This topic describes how to synchronize data from a self-managed MySQL database hosted on Elastic Compute Service (ECS) to an AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance by using Data Transmission Service (DTS).
Prerequisites
A MySQL database of version 5.1, 5.5, 5.6, 5.7, or 8.0 is created. The database is hosted on an ECS instance.
The binary logging feature is enabled for the source database. A database account is created for the data synchronization task. For more information, see Create an account for a self-managed MySQL database and configure binary logging.
NoteThe database account must have the SELECT permission on the objects to be synchronized, the REPLICATION CLIENT permission, the REPLICATION SLAVE permission, and the SHOW VIEW permission.
The tables to be synchronized from the source database contain primary keys.
The destination AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance is created. For more information, see Create an AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance.
Precautions
DTS uses read and write resources of the source and destination databases during initial full data synchronization. This may increase the loads of the database servers. If the database performance is unfavorable, the specification is low, or the data volume is large, database services may become unavailable. For example, DTS occupies a large amount of read and write resources in the following cases: a large number of slow SQL queries are performed on the source database, the tables have no primary keys, or a deadlock occurs in the destination database. Before you synchronize data, evaluate the impact of data synchronization on the performance of the source and destination databases. We recommend that you synchronize data during off-peak hours. For example, you can synchronize data when the CPU utilization of the source and destination databases is less than 30%.
Limits
You can select only tables as the objects to be synchronized.
DTS does not synchronize the following types of data: BIT, VARBIT, GEOMETRY, ARRAY, UUID, TSQUERY, TSVECTOR, TXID_SNAPSHOT, and POINT.
Prefix indexes cannot be synchronized. If the source database contains prefix indexes, data may fail to be synchronized.
We recommend that you do not use gh-ost or pt-online-schema-change to perform DDL operations on objects during data synchronization. Otherwise, data synchronization may fail.
SQL operations that can be synchronized
DML operations: INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE
DDL operation: ADD COLUMN
NoteThe CREATE TABLE operation is not supported. To synchronize data from a new table, you must add the table to the selected objects. For more information, see Add an object to a data synchronization task.
Supported synchronization topologies
One-way one-to-one synchronization
One-way one-to-many synchronization
One-way many-to-one synchronization
Term mappings
