This topic describes how to configure HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS). After you configure HSTS, clients such as browsers can establish only HTTPS connections to points of presence (POPs). This improves security.
Prerequisites
An SSL certificate is configured. For more information, see Configure an SSL certificate.
Background information
HSTS is a policy mechanism that allows websites to accept only HTTPS connections.
After you configure HSTS, the first time a client connects to a POP over HTTPS, the POP uses a response header to inform the client that only HTTPS requests are allowed within a period of time and blocks HTTP requests. The HSTS response header is in the Strict-Transport-Security:max-age=expireTime [;includeSubDomains] [;preload] format. The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter | Description |
max-age | The time-to-live (TTL) of the HSTS header. Unit: seconds. Clients can initiate only HTTPS requests during this period. |
includeSubDomains | Optional. If you configure this parameter, HSTS is enabled for the domain name and its subdomains. |
preload | Optional. This parameter allows you to add the domain name to the HSTS preloaded list of the browser. |
The client uses HSTS for the domain name until the TTL that is specified by the max-age parameter expires. During the TTL, HTTP requests are blocked and converted to HTTPS requests.
After you enable HSTS, the first HTTP request that is initiated by the client is allowed because the HSTS setting is not synchronized to the client. In this case, the request may be intercepted or tampered with, which poses security risks. You can configure URL redirection to redirect HTTP to HTTPS. This way, POPs redirect HTTP to HTTPS based on HTTP 301 or 302 status code to prevent security risks.
Limits
After you configure HSTS, clients can access POPs only over HTTPS. Do not configure URL redirection to HTTP at the same time.
The HSTS response header applies to responses to HTTPS requests but does not apply to responses to HTTP requests. Before HSTS takes effect, you can configure force redirect to redirect the first HTTP request from a client to HTTPS by using 301 redirection. For more information, see Configure force redirect.
HSTS applies only to domain names and does not apply to IP addresses.
HSTS takes effect on clients. Disabling HSTS does not take effect immediately. You need to refresh the HSTS status and send the HSTS status to clients when the client initiates the next HTTPS request.
Procedure
Log on to the DCDN console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Domain Names.
- On the Domain Names page, find the domain name whose acceleration region you want to change and click Configure.
In the left-side navigation tree of the domain name, click HTTPS Settings.
In the HSTS section, turn on HSTS and specify the Expire In and Include Subdomains parameters.
Expire In: Specify the TTL for the HSTS response header to be cached on the browser. We recommend that you set the value to 60. Unit: days.
Include Subdomains: Proceed with caution. Make sure that HTTPS is enabled for all subdomains of the accelerated domain name. Otherwise, the subdomains become inaccessible after the requests are redirected to HTTPS.
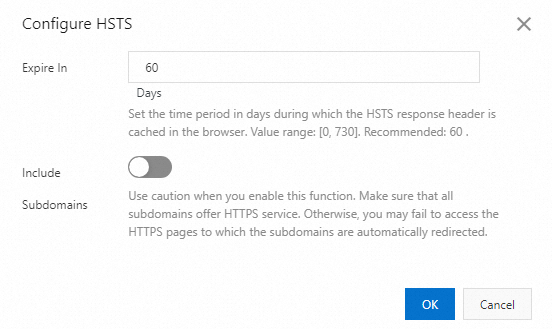
Click OK.