This topic answers common questions about using Data Disaster Recovery (DBS).
How do I configure RAM authorization to back up or restore data across Alibaba Cloud accounts?
Log on to the Resource Access Management (RAM) console using the Alibaba Cloud account that owns the source database instance.
NoteEnsure the account has
AliyunDBSDefaultRolepermissions.In the navigation pane on the left, click Identities > Roles.
Create a RAM role:
Click Create Role and set Principal Type to Cloud Account.
For Principal Name, select
Current account 164882xxxxand click OK.In the dialog box, enter a role name, such as
ram-for-dbs, and click OK.
Grant permissions to the role:
On the details page for the role you created, click the Permissions tab and then click Grant Permission.
In the panel that appears, set Permission Type to System Policy.
Select the required policies based on the Database Location.
RDS Instance:
AliyunRDSReadOnlyAccessandAliyunVPCReadOnlyAccess.Self-managed database connected via an Express Connect circuit, a VPN Gateway, or a Smart Access Gateway:
AliyunVPCReadOnlyAccessPolarDB:
AliyunPolardbFullAccess
Click OK.
Edit the trust policy:
In the basic information section of the role, click Trust Policy > Edit Trust Policy.
On the Edit Trust Policy page, click JSON Editor. Copy and paste the code below into the box:
Replace
<Account ID>with the ID of the Alibaba Cloud account that manages the backup schedule.{ "Statement": [ { "Action": "sts:AssumeRole", "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "RAM": [ "acs:ram::<Account ID>:root" ], "Service": [ "<Account ID>@dbs.aliyuncs.com" ] } } ], "Version": "1" }
Click OK to complete the RAM authorization.
How do I back up and restore data across Alibaba Cloud accounts?
Configure cross-account backup
In the Database Location section, select a destination instance that supports the cross-account feature. Then, click Cross Alicloud instance.

Enter the following information:
Cross Alicloud UID: The ID of the Alibaba Cloud account that owns the source database.
Role name: The name of the role that you created in the source account, such as
ram-for-dbs. This role must have the required trust policy.

Configure cross-account restoration
For detailed instruction, see Configure a backup schedule and restore data.
You cannot migrate backup sets across Alibaba Cloud accounts in the console.
How do I back up a database across accounts using a public endpoint?
Set Database Location to User-Created Database with Public IP Address <IP Address:Port Number>.
If the User-Created Database with Public IP Address <IP Address:Port Number> option is unavailable, search for DingTalk group ID 35585947 or submit a ticket to request access.
How do I automatically archive backup sets to a backup server?
Using an operations account, create a backup schedule.
Using an operations account, Manage the backup schedule.
Using the backup account, install a backup gateway on the backup server.
NoteIf you do not have a backup server, purchase a server first.
Using the operations account, find the target schedule in the backup schedule list and click Manage in the Actions column. On the Configure Task page, go to the Backup Set Download section at the bottom and click Set Backup Set Download Rules. In the dialog box that appears, configure the parameters as described in the table below.
NoteThis button is displayed only if the database engine supports backup set downloads and the destination backup storage type is DBS Storage.
Parameter
Description
Auto download status
Select Enable.
Target type
Fixed to Backup gateway installed.
Backup Gateway
Select a backup gateway. DBS uses the backup gateway to connect to the on-premises device.
ImportantThe automatic download feature is in beta and may cause performance bottlenecks. To prevent data accumulation and other issues, do not use the same backup gateway for multiple backup schedules.
Target location
Select the destination type and specify the directory or path to store the backup data. The following destination types are supported:
Dump direction
FTP direction
NAS direction
Minio direction
Full data format
Uses the system default value and cannot be modified.
NoteFor more information about the data formats of full and incremental backup sets, see the preceding feature limits and format description.
Incremental data format
Defaults to the native format and cannot be modified.
After you complete the configuration, click OK.
Using the operations account, navigate to the Configure Task page and click Backup Set Download in the left navigation pane to view the download progress.
How do I modify the backup lifecycle?