MySQL | AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL |
Database | Schema |
Table | Table |
Procedure
Purchase a data synchronization instance. For more information, see Purchase a DTS instance.
NoteOn the buy page, set Source Instance to MySQL, set Target Instance to AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL, and set Synchronization Topology to One-Way Synchronization.
Log on to the DTS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Data Synchronization.
At the top of the Synchronization Tasks page, select the region where the destination instance resides.
Find the data synchronization instance and click Configure Synchronization Channel in the Actions column.
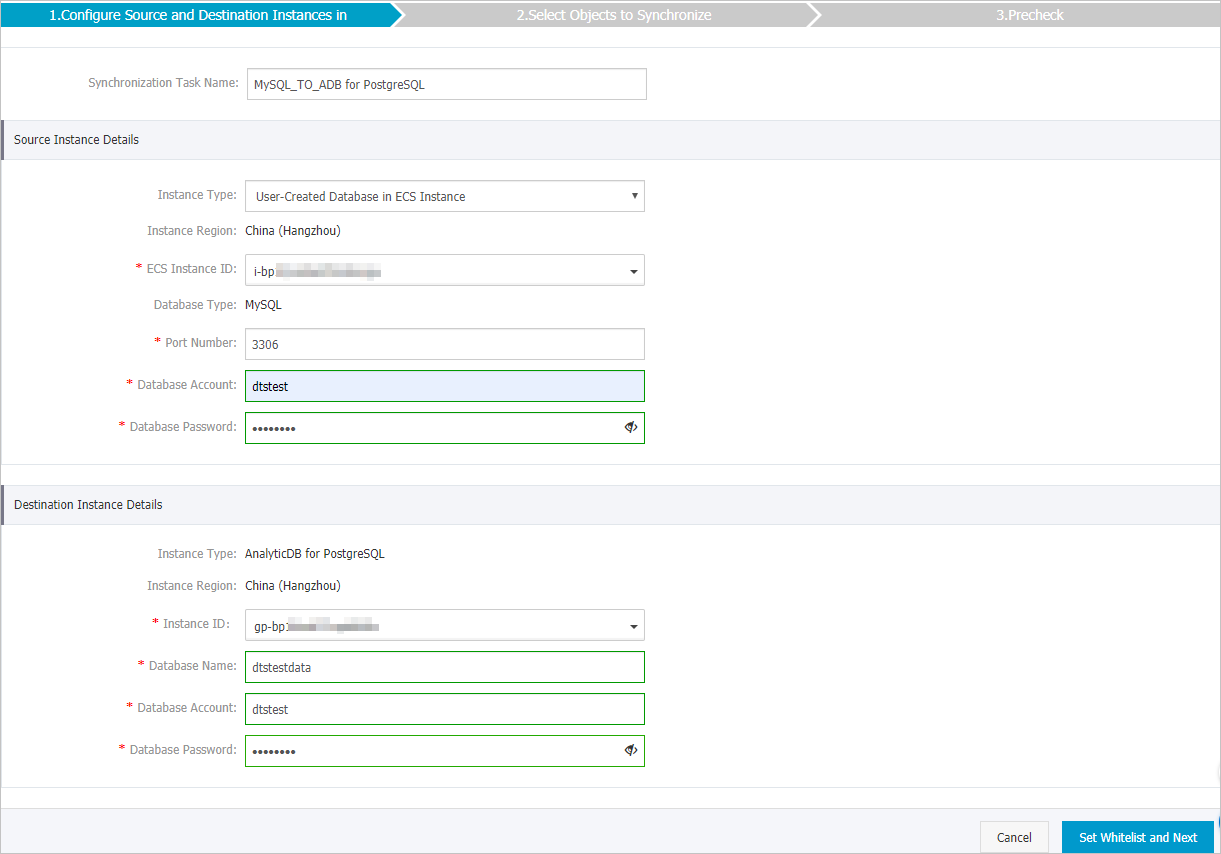
Configure the source and destination instances.
Section
Parameter
Description
N/A
Synchronization Task Name
DTS automatically generates a task name. We recommend that you specify an informative name for easy identification. You do not need to use a unique task name.
Source Instance Details
Instance Type
Select User-Created Database in ECS Instance.
Instance Region
The source region that you selected on the buy page. You cannot change the value of this parameter.
Instance ID
Select the ID of the ECS instance that hosts the self-managed MySQL database.
Database Type
The value of this parameter is set to MySQL and cannot be changed.
Port Number
Enter the service port number of the source database. The default port number is 3306.
Database Account
Enter the account of the self-managed MySQL database.
NoteThe database account must have the SELECT permission on the objects to be synchronized, the REPLICATION CLIENT permission, the REPLICATION SLAVE permission, and the SHOW VIEW permission.
Database Password
Enter the password of the source database account.
Destination Instance Details
Instance Type
The value of this parameter is set to AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL and cannot be changed.
Instance Region
The destination region that you selected on the buy page. You cannot change the value of this parameter.
Instance ID
Select the ID of the destination AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance.
Database Name
Enter the name of the destination database.
Database Account
Enter the initial account of the AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance. For more information, see Create a database account.
NoteYou can also enter an account that has the RDS_SUPERUSER permission. For more information, see Manage users and permissions.
Database Password
Enter the password of the destination database account.
In the lower-right corner of the page, click Set Whitelist and Next.
NoteDTS adds the CIDR blocks of DTS servers to the inbound rule of the ECS instance and the whitelist of the AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance. This ensures that DTS servers can connect to the source and destination instances.
