For applications that require shared data and high I/O performance, you can use Apsara File Storage NAS (NAS) file systems as persistent volumes (PVs). This topic describes how to mount a NAS volume to an application and verify the shared storage and data persistence features of NAS.
Background information
NAS is a distributed file system that provides shared access, scalability, high reliability, and high performance. It is suitable for applications that require shared data and high I/O performance. For more information, see Storage overview.
For more information about the storage specifications, performance, billing, and supported regions and zones of different types of NAS file systems, see General-purpose NAS file systems and Extreme NAS file systems.
General-purpose NAS file systems and Extreme NAS file systems have different limits on mount connectivity, the number of file systems, and protocol types. For more information, see Limits.
You can mount and use NAS volumes in one of the following ways, depending on whether you have a NAS file system:
If you have a NAS file system, you can mount and share it directly. For more information, see Use an existing NAS file system as a persistent volume.
If you do not have a NAS file system, you can create and mount one automatically using a StorageClass. For more information, see Create a new NAS file system as a persistent volume.
Prerequisites
The managed-csiprovisioner component is installed in the ACS cluster.
Go to the ACS cluster management page in the ACS console. In the left-side navigation pane of the cluster management page, choose . On the Storage tab, you can check whether managed-csiprovisioner is installed.
Limits
Mounting NAS file systems that use the SMB protocol is not supported.
A NAS file system can be mounted only to pods in the same VPC. Cross-VPC mounting is not supported.
NoteIn the same VPC, a NAS file system can be mounted across zones.
Only the NFSv3 protocol is supported for mounting NAS file systems.
Considerations
NAS provides shared storage. A single NAS volume can be mounted to multiple pods. If multiple pods modify the same data at the same time, your application must handle data synchronization.
When you mount a NAS volume, do not configure
securityContext.fsgroupin the application's YAML file. Otherwise, the mount may fail.NoteYou cannot modify the permissions, owner, or group of the
/root directory of a NAS file system.After you mount a NAS volume, do not delete its mount target. If you delete the mount target, the operating system may stop responding.
Use an existing NAS file system as a persistent volume
Step 1: Get NAS file system information
Obtain the VPC ID and vSwitch ID used by the ACS pods.
NoteThe following steps describe how to obtain the information from the console. You can also run the
kubectl get cm -n kube-system acs-profile -o yamlcommand to view the YAML file of acs-profile. Obtain the VPC ID and vSwitch ID from thevpcIdandvSwitchIdsfields.Log on to the ACS console.
On the Clusters, click the name of the cluster to go to the cluster management page.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
At the top of the ConfigMaps page, set the namespace to kube-system. Then, find acs-profile and click Edit YAML.
Obtain the VPC ID and vSwitch ID from the
vpcIdandvSwitchIdsfields.
Confirm that the existing NAS file system meets the requirements and obtain the mount target address.
Log on to the NAS console. In the navigation pane on the left, click File System List.
Find the target NAS file system. Confirm that its region, zone, and protocol type meet the requirements.
NAS file systems cannot be mounted across VPCs and therefore cannot be used across regions. Make sure the region of the NAS file system is the same as that of the ACS cluster.
In the same VPC, a NAS file system can be mounted across zones. However, for better performance, use a NAS file system in the same zone as the pods in the ACS cluster.
Confirm that the NAS file system uses the NFS protocol. You cannot mount NAS file systems that use the SMB protocol.

Confirm that the mount target meets the requirements and obtain its address.
Click the file system ID.
In the navigation pane on the left of the file system details page, click Mount Targets.
In the Mount Target area, confirm that the existing mount target meets your requirements and obtain the mount target address.
NoteA mount target is automatically created for a General-purpose NAS file system. You must manually create mount targets for Extreme NAS file systems.
If the existing mount target does not meet the requirements, create a new one. For more information, see Manage mount targets.
The VPC of the mount target must be the same as the VPC used by the pods in the ACS cluster. Otherwise, the mount fails.
For better performance, the vSwitch of the mount target should be the same as the vSwitch used by the pods in the ACS cluster.
The status of the mount target is Available.

Step 2: Create a PVC
kubectl
Save the following content as a file named nas-pvc.yaml.
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: nas-pvc annotations: csi.alibabacloud.com/mountpoint: *******-mw***.cn-shanghai.nas.aliyuncs.com csi.alibabacloud.com/mount-options: nolock,tcp,noresvport spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteMany resources: requests: storage: 20Gi storageClassName: alibaba-cloud-nasThe following table describes the parameters.
ImportantWhen you create a persistent volume claim (PVC) from the preceding YAML file, the system first creates a static PV based on the NAS configuration in the
annotations. Then, the system creates a PVC and associates it with the PV.Parameter
Description
csi.alibabacloud.com/mountpointThe directory of the NAS file system to mount. This associates the volume with the NAS file system you created.
If you enter a mount target address, such as
****-****.<region>.nas.aliyuncs.com, the root directory (/) of the NAS file system is mounted.If you enter a mount target address and a subdirectory, such as
****-****.<region>.nas.aliyuncs.com:/dir, the/dirdirectory of the NAS file system is mounted. If the/dirdirectory does not exist, it is automatically created.
csi.alibabacloud.com/mount-optionsThe mount parameters. Use
nolock,tcp,noresvport.accessModesThe access mode.
storageThe storage capacity to allocate to the pod. This is the capacity of the NAS volume to create.
