After you deploy a DataCache CRD (custom resource definition), you can create a DataCache to pull data required by your business in advance, such as AI training models. This topic describes the parameters that are required to create a DataCache. This topic also describes how to query and delete a DataCache.
Prerequisites
A DataCache CRD is deployed in the cluster. For more information, see Deploy a DataCache CRD.
Create a DataCache
Configuration description
The following code provides parameters in the YAML configuration file of a DataCache:
apiVersion: eci.aliyun.com/v1alpha1
kind: DataCache
metadata:
name: test-url
spec:
bucket: default
path: /demo/url
size: 20
retentionDays: 3
dataSource:
type: URL
options:
url: https://www.example.com
netConfig:
securityGroupId: sg-2ze63v3jtm8e6sy******
vSwitchId: vsw-2ze94pjtfuj9vaym******Parameter description:
apiVersion: the API version. Set the value to eci.aliyun.com/v1alpha1.
kind: the resource type. Set the value to DataCache.
metadata
name: the name of the DataCache.
spec
bucket: the name of the bucket to store the DataCache. Default value: default. You can also specify another value. The bucket named eci-system is reserved to store common caches of Elastic Container Instance and cannot be used as a value of this parameter.
path: the path in which data is stored.
size: the size of the DataCache. Unit: GiB. Default value: 20. Evaluate the required size based on the actual data size.
retentionDays: retention days of the DataCache. When the retention days elapse, the DataCache is deleted. By default, DataCaches do not expire.
dataSource: the data source. The following table describes the type parameter of data sources and the options parameter of each type.
type
Description
options
URL
Hyperlink addresses
url: the URL from which data is downloaded.
accessToken: the token that is used for authentication before you pull private data.
HuggingFace or ModelScope
repoSource: pulls a model or dataset from the ModelScope or HuggingFace community. Valid values: ModelScope/Model, ModelScope/DataSet, HuggingFace/Model, and HuggingFace/DataSet.
repoId: the ID of the model or dataset.
revision: the version. Default value: main or master.
accessToken: the token that is used for authentication before you pull private data.
NAS
File Storage NAS (NAS) file systems
server: the mount target of the NAS file system.
path: the sub-directory of the NAS file system. For extreme NAS file systems, prefix
/shareto the path. Example:/share/path.vers: the version number of the NFS (Network File System) protocol based on which the NAS file system is mounted. We recommend that you use NFS v3. Extreme NAS only supports NFS v3.
options: the parameters that are used when you set the type parameter to NAS. We recommend that you use the recommended parameters in the NAS service. Example:
nolock,tcp,noresvport.
OSS
Object Storage Service (OSS) buckets
bucket: the name of the OSS bucket.
url: the endpoint of the OSS bucket.
path: the sub-directory of the OSS bucket. The path is relative to the root directory of the OSS bucket. Default value:
/.otherOpts: The custom options that are specified to mount the OSS bucket. Format:
-o *** -o ***. Example:-o max_stat_cache_size=0 -o allow_other.ramRole: the Resource Access Management (RAM) role that is used if you use RAM to grant permissions.
NoteCreate a RAM role and grant the RAM role the permissions to access OSS buckets. For more information, see Create a RAM role for a trusted Alibaba Cloud service and Grant permissions to a RAM role.
When you create a RAM role, select Alibaba Cloud Service for the Select Trusted Entity parameter, Normal Service Role for the Role Type parameter, and Elastic Compute Service for the Select Trusted Service parameter. When you grant permissions to the RAM role, attach the AliyunOSSFullAccess policy to the RAM role.
akId: the AccessKey ID that is used if you use AccessKey pairs to grant permissions. For more information, see Obtain an AccessKey pair.
akSecret: the AccessKey secret that is used if you use AccessKey pairs to grant permissions. For more information, see Obtain an AccessKey pair.
SNAPSHOT
Snapshot
snapshotId: the ID of the snapshot.
netConfig
securityGroupId: the ID of the security group to which the generated elastic container instance belongs.
vSwitchId: the ID of the vSwitch to which the generated elastic container instance is connected.
If you want to pull data over the Internet, you can associate an elastic IP address (EIP) with the elastic container instance if the vSwitch is not configured with a source NAT (SNAT) gateway. In this case, you can add EIP-related parameters in the netConfig section.
netConfig: eipInstanceId: eip-2zey74a7zienoxf***** # Specify eipInstanceId or eipCreateParam. eipCreateParam: # Specify eipInstanceId or eipCreateParam. bandwidth: 5 commonBandwidthPackage: cbwp-2zeukbj916scmj5****** internetChargeType: PayByTraffic publicIpAddressPoolId: pippool-bp187arfugi543y1s**** ISP: BGPeipInstanceId: the EIP ID. If the specified vSwitch is not configured with a SNAT gateway, you can associate an existing EIP with the elastic container instance to pull data over the Internet.
eipCreateParam: If the specified vSwitch is not configured with a SNAT gateway and no existing EIP exists, you can configure the following parameters to create an EIP and associate the EIP with the elastic container instance. This way, you can pull data over the Internet.
bandwidth: the bandwidth of the EIP. Unit: Mbit/s. Default value: 5.
commonBandwidthPackage: an existing EIP bandwidth plan that is bound to the EIP. For more information, see What is an Internet Shared Bandwidth?
internetChargeType: the metering method of the EIP. Valid values: PayByBandwidth (pay by bandwidth) and PayByTraffic (pay by data transfers). For more information, see the "Metering methods" section of the Billing overview topic.
publicIpAddressPoolId: the ID of the public IP address pool. The EIP is allocated from the IP address pool. You cannot use the IP address pool feature by default. To use this feature, you must apply for the privilege in the Quota Center console. For more information, see Create and manage IP address pools.
