When you use JindoFS in cache mode, files are stored as objects in Object Storage Service (OSS), and the frequently used files are cached in an EMR cluster to improve the data access efficiency. In cache mode, JindoFS can access files in OSS without the need to convert the file formats, and JindoFS is fully compatible with OSS clients. This topic describes how to use JindoFS in cache mode.
Background information
In cache mode, JindoFS supports the object semantics of OSS and is fully compatible with various OSS clients. This ensures that you can access files in OSS without the need to migrate data or convert data formats. In cache mode, JindoFS caches frequently used files in an EMR cluster. This improves the read and write performance and relieves pressure on bandwidth.
Methods to access files in OSS
- OSS Scheme
For more information, see (Recommended) Configure OSS Scheme.
- JFS Scheme
For more information, see Configure JFS Scheme.
(Recommended) Configure OSS Scheme
OSS Scheme refers to the original method of accessing files in OSS. You can use the
oss://<bucket_name>/<path_of_your_file> command to access files in OSS. After you create an EMR cluster, you can use this
method to access files in OSS without additional configurations. You can also run
existing jobs to read or write data from or to OSS without the need to modify the
configurations.
Configure JFS Scheme
Enable local cache
After you enable local cache, hot data blocks are cached on local disks. By default, this feature is disabled, and EMR directly reads data from OSS.
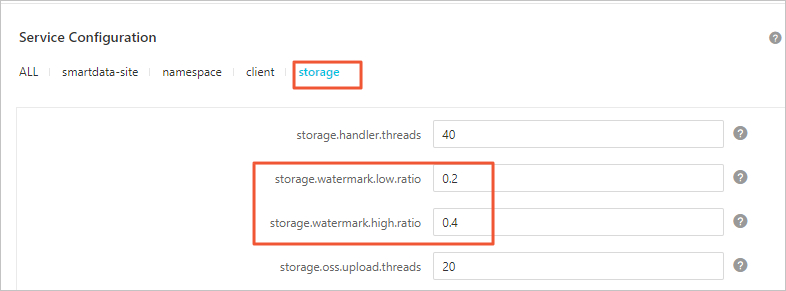
After you enable local cache, Jindo automatically manages cached data. It clears cache based on the high and low watermarks that you configured. For more information about how to configure the watermarks, see Control disk space usage.
Control disk space usage
JindoFS uses OSS as the data storage backend, which allows you to store large volumes
of data. However, the capacity of local disks is limited. JindoFS automatically deletes
cold data in local disks. The storage.watermark.high.ratio and storage.watermark.low.ratio parameters are used to adjust the space usage of local disks. You can set the parameters
to decimal numbers between 0 and 1.
Access an OSS bucket
If you access an OSS bucket that is under the same Alibaba Cloud account and in the same region as your EMR cluster, you do not need to configure an AccessKey pair. In other cases, you must configure an AccessKey pair and an OSS bucket endpoint. Configure the parameters based on the method that you use to access files in OSS:
- OSS Scheme
- In the left-side navigation pane, click Cluster Service and then SmartData. On the SMARTDATA page, click the Configure tab. In the Service Configuration section, click the smartdata-site tab.
- Click Custom Configuration. In the Add Configuration Item dialog box, configure the parameters described in the following table and click OK.
Parameter Description fs.jfs.cache.oss-accessKeyId The AccessKey ID of the OSS bucket that serves as the storage backend. fs.jfs.cache.oss-accessKeySecret The AccessKey secret of the OSS bucket that serves as the storage backend. fs.jfs.cache.oss-endpoint The endpoint of the OSS bucket that serves as the storage backend.
- JFS Scheme
- In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the SMARTDATA page, click the Configure tab. In the Service Configuration section, click the namespace tab.
- Set jfs.namespaces to test.
- Click Custom Configuration. In the Add Configuration Item dialog box, configure the parameters described in the following table and click OK.
Parameter Description jfs.namespaces.test.oss.uri The storage backend of the test namespace. Example: oss://<oss_bucket.endpoint>/<oss_dir>. The OSS bucket endpoint is specified in this parameter.
jfs.namespaces.test.oss.access.key The AccessKey ID of the OSS bucket that serves as the storage backend. jfs.namespaces.test.oss.access.secret The AccessKey secret of the OSS bucket that serves as the storage backend.
Advanced configurations
You can configure some advanced parameters to optimize cache performance. After you configure the parameters, you do not need to restart the SmartData service. The configurations take effect immediately on the client.
- In the Service Configuration section, click the client tab and configure the parameters described in the following table.
Parameter Description client.oss.upload.threads The number of OSS upload threads for each data write stream. Default value: 4. client.oss.upload.max.parallelism The maximum number of concurrent OSS upload threads of a process. This parameter prevents upload threads from occupying an excessive amount of bandwidth and memory. Default value: 16. - In the Service Configuration section, click the smartdata-site tab and configure the parameters described in the following table.
Parameter Description fs.jfs.cache.copy.simple.max.byte The threshold for the size of a file that is renamed over a common copy interface. If the size of a file is smaller than this threshold, a common copy interface is used. If the size is larger than this threshold, the Multipart Copy interface is used to improve copy efficiency. Note If you have enabled the fast copy feature of OSS, set this parameter to -1. This value indicates that all files are renamed over a common copy interface. This way, you can obtain the optimal rename performance.fs.jfs.cache.write.buffer.size The buffer size of data write streams. Unit: bytes. You must set this parameter to a power of 2. The maximum value is 8388608 (8 MB). If too much memory is occupied by write streams, we recommend that you set this parameter to a small value. Default value: 1048576. fs.oss.committer.magic.enabled Specifies whether to enable Jindo Job Committer. This Job Committer does not require rename operations and improves job commit performance. Default value: true. Note In cache mode, the performance of renaming files in OSS is less than standard. We recommend that you use Jindo Job Committer.