RabbitMQ is an open source message broker that supports multiple messaging protocols, including Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP), Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT), Streaming Text Oriented Messaging Protocol (STOMP), HTTP, and WebSockets. RabbitMQ is easy to use, extensible, and highly available. RabbitMQ coordinates and manages communication in distributed systems, and implements asynchronous messaging to improve system decoupling, scalability, concurrent processing capabilities, and fault tolerance. RabbitMQ is widely used in messaging and task processing of enterprise-level applications because of its stable performance, diverse features, and active community support. This topic describes how to deploy open source RabbitMQ on an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance.
Deploy RabbitMQ
Manual deployment: This method is suitable for users who have a basic knowledge of Linux commands and can perform custom RabbitMQ deployment.
Quick deployment: This method eliminates the need to install and configure RabbitMQ and greatly reduces the deployment time.
Manual deployment
This example describes how to install the latest version of RabbitMQ. For information about how to install other versions of RabbitMQ, see Installing RabbitMQ.
Prerequisites
An ECS instance that meets the following requirements is created:
The instance is assigned a public IP address by the system or is associated with an elastic IP address (EIP). For more information, see EIPs.
The instance runs Ubuntu 20.04, Ubuntu 22.04, or a Debian version of Debian 11.0 to Debian 12.5.
For information about other supported operating systems and installation methods, see Installing RabbitMQ.
Inbound rules are added to the security groups of the instance to allow traffic on ports 22, 80, and 15672.
NoteTo connect to the RabbitMQ server by using a Message Queue (MQ) tool, you must also open port 5672.
Procedure
Connect to an ECS instance on which you want to deploy RabbitMQ.
For more information, see Use Workbench to connect to a Linux instance over SSH.
Install RabbitMQ.
Install basic RabbitMQ dependencies.
sudo apt-get install curl gnupg apt-transport-https -yDownload the GNU Privacy Guard (GPG) public keys for RabbitMQ and Erlang and add the public key information to the trust keyring of the operating system.
curl -1sLf "https://keys.openpgp.org/vks/v1/by-fingerprint/0A9AF2115F4687BD29803A206B73A36E6026DFCA" | sudo gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/com.rabbitmq.team.gpg > /dev/null curl -1sLf https://github.com/rabbitmq/signing-keys/releases/download/3.0/cloudsmith.rabbitmq-erlang.E495BB49CC4BBE5B.key | sudo gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/rabbitmq.E495BB49CC4BBE5B.gpg > /dev/null curl -1sLf https://github.com/rabbitmq/signing-keys/releases/download/3.0/cloudsmith.rabbitmq-server.9F4587F226208342.key | sudo gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/rabbitmq.9F4587F226208342.gpg > /dev/nullAdd the official Advanced Packaging Tool (APT) repositories for RabbitMQ and Erlang to the
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/rabbitmq.listfile.sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/rabbitmq.list <<EOF deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/rabbitmq.E495BB49CC4BBE5B.gpg] https://ppa1.novemberain.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-erlang/deb/ubuntu jammy main deb-src [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/rabbitmq.E495BB49CC4BBE5B.gpg] https://ppa1.novemberain.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-erlang/deb/ubuntu jammy main deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/rabbitmq.E495BB49CC4BBE5B.gpg] https://ppa2.novemberain.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-erlang/deb/ubuntu jammy main deb-src [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/rabbitmq.E495BB49CC4BBE5B.gpg] https://ppa2.novemberain.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-erlang/deb/ubuntu jammy main deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/rabbitmq.9F4587F226208342.gpg] https://ppa1.novemberain.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-server/deb/ubuntu jammy main deb-src [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/rabbitmq.9F4587F226208342.gpg] https://ppa1.novemberain.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-server/deb/ubuntu jammy main deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/rabbitmq.9F4587F226208342.gpg] https://ppa2.novemberain.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-server/deb/ubuntu jammy main deb-src [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/rabbitmq.9F4587F226208342.gpg] https://ppa2.novemberain.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-server/deb/ubuntu jammy main EOFUpdate the local package indexes.
sudo apt-get update -yInstall Erlang-related packages.
sudo apt-get install -y erlang-base \ erlang-asn1 erlang-crypto erlang-eldap erlang-ftp erlang-inets \ erlang-mnesia erlang-os-mon erlang-parsetools erlang-public-key \ erlang-runtime-tools erlang-snmp erlang-ssl \ erlang-syntax-tools erlang-tftp erlang-tools erlang-xmerlInstall RabbitMQ.
sudo apt-get install rabbitmq-server -y --fix-missing
Configure RabbitMQ.
