To solve pain points in open source RabbitMQ clusters, such as message accumulation and split-brain issues, and achieve high concurrency, distributed storage, and flexible scaling, you can migrate open source RabbitMQ clusters to ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ instances. This topic describes the prerequisites, procedure, and usage notes for this type of migration.
Usage notes
ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ is an advanced message service that is developed based on highly available distributed storage. This service strictly follows the AMQP 0-9-1 protocol but is not simply a managed version of open source RabbitMQ. The architecture of ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ can prevent memory leaks and broker failures caused by message accumulation and resolves split-brain issues in distributed systems. ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ provides high scalability and supports the pay-as-you-go billing method. This enhances service elasticity and reduces costs.
Compared with open source RabbitMQ, ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ uses different implementation methods for specific features. Before you migrate an open source RabbitMQ cluster to an ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ instance, you must evaluate technology capabilities and cost-effectiveness to select an instance type that meets your business requirements.
Evaluate migration
Evaluate technology
ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ and open source RabbitMQ differ in terms of features, service and performance, exchanges, and queues. Before you migrate an open source RabbitMQ cluster to an ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ instance, check the differences and evaluate whether the features provided by ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ meet your expectations. For information about the differences between ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ and open source RabbitMQ, see Comparison with open source RabbitMQ.
ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ imposes limits on clusters, API operations, and string characters. When you use ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ, you cannot exceed the limits. Before you migrate an open source RabbitMQ cluster to an ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ instance, evaluate whether the limits meet your business requirements. For more information, see Instance types.
We recommend choosing a Serverless series dedicated instance. With its support for open-source identity verification and permission management, you can seamlessly migrate open-source RabbitMQ to the cloud.
Evaluate costs
ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ provides subscription and serverless instances of various types. For information about the differences among the instance types, see Instance types.
Compared with subscription ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ instances, serverless ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ instances have higher scalability and lower costs. For information about the billing rules of serverless instances, see Billing of serverless instances.
You can evaluate the number of messaging requests, the number of queues, and the number of messages in an open source RabbitMQ cluster by using the following methods:
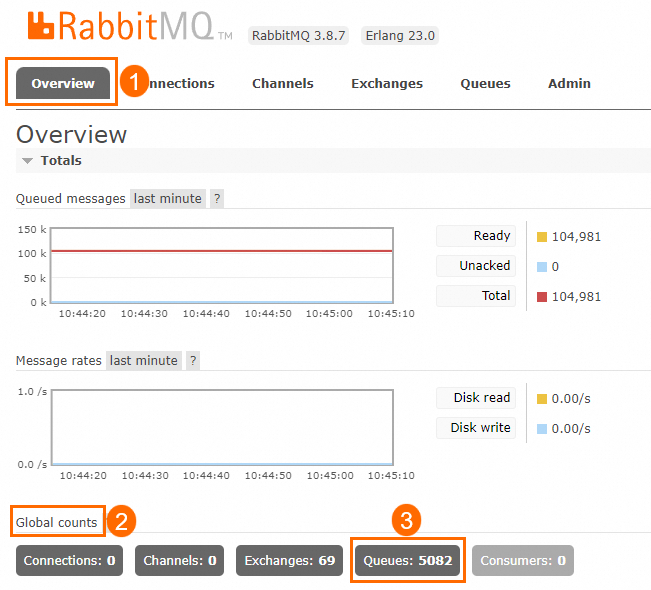
Number of queues: Go to the Overview page in the open source RabbitMQ console and view the number of queues and exchanges in the Global counts section.