Log on to Data Management (DMS) 5.0.
In the top navigation bar, choose Security and disaster recovery (DBS) > Data Disaster Recovery (DBS) > Backup Plan.
NoteIf you use the DMS console in simple mode, move the pointer over the
 icon in the upper-left corner of the DMS console and choose All Features > Security and disaster recovery (DBS) > Data Disaster Recovery (DBS) > Backup Plan.
icon in the upper-left corner of the DMS console and choose All Features > Security and disaster recovery (DBS) > Data Disaster Recovery (DBS) > Backup Plan. In the Actions column of the target backup schedule, click Manage to go to the Configure Task page.
In the Lifecycle Information section, click Edit Lifecycle.
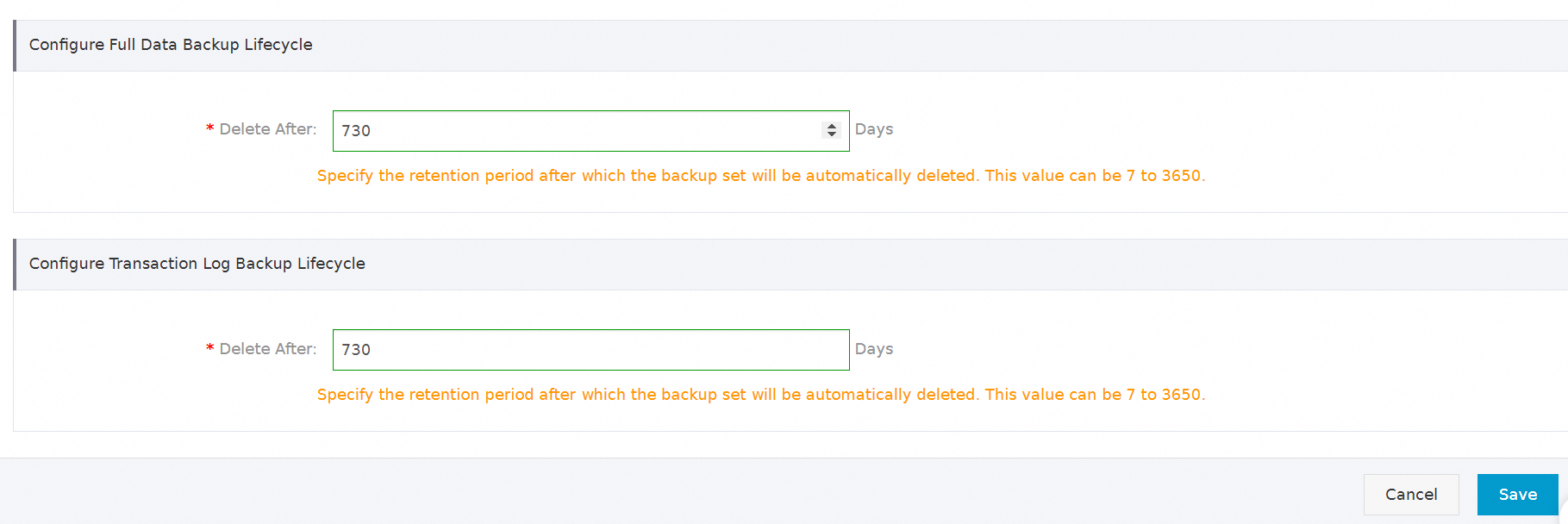
Set the retention period for full or incremental backups, and then click Save.
 Important
ImportantThe minimum retention period is 7 days and the maximum is 3,650 days. After the retention period expires, the backup set is automatically deleted and cannot be restored.
If you do not enable incremental backup, the console displays only the lifecycle configuration for full backups. To learn how to enable incremental backup, see Enable or disable incremental log backup.
How do I set the minimum retention policy for backup sets?
You can set the lifecycle of backup sets when you configure a backup schedule, or modify it later as needed. You can use one of the following methods:
Console: See Manage a backup schedule and Modify the backup lifecycle.
API operations: See CreateAndStartBackupPlan and ModifyStorageStrategy.