Configure RabbitMQ to start on instance startup and start RabbitMQ.
sudo systemctl enable rabbitmq-server sudo systemctl start rabbitmq-serverTo ensure security, we recommend that you run the following command to delete the default account of RabbitMQ.
The default username and password of RabbitMQ are both
guest.sudo rabbitmqctl delete_user guestCreate a RabbitMQ administrator user.
Create a user.
sudo rabbitmqctl add_user <Username> <Password>Specify the
<Username>and<Password>parameters.Set the new user as an administrator.
sudo rabbitmqctl set_user_tags <Username> administratorGrant all permissions to the new user.
sudo rabbitmqctl set_permissions -p / <Username> ".*" ".*" ".*"
Start RabbitMQ and go to the open source RabbitMQ console.
sudo rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
Quick deployment
Deploy RabbitMQ by using an Alibaba Cloud Marketplace image
You can use Alibaba Cloud Marketplace images to deploy RabbitMQ. This eliminates the need to install and configure RabbitMQ and greatly reduces the deployment time. The prices displayed on the Pricing tab of the image details page in Alibaba Cloud Marketplace shall prevail.
Click Cloud Native MQ for Apache RabbitMQ Powered by Websoft9 to go to the image details page.
You can obtain the image information and user guide on the image details page.
Click Choose Your Plan.
On the Custom Launch tab on the ECS instance buy page, configure and purchase an ECS instance as prompted.
Take note of the following parameters. Configure other parameters based on your business requirements. For information about other parameters, see Create an instance on the Custom Launch tab.
Image: The image that you purchased is automatically selected in the Image section.
Public IP Address: Select Assign Public IPv4 Address.
Security Group: Configure inbound security group rules that allow traffic on ports 22, 80, and 15672.
Obtain the username and password that you use to log on to the RabbitMQ server.
Connect to the RabbitMQ server.
For more information, see Use Workbench to connect to a Linux instance over SSH.
Run the following command to obtain the username and password for logon to the RabbitMQ server:
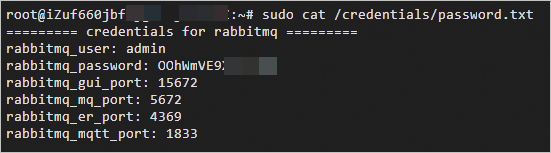
sudo cat /credentials/password.txtThe command output shown in the following figure is returned.
rabbitmq_user: the username for logon to the RabbitMQ server.
rabbitmq_password: the password for logon to the RabbitMQ server.
rabbitmq_gui_port: the web server port of RabbitMQ.
rabbitmq_mq_port: the remote connection port of RabbitMQ.
rabbitmq_er_port: the internal port used by the RabbitMQ server for inter-process communication in Erlang.
rabbitmq_mqtt_port: the listening port of the MQTT service provided by the RabbitMQ server.
Deploy RabbitMQ by using Terraform
Terraform is an Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tool that helps developers and O&M teams automate the creation, deployment, and management of cloud infrastructure. Terraform allows you to write simple code to define and configure cloud infrastructure without the need for manual operations or configurations.
Procedure
Click here to go to the Terraform Explorer page to automatically load the following Terraform code.
By default, one virtual private cloud (VPC), one vSwitch, one security group, and one pay-as-you-go ECS instance are created in the cn-beijing region. Replace the parameter values with actual values based on your business requirements. For information about the billing of ECS instances, see Billing overview.
Click Initiate Debugging to preview the details of the resources that you want to create. If the resource information is correct, click Plan & Apply to create the resources. If the task status is Successful, the deployment task is complete.
Log on to the open source RabbitMQ console
Open your on-premises browser and enter
http://<Public IP address of the Linux instance>:15672in the address bar.The following figure shows that RabbitMQ is installed.
