The block storage mode ensures efficient read/write operations and high metadata accessibility. JindoFS stores data as blocks in OSS and caches data in local disks of clusters to accelerate data access. JindoFS uses Namespace Service to manage metadata and ensure high metadata accessibility. This topic describes how to use JindoFS in block storage mode.
Background information
The block storage mode of JindoFS has the following features:
- JindoFS offers tremendous and scalable storage capacity by using OSS as the storage backend. The storage capacity is independent of the EMR cluster scale. The local cluster can be scaled in or out as required.
- JindoFS stores some backup data in the local cluster to accelerate read operations. This improves the throughput by using limited local storage capacity, especially for Write Once Read Many (WORM) solutions.
- JindoFS provides efficient metadata query similar to HDFS. Compared with OssFileSystem, JindoFS saves much time in metadata query. In addition, JindoFS avoids system instability when data and metadata are frequently accessed.
- JindoFS ensures maximal data locality when jobs are executed in the EMR cluster. This reduces the load on network transmission and improves the read performance.
Configure the block storage mode
Control disk space usage
JindoFS uses OSS as the data storage backend, which allows you to store large volumes
of data. However, the capacity of local disks is limited. JindoFS automatically deletes
cold data in local disks. The storage.watermark.high.ratio and storage.watermark.low.ratio parameters are used to adjust the space usage of local disks. You can set the parameters
to decimal numbers between 0 and 1.
- Modify disk usage configurations.
In the Service Configuration section for the SmartData service, click the storage tab and configure the parameters described in the following table.
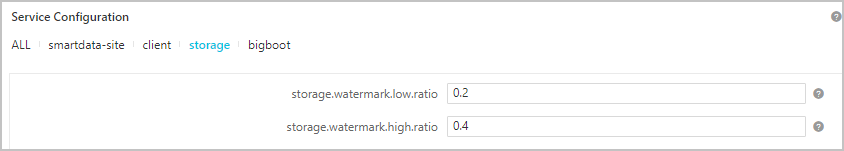
Parameter Description storage.watermark.high.ratio The upper limit of disk usage. When the disk usage of JindoFS data exceeds this limit, JindoFS automatically deletes data in the disk. Default value: 0.4. storage.watermark.low.ratio The lower limit of disk usage. After automatic data deletion is triggered, JindoFS starts to delete data until the disk usage of JindoFS data is reduced to this limit. Default value: 0.2. Note You can configure the upper limit and lower limit to adjust the disk space assigned to JindoFS. Make sure that the upper limit is greater than the lower limit. - Save the configurations.
- In the upper-right corner of the Service Configuration section, click Save.
- In the Confirm Changes dialog box, specify Description and turn on Auto-update Configuration.
- Click OK.
- Restart Jindo Storage Service to apply the configurations.
- Select Restart Jindo Storage Service from the Actions drop-down list in the upper-right corner.
- In the Cluster Activities dialog box, specify related parameters.
- Click OK.
- In the Confirm message, click OK.