Number of messaging requests and number of messages
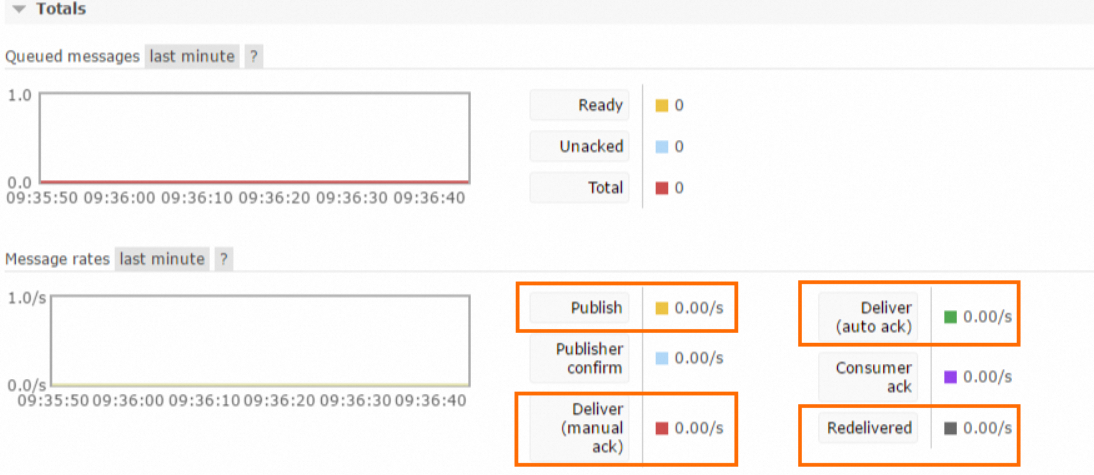
Method 1: Go to the Overview page in the open source RabbitMQ console, view the information in the Message rates section, and calculate the total value of the Publish, Deliver (manual ack), Deliver (auto ack), and Redelivered metrics.
Method 2: Check the queries per second (QPS) and the number of inbound and outbound messages of the cluster on the Prometheus or Grafana dashboard.
Migrate an open source RabbitMQ cluster to an ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ instance
Migrate metadata
Metadata migration is the process in which the metadata of an open source RabbitMQ cluster is exported and then imported to an ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ instance. After the metadata is imported, ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ creates vhosts, queues, exchanges, and bindings on the ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ instance based on the imported metadata. Then, the metadata of the open source RabbitMQ cluster is migrated. For more information, see Migrate the metadata of an open source RabbitMQ cluster to an ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ instance.
Create a username
When you access an ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ broker from an open source RabbitMQ client, you must specify the username and password for authentication. You can access the ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ broker only after the authentication is passed. The system supports two modes for managing users and permissions. For more information, see Manage static usernames and passwords.
Open-source identity verification and permission management
You can create custom usernames and passwords, and import metadata to manage permissions.
Alibaba Cloud Resource Access Management (RAM)
RAM generates usernames and passwords from an AccessKey and an AccessKey secret.
Establish network connection
ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ provides PrivateLink endpoints that allow you to build networks in Alibaba Cloud by using Cloud Enterprise Network (CEN). For more information, see PrivateLink endpoints.
Migrate message data
Migration solution
Message data is migrated by using the Shovel plug-in based on virtual hosts.
Benefits
Business can be smoothly migrated without data loss.
You do not need to sort out the mesh typology of inter-application calls.
You do not need to migrate the call chains of producers and consumers one by one. This helps resolve issues related to the migration of circular call chains.
Procedure

Sort out all the producers and consumers of Virtual Host A.
Migrate all producers and consumers of Virtual Host A. To access ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ, you must change the URLs, usernames, and passwords of the producers and consumers.
Check message accumulation in all queues of Virtual Host A in the open source RabbitMQ cluster.
Enable the Shovel plug-in in the open source RabbitMQ cluster. Create a temporary synchronization task Sync a for queues that have accumulated messages and then forward the messages to the ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ instance. When you configure the temporary synchronization task, specify the queues in the open source RabbitMQ cluster as the source and the queues on the ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ instance as the destination.
If the synchronization task Sync b is used to migrate message data from Virtual Host B to Virtual Host A in the open source RabbitMQ cluster, specify queues on the ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ instance as the destination of Sync b.
Check whether messages are accumulated in the queues of Virtual Host A in the open source RabbitMQ cluster. After all accumulated messages are migrated to the ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ instance, delete the temporary synchronization task Sync a.
After you perform the preceding steps, message data in Virtual Host A is migrated. You can perform similar steps to migrate message data in other virtual hosts.
References
For more information about the Shovel plug-in, see Shovel Plugin.