DataWorks is an all-in-one big data development and governance platform that supports end-to-end data processing. Use DataWorks to integrate, develop, model, analyze, monitor, serve, and govern data across your organization, and build an enterprise-level data middle platform.
Module overview
Module | Description |
Data Integration | Synchronize data across 50+ heterogeneous sources in offline, real-time, or integrated modes |
Data Studio and Operation Center | Develop, orchestrate, deploy, and monitor data processing tasks across multiple compute engines |
Data modeling | Plan data warehouse layers, define standards, build dimensional models, and manage metrics |
Data Analysis | Run SQL queries, upload datasets, and visualize data without data engineering skills |
Data Quality | Monitor data at the table and field levels and block problematic tasks to prevent dirty data propagation |
Data Map | Search, categorize, and trace data lineage across your data assets |
DataService Studio | Build, publish, and manage data APIs with serverless architecture |
Open Platform | Integrate external systems through OpenAPI, OpenEvent, and Extensions |
Migration Assistant | Migrate jobs from open-source scheduling engines or between DataWorks environments |
Data Integration
Data Integration is a stable, efficient, and elastic data synchronization platform that connects heterogeneous data sources across network environments.
Synchronization modes and capabilities
Data Integration supports full and incremental data synchronization in offline, real-time, or integrated modes.
Batch synchronization: Configure scheduling cycles for synchronization tasks.
50+ data sources: Synchronize data between relational databases, data warehouses, non-relational databases, file storage, and message queues.
Network flexibility: Connect to data sources across public internet, IDCs, or VPCs.
Security: Monitor operations and enforce access controls during synchronization.
Engine architecture
Data Integration uses a star-shaped engine architecture. Any connected data source can form synchronization links with any other supported source. For a list of supported data sources, see Supported data sources and synchronization solutions.

Before synchronizing data, establish network connectivity between your data source and a resource group. Data Integration tasks run on serverless resource groups (recommended) or exclusive resource groups for Data Integration (legacy). For network solutions, see Network connectivity solutions.
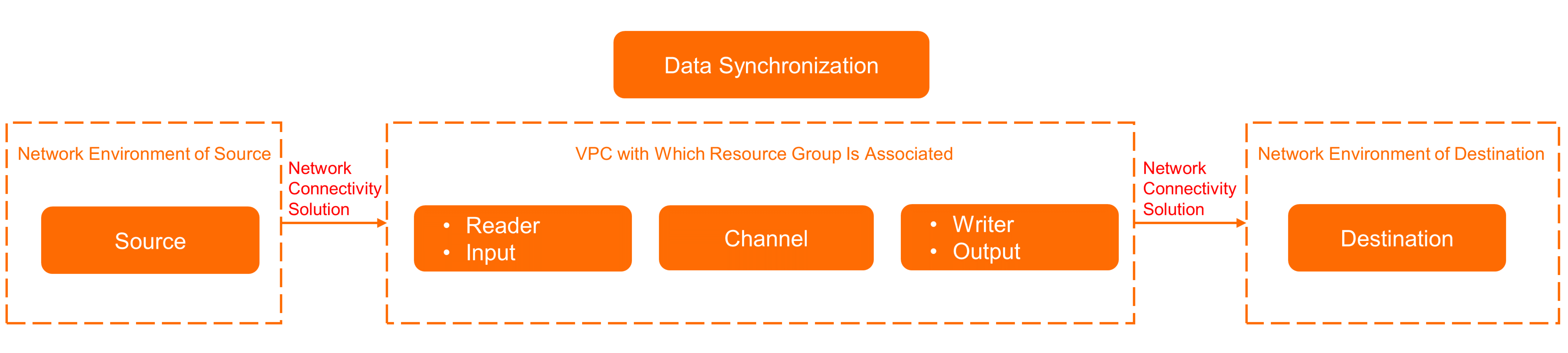
Typical use cases
Ingesting data into data lakes and data warehouses
Sharding databases and tables
Archiving real-time data
Moving data between clouds
Data Studio and Operation Center
Data Studio is a development platform for data processing. Operation Center is an intelligent operations and maintenance (O&M) platform. Together, they provide a standardized way to build and manage data development workflows.
Multi-engine development and environment isolation
Multi-engine support: Develop, test, deploy, and manage tasks across MaxCompute, E-MapReduce, CDH, Hologres, AnalyticDB, and ClickHouse from a unified platform.
Intelligent editor and visual orchestration: An intelligent editor and drag-and-drop dependency orchestration for building task workflows. The scheduling system is proven by Alibaba Group's internal workloads.
Environment isolation: Separate development and production environments in standard mode. Version control, code review, smoke testing, deployment control, and operational auditing standardize your development lifecycle.