ISP: the line type of the EIP. Valid values: BGP and BGP_PRO. Default value: BGP. For more information, see the "Line types" section of the What is EIP topic.
Configuration examples
Write a YAML configuration file and run the kubectl command to create a DataCache. Assume the YAML configuration file is named datacache.yaml.
Create a new DataCache.
kubectl create -f datacache.yamlUpdate a DataCache.
kubectl apply -f datacache.yaml
YAML configuration files of the DataCache:
URL
Pull data from a URL.
apiVersion: eci.aliyun.com/v1alpha1 kind: DataCache metadata: name: test-url-1 spec: path: /demo/url dataSource: type: URL options: url: https://www.example.com netConfig: securityGroupId: sg-2ze63v3jtm8e6sy****** vSwitchId: vsw-2ze94pjtfuj9vaym******Pull a model from HuggingFace.
apiVersion: eci.aliyun.com/v1alpha1 kind: DataCache metadata: name: test-url-2 spec: path: /demo/url dataSource: type: URL options: repoSource: "HuggingFace/Model" repoId: "decapoda-research/llama-7b-hf" netConfig: securityGroupId: sg-2ze63v3jtm8e6sy****** vSwitchId: vsw-2ze94pjtfuj9vaym******
NAS
apiVersion: eci.aliyun.com/v1alpha1
kind: DataCache
metadata:
name: test-nas
spec:
path: /demo/nas
dataSource:
type: NAS
options:
server: "0389a***-nh**.cn-beijing.extreme.nas.aliyuncs.com"
path: "/"
vers: "3"
options: "nolock,tcp,noresvport"
netConfig:
securityGroupId: sg-2ze63v3jtm8e6sy******
vSwitchId: vsw-2ze94pjtfuj9vaym******OSS
apiVersion: eci.aliyun.com/v1alpha1
kind: DataCache
metadata:
name: test-oss
spec:
path: /demo/oss
dataSource:
type: OSS
options:
bucket: "oss-***"
url: "oss-cn-beijing-internal.aliyuncs.com"
path: "/test"
otherOpts: "-o max_stat_cache_size=0 -o allow_other"
ramRole: "<your RAM Role Name>"
netConfig:
securityGroupId: sg-2ze63v3jtm8e6sy******
vSwitchId: vsw-2ze94pjtfuj9vaym******SNAPSHOT
apiVersion: eci.aliyun.com/v1alpha1
kind: DataCache
metadata:
name: test-snapshot
spec:
path: /demo/snapshot
dataSource:
type: SNAPSHOT
options:
snapshotId: s-uf6j98q2tvfcjz******
netConfig:
securityGroupId: sg-2ze63v3jtm8e6sy******
vSwitchId: vsw-2ze94pjtfuj9vaym***Manage a DataCache
When you query or delete a DataCache, you can use one of the following names as the name of the resource type:
edc
datacache
datacaches
datacaches.eci.aliyun.com
Query a DataCache
After you create DataCaches, you can query all DataCaches in a cluster or view the details of a DataCache.
Query all DataCaches in a cluster.
kubectl get edcThe following example shows an output. The Available state indicates that the DataCache is ready for use.

View the details of a DataCache.
kubectl describe edc <edc-name>The following output shows the basic information, metadata, configuration, status, and event information of the DataCache.
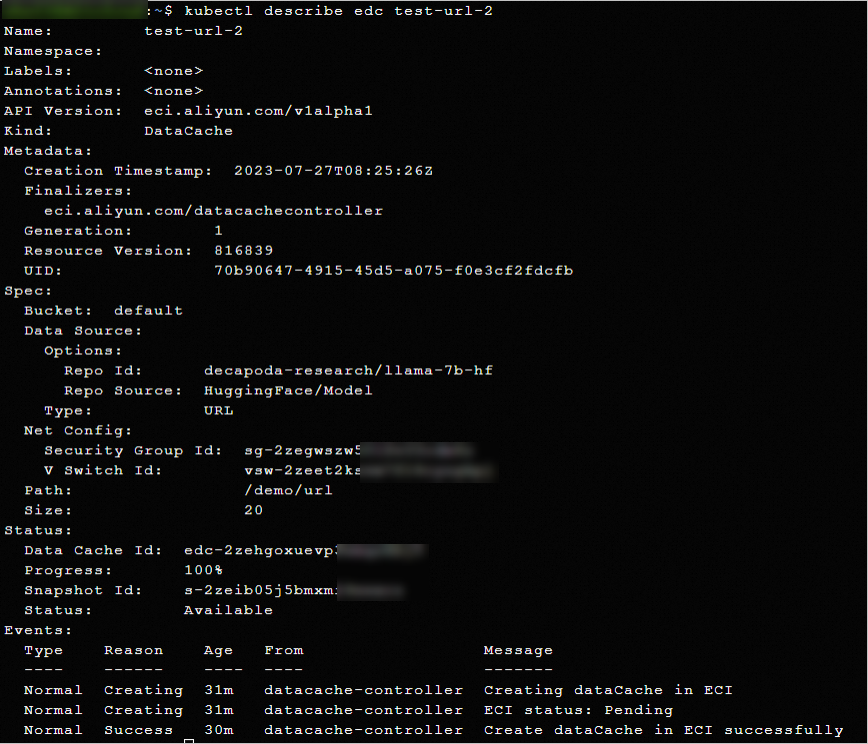
Delete a DataCache
Each DataCache corresponds to a snapshot. To retain snapshots, you must pay for the storage of the snapshots. We recommend that you delete a DataCache that you no longer use.
If you want to delete a DataCache, run the following command:
kubectl delete edc <edc-name>