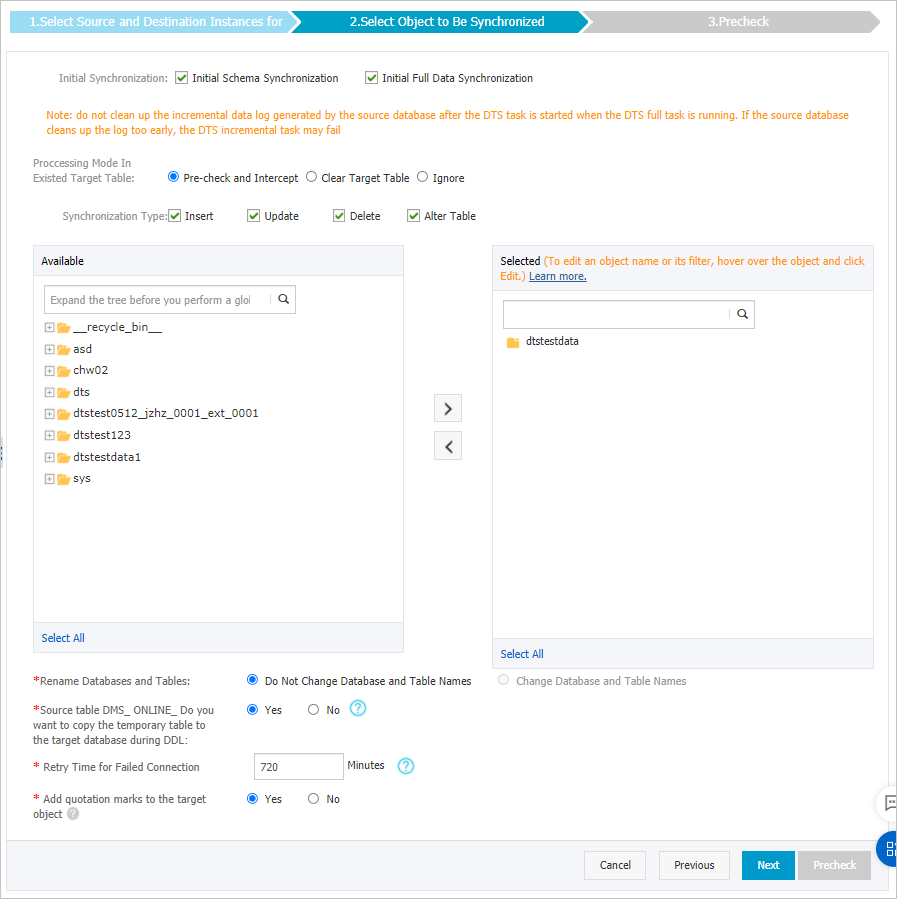
Select the synchronization policy and the objects to be synchronized.
Setting
Parameter
Description
Select the synchronization policy
Initial Synchronization
You must select both Initial Schema Synchronization and Initial Full Data Synchronization in most cases. After the precheck, DTS synchronizes the schemas and data of the required objects from the source instance to the destination instance. The schemas and data are the basis for subsequent incremental synchronization.
Processing Mode of Conflicting Tables
Clear Target Table
Skips the Schema Name Conflict item during the precheck. Clears the data in the destination table before initial full data synchronization. If you want to synchronize your business data after testing the data synchronization task, you can select this mode.
Ignore
Skips the Schema Name Conflict item during the precheck. Adds data to the existing data during initial full data synchronization. If you want to synchronize data from multiple tables to one table, you can select this mode.
Synchronization Type
Select the types of operations that you want to synchronize based on your business requirements.
Insert
Update
Delete
AlterTable
Select the objects to be synchronized
N/A
Select one or more tables from the Available section and click the
 icon to move the tables to the Selected section. Note
icon to move the tables to the Selected section. NoteYou can select only tables as the objects to be synchronized.
You can use the object name mapping feature to change the names of the columns that are synchronized to the destination database. For more information, see Rename an object to be synchronized.
Rename Databases and Tables
N/A
You can use the object name mapping feature to rename the objects that are synchronized to the destination instance. For more information, see Object name mapping.