Operational monitoring: Operation Center provides data timeliness assurance, task diagnostics, impact analysis, automated O&M, and mobile-based O&M.
DataWorks provides workspaces in standard mode to isolate development and production environments. For more information, see Differences between workspace modes.
Development and operations workflow
Development workflow
Task monitoring, troubleshooting, and resolution
Data modeling
Data modeling in DataWorks incorporates over a decade of best practices from Alibaba's data warehouse modeling methodologies. Build enterprise data assets through structured modeling and reverse modeling for data marts and data middle platforms.
Four core modules
Data modeling includes four modules: Data Warehouse Planning, Data Standard, Dimensional Modeling, and Data Metrics.
Module | Capabilities |
Data Warehouse Planning | Plan data warehouse layers, data domains, and data marts. Configure model design spaces so that different departments share a common set of data standards and models. |
Data Standard | Define field standards, standard codes, units of measurement, and naming dictionaries. Automatically generate data quality rules from standard codes to simplify compliance checks. |
Dimensional Modeling | Reverse modeling addresses the cold-start problem for existing data warehouses. Import models from Excel files or build them with FML, an SQL-like domain-specific language. Visual dimensional modeling integrates with Data Studio to automatically generate ETL code. |
Data Metrics | Define atomic metrics and derived metrics. Batch-create derived metrics based on atomic metrics and various dimensions. Integrates with dimensional modeling. |
Architecture
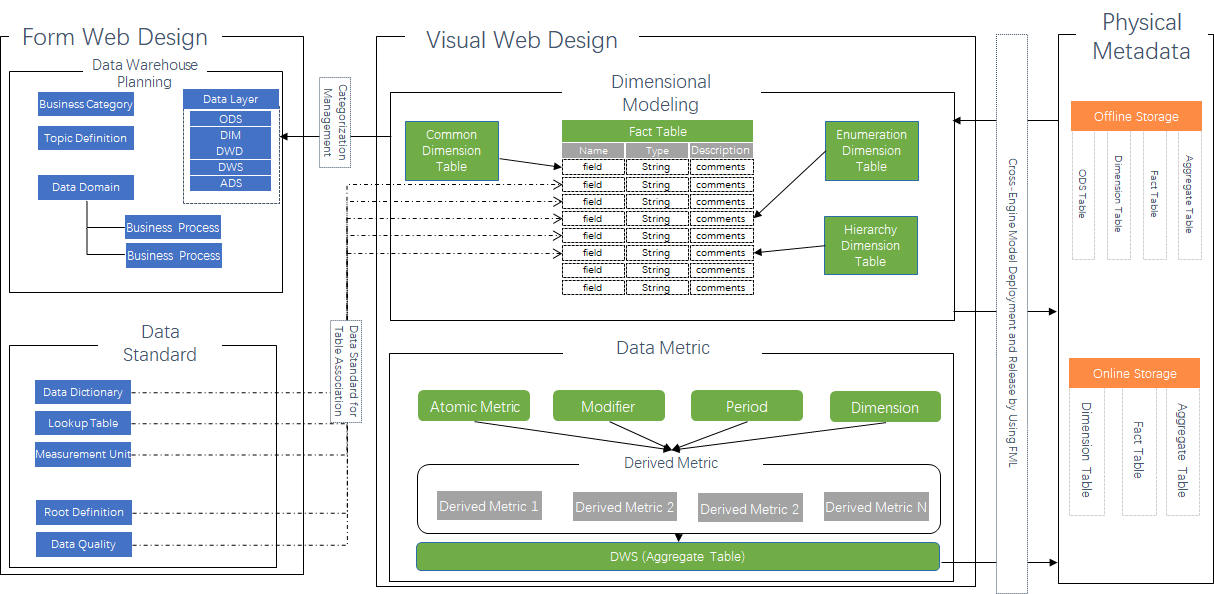
Typical use cases
Structured data management: Organize and store large-scale enterprise data in a structured and consistent manner.
Cross-department data integration: Break data silos between departments and business domains to give decision-makers a complete view of business data.
Unified data standards: Establish consistent data definitions across systems without changing existing architectures. Enable upstream and downstream data interconnection.
Data value realization: Use various types of enterprise data to deliver more effective data services.
Data Analysis
Data Analysis provides tools for data analysts, product managers, and operations staff to retrieve and analyze data without requiring data engineering skills -- making everyone a data analyst.