Enter the username and password of the RabbitMQ administrator user that you created and click Login to access the open source RabbitMQ console.
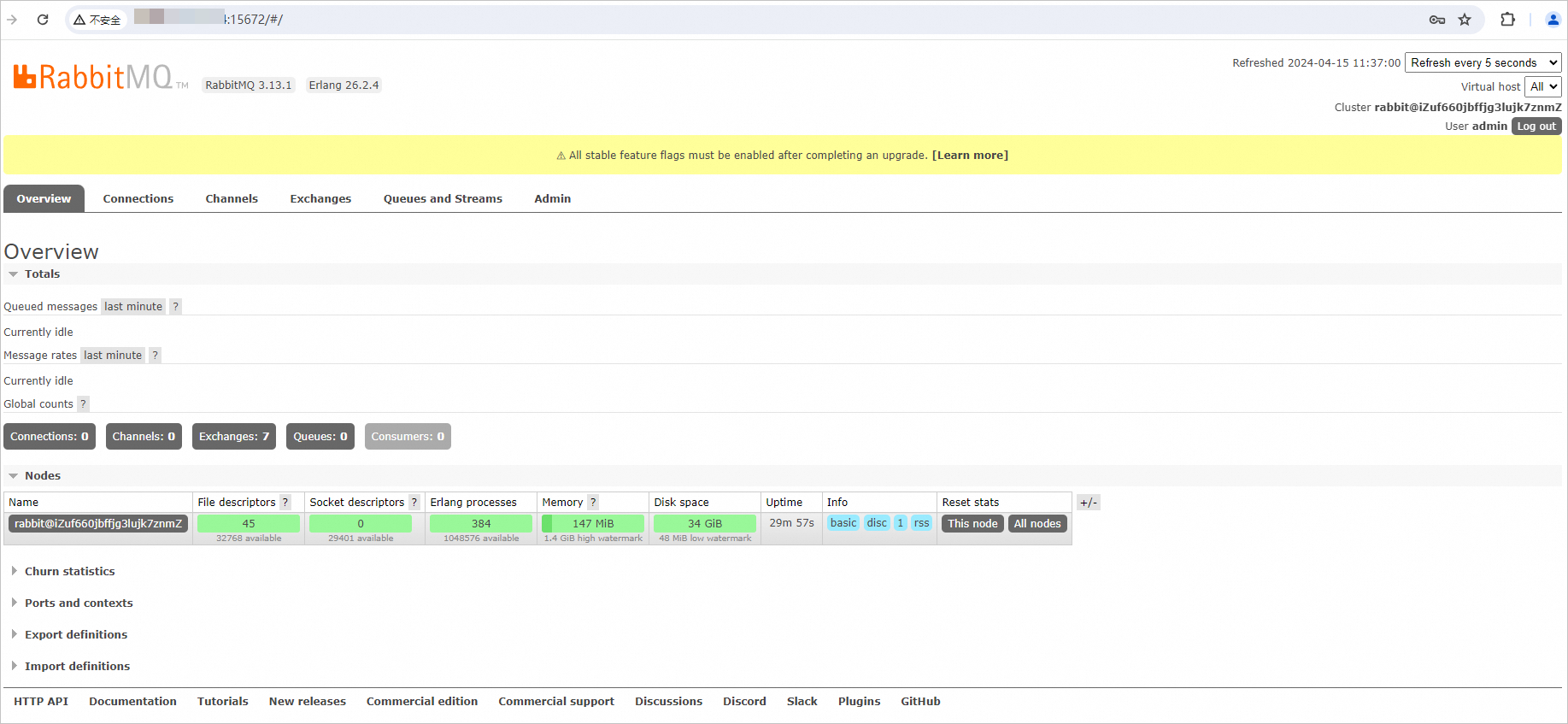
The following figure shows the open source RabbitMQ console.
Migrate open source RabbitMQ clusters to ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ instances
If you want to resolve various stability issues, such as message accumulation and split-brain issues, and implement high-concurrency, distributed, and flexible scaling, you can migrate an open source RabbitMQ cluster to ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ. For more information, see Migrate open source RabbitMQ clusters to ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ instances.