Storage costs depend on the backup destination. Storing data in your own OSS bucket incurs no DBS storage fees, while storing data in DBS Storage incurs fees based on data volume and storage duration. For more information, see Differences between DBS Storage and user-owned OSS buckets and Storage billing.
NoteIf you have a large data volume, purchase a DBS storage plan to offset the storage fees generated by the backup schedule. For more information, see Use a storage plan.
If necessary, you can also manually delete backup sets to reduce storage fees.
How do I perform disaster recovery and ensure security for a self-managed database on an ECS instance?
Create a backup schedule and set the Backup Method to Logical Backup.
Set Database Location to ECS-Hosted Database, as described in Manage the backup schedule.
How do I perform geo-redundant backup for an RDS for MySQL instance?
Apply for a public endpoint for the source RDS MySQL instance.
Create a backup schedule. For geo-redundant backups, purchase a backup schedule in a region different from the source region and set Backup Method to Logical Backup.
How do I perform geo-redundant backup for a self-managed database?
Create a backup schedule and set Backup Method to Logical Backup.
When you configure the backup schedule, set Database Location to User-Created Database with Public IP Address <IP Address:Port Number>.
If the User-Created Database with Public IP Address <IP Address:Port Number> option is not available, search for DingTalk group 35585947 or submit a ticket to request access.
How do I use Database Gateway (DG) to back up a private database on premises or in a third-party cloud to cloud storage?
Create a backup schedule and set the Backup Method to Logical Backup.
Configure the backup schedule, and then set Database Location to No public network IP: Port's self-built database (accessed through the database gateway).
How do I back up an on-premises database accessed over an Express Connect circuit to cloud storage?
Create a backup schedule and set Backup Method to Logical Backup.
Connect your on-premises IDC to Alibaba Cloud via an Express Connect circuit to enable network interoperability between the VPC and the local IDC. For more information, see Connect an on-premises IDC to a VPC using an Express Connect circuit.
Add a static route pointing to the DBS IP address range on the client-side access device in the local IDC. The configuration format is:
ip route <DBS CIDR block> {Alibaba Cloud-side interconnection IP}. For a list of DBS IP address ranges, see DBS IP address ranges.Configure the backup schedule, and set Database Location to Express Connect DB/VPN Gateway/Intelligent Gateway.
How do I back up a self-managed Redis database to the cloud?
How do I perform disaster recovery for a self-managed MySQL database?
Prerequisites
The logical backup is complete.
Only logical backup schedules are supported. Physical backups do not support individual database/table restoration.
Logical backups of PolarDB for Xscale instances support only the backup of the entire instance. Therefore, individual database/table restoration is not supported.
Backup and recovery
For more information, see Cross-cloud or self-managed MySQL logical backup and restoration.
DBS IP address ranges
Region | DBS IP address range |
China (Hangzhou) | 100.104.217.0/24 |
China (Beijing) | 100.104.119.0/24 |
China (Qingdao) | 100.104.183.0/24 |
China (Shanghai) | 100.104.191.0/24 |
China (Shenzhen) | 100.104.81.0/24 |
China (Chengdu) | 100.104.133.128/26 |
China (Ulanqab) | 100.104.76.192/26 |
China (Heyuan) | 100.104.127.0/26 |
South Korea (Seoul) | 100.104.150.192/26 |
Thailand (Bangkok) | 100.104.119.128/26 |
China (Hong Kong) | 100.104.10.0/24 |
Singapore | 100.104.10.0/24 |
Japan (Tokyo) | 100.104.144.0/24 |
China (Hohhot) | 100.104.40.0/24 |
China (Zhangjiakou) | 100.104.48.0/24 |
US (Virginia) | 100.104.220.0/24 |
US (Silicon Valley) | 100.104.17.0/24 |
Germany (Frankfurt) | 100.104.133.0/24 |
Malaysia (Kuala Lumpur) | 100.104.10.0/24 |
Indonesia (Jakarta) | 100.104.209.0/24 |