Core capabilities
Upload personal datasets and access public datasets
Search and bookmark tables
Run online SQL queries
Share SQL files and download query results
Visualize data on large screens using spreadsheets
Typical use cases
Use case | Description |
Scalable analysis | Leverage compute engine resources to analyze full-scale datasets. |
Cross-system data flow | Analyze data from databases across different business systems. Export data to MaxCompute tables or share result sets with specified users and grant them permissions. |
Secure operations | Integrate SQL queries and result downloads with security auditing. |
Data Quality
Data Quality monitors data at the table and field levels using over 30 preset monitoring templates and custom templates. It detects source data changes, identifies dirty data during ETL (extract, transform, load) processing, and automatically blocks problematic tasks to prevent dirty data from propagating downstream.
Monitoring and verification
Data Quality monitors datasets across various engines, including MaxCompute. When offline data changes, Data Quality verifies the data and blocks the production pipeline to prevent data pollution. It stores historical verification results for quality analysis and classification. For more information, see Data Quality.
Data Quality addresses the following issues:
Frequent database changes
Frequent business changes
Data definition issues
Dirty data from business systems
Quality issues caused by system interactions
Issues caused by data correction
Quality issues originating from the data warehouse
Data Map
Data Map is built on data search capabilities. It provides tools for table usage instructions, data categories, data lineage, and field lineage. Data consumers and data owners use Data Map to manage data and collaborate on development.
DataService Studio
DataService Studio is a flexible, lightweight, secure, and stable platform for building and publishing data APIs. It provides publication approval, access control, usage metering, and resource isolation.
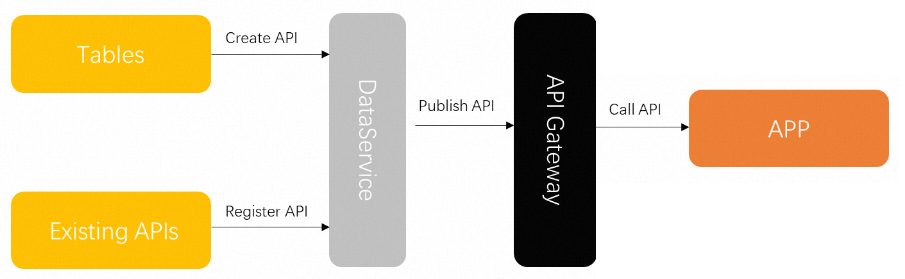
Unified API service bus
DataService Studio acts as a unified service bus between the data warehouse and applications. It unifies the creation and management of API services, closing the gap between the data warehouse, databases, and data applications.

Generate data APIs from tables in various data sources using no-code or self-service SQL mode. Use Function Compute to process API request parameters and returned results.
Publish API services to an API gateway with a single click.
Serverless architecture
DataService Studio uses a serverless architecture. Focus on API query logic instead of managing infrastructure. DataService Studio automatically provisions computing resources with elastic scaling, resulting in zero O&M costs.
Open Platform
Open Platform exposes DataWorks data and capabilities to external systems through OpenAPI, OpenEvent, and Extensions. Integrate applications with DataWorks to manage data workflows, govern data, and respond to business status changes.
Three integration capabilities
OpenAPI: Integrate your applications with DataWorks. Batch create, publish, and manage tasks to improve processing efficiency and reduce manual operations. For more information, see OpenAPI.
OpenEvent: Subscribe to system events for real-time notifications. For example, subscribe to table change events to monitor core tables, or subscribe to task change events to build a real-time task monitoring dashboard. For more information, see OpenEvent.
Extensions: Service-level plug-ins that combine OpenAPI and OpenEvent. Customize workflow controls in DataWorks. For example, create a deployment control plug-in to block tasks that do not comply with your standards. For more information, see Extensions.
Typical use cases
Open Platform supports deep system integration, automated operations, workflow definition, and business monitoring. Build industry-specific and scenario-based data applications and plug-ins on the DataWorks Open Platform.
Migration Assistant
Migration Assistant migrates jobs from open-source scheduling engines to DataWorks. It supports cross-cloud, cross-region, and cross-account job migration, allowing you to quickly clone and deploy DataWorks jobs. The DataWorks team, in collaboration with big data expert service teams, also offers cloud migration services to help you move your data and tasks to the cloud.
Migration capabilities
Capability | Description |
Task migration to the cloud | Migrate jobs from open-source scheduling engines to DataWorks. |
DataWorks migration | Migrate development assets within the DataWorks ecosystem. |
Typical use cases
Use case | Description |
Task migration to the cloud | Migrate jobs from open-source scheduling engines to DataWorks. |
Task backup | Regularly back up task code to minimize losses from accidental project deletion. |
Business replication | Abstract common business logic and use the export/import feature to replicate it across projects. |
Test environment setup | Replicate business code and change the data input from production to test data. |
Cross-cloud development | Import and export between DataWorks on the public cloud and DataWorks in a private cloud for collaborative development. |