Replicate Temporary Tables When DMS Performs DDL Operations
N/A
If you use DMS to perform online DDL operations on the source database, you can specify whether to synchronize temporary tables generated by online DDL operations.
Yes: DTS synchronizes the data of temporary tables generated by online DDL operations.
NoteIf online DDL operations generate a large amount of data, the data synchronization task may be delayed.
No: DTS does not synchronize the data of temporary tables generated by online DDL operations. Only the original DDL data of the source database is synchronized.
NoteIf you select No, the tables in the destination database may be locked.
Retry Time for Failed Connections
N/A
By default, if DTS fails to connect to the source or destination database, DTS retries within the next 720 minutes (12 hours). You can specify the retry time based on your needs. If DTS reconnects to the source and destination databases within the specified time, DTS resumes the data synchronization task. Otherwise, the data synchronization task fails.
NoteWhen DTS retries a connection, you are charged for the DTS instance. We recommend that you specify the retry time based on your business needs. You can also release the DTS instance at your earliest opportunity after the source and destination instances are released.
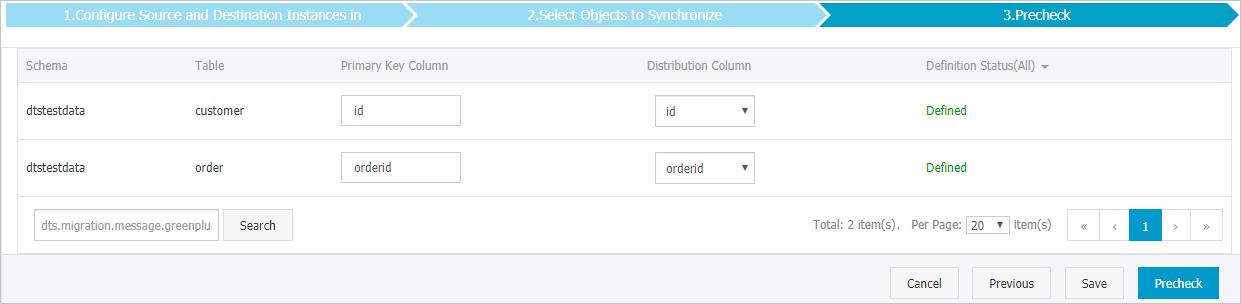
Specify the primary key column and distribution column of the table that you want to synchronize to the AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance.
 Note
NoteThe page in this step appears only if you select Initial Schema Synchronization. For more information about primary key columns and distribution columns, see Manage tables and Define table distribution.
In the lower-right corner of the page, click Precheck.
NoteBefore you can start the data synchronization task, DTS performs a precheck. You can start the data synchronization task only after the task passes the precheck.
If the task fails to pass the precheck, you can click the
 icon next to each failed item to view details.
icon next to each failed item to view details. After you troubleshoot the issues based on the details, initiate a new precheck.
If you do not need to troubleshoot the issues, ignore the failed items and initiate a new precheck.
Close the Precheck dialog box after the following message is displayed: The precheck is passed. Then, the data synchronization task starts.
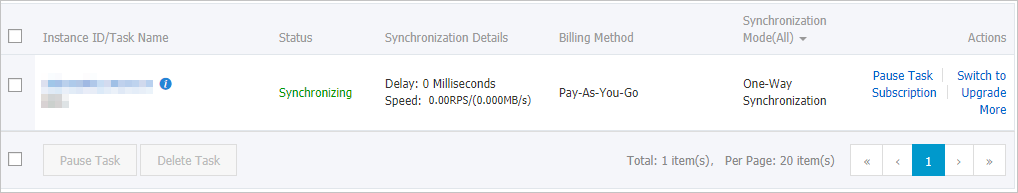
Wait until the initial synchronization is complete and the data synchronization task is in the Synchronizing state.
You can view the status of the data synchronization task on the Synchronization Tasks page.