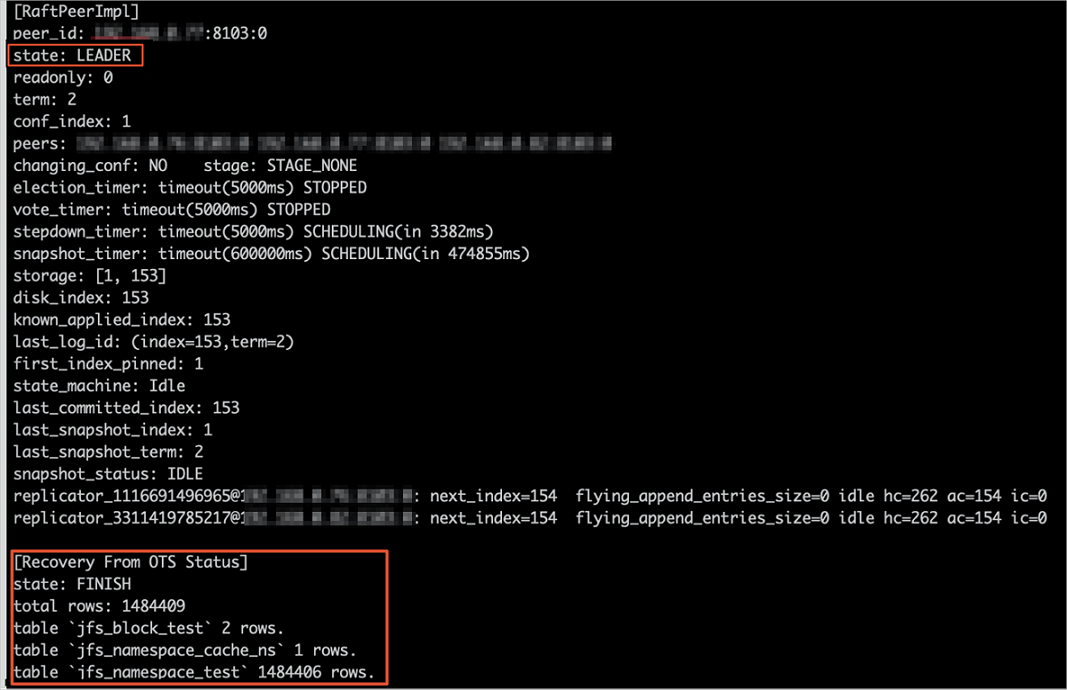
jindo jfs -metaStatus -detail
If the state of the LEADER node is FINISH, the recovery is completed, as shown in
the following figure.
- Optional:Check whether the numbers of files and folders of the new EMR cluster are consistent
with those of the original EMR cluster.
The new EMR cluster is in recovery mode and is read-only.
# Count the numbers of files and folders for the new EMR cluster. The results are consistent with those of the original EMR cluster.
[hadoop@emr-header-1 ~]$ hadoop fs -count jfs://test/
1596 1482809 25 jfs://test/
# Use the CAT or GET command to read data from the files.
[hadoop@emr-header-1 ~]$ hadoop fs -cat jfs://test/testfile
this is a test file
# View file directories.
[hadoop@emr-header-1 ~]$ hadoop fs -ls jfs://test/
Found 3 items
drwxrwxr-x - root root 0 2020-03-25 14:54 jfs://test/emr-header-1.cluster-50087
-rw-r----- 1 hadoop hadoop 5 2020-03-25 14:50 jfs://test/haha-12096RANDOM.txt
-rw-r----- 1 hadoop hadoop 20 2020-03-25 15:07 jfs://test/testfile
# Remove a file. A read-only error is returned.
[hadoop@emr-header-1 ~]$ hadoop fs -rm jfs://test/testfile
java.io.IOException: ErrorCode : 25021 , ErrorMsg: Namespace is under recovery mode, and is read-only.
- Enable asynchronous upload to Tablestore and disable recovery from Tablestore.
On the
bigboot tab for the SmartData service, configure the parameters described in the following
table.
| Parameter |
Description |
Required value |
| namespace.backend.raft.async.ots.enabled |
Specifies whether to enable asynchronous upload to Tablestore. Valid values:
|
true |
| namespace.backend.raft.recovery.mode |
Specifies whether to enable metadata recovery from Tablestore. Valid values:
|
false |
- Restart the new EMR cluster.
- Click the Cluster Management tab.
- On the Cluster Management page, find the cluster. In the Actions column of this cluster, click More and select .