Create the PVC.
kubectl create -f nas-pvc.yamlYou can view the PV.
kubectl get pvThe output shows that a PV was automatically created based on the NAS file system information, such as the mount target, from the PVC.
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE nas-ea7a0b6a-bec2-4e56-b767-47222d3a**** 20Gi RWX Retain Bound default/nas-pvc alibaba-cloud-nas 1m58sView the PVC.
kubectl get pvcThe output shows that the PVC is associated with the automatically created PV.
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS VOLUMEATTRIBUTESCLASS AGE nas-pvc Bound nas-ea7a0b6a-bec2-4e56-b767-47222d3a**** 20Gi RWX alibaba-cloud-nas <unset> 2m14s
Console
Log on to the ACS console.
On the Clusters, click the name of the cluster to go to the cluster management page.
In the left-side navigation pane of the cluster management page, choose .
On the Persistent Volume Claims page, click Create.
In the dialog box, configure the parameters and click Create.
Parameter
Description
Example
PVC Type
Select NAS.
NAS
Name
Enter a name for the PVC. For the format requirements, see the prompt on the page.
nas-pvc
Allocation Mode
Select Use Mount Target Domain Name.
Create with Mount Target Domain Name
Volume Plug-in
CSI is selected by default.
CSI
Capacity
The storage capacity to allocate to the pod. This is the capacity of the NAS volume.
20 GiB
Access Mode
ReadWriteMany and ReadWriteOnce are supported.
ReadWriteMany
Mount Target Domain Name:
Configure the directory of the NAS file system to mount.
If you enter a mount target address, such as
****-****.<region>.nas.aliyuncs.com, the root directory (/) of the NAS file system is mounted.If you enter a mount target address and a subdirectory, such as
****-****.<region>.nas.aliyuncs.com:/dir, the/dirdirectory of the NAS file system is mounted. If the/dirdirectory does not exist, it is automatically created.
350514****-mw***.cn-shanghai.nas.aliyuncs.com
After the PVC is created, it appears on the Persistent Volume Claims page. The PVC is bound to an automatically created PV, which is a NAS volume. You can view the details of this PV on the Persistent Volumes page.
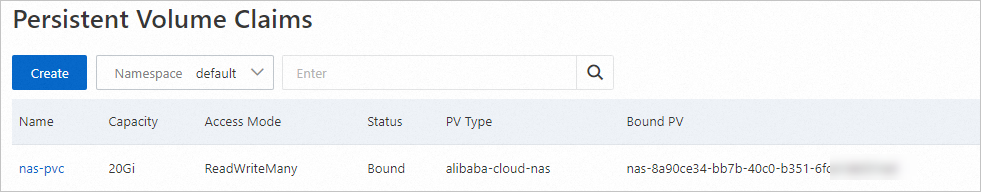
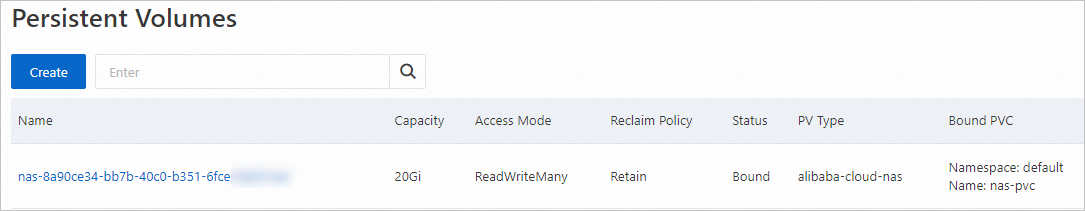
Step 3: Create an application and mount the NAS volume
kubectll
Create a file named nas-test.yaml that contains the following content.
The following YAML file creates a deployment with two pods. Both pods request storage resources from a PVC named
nas-pvcand mount the volume to the/datapath.apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: nas-test labels: app: nginx spec: replicas: 2 selector: matchLabels: app: nginx template: metadata: labels: app: nginx spec: containers: - name: nginx image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/acs-sample/nginx:latest ports: - containerPort: 80 volumeMounts: - name: pvc-nas mountPath: /data volumes: - name: pvc-nas persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: nas-pvcCreate the deployment and mount the NAS volume.
kubectl create -f nas-test.yamlCheck the status of the pods in the deployment.
kubectl get pod | grep nas-testThe following output shows that two pods are created.
nas-test-****-***a 1/1 Running 0 40s nas-test-****-***b 1/1 Running 0 40sCheck the mount path.
kubectl exec nas-test-****-***a -- df -h /dataExpected output:
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on 350514*****-mw***.cn-shanghai.nas.aliyuncs.com:/ 10P 0 10P 0% /dataIf a similar output is returned, the file system is mounted.
Console
In the left-side navigation pane of the cluster management page, choose .
On the Deployments page, click Create from Image.
Configure the deployment parameters and click Create.
The following table describes the key parameters. You can keep the default values for other parameters. For more information, see Create a stateless application using a deployment.
Configuration page
Parameter
Description
Example
Basic Information
Name
Enter a name for the deployment. For the format requirements, see the prompt on the page.
nas-test
Replicas
Configure the number of replicas for the deployment.
2
Container
Image Name
Enter the address of the image to deploy the application.
registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/acs-sample/nginx:latest
Required Resources
Set the required vCPU and memory resources.
0.25 vCPU, 0.5 GiB
Volume
Click Add PVC and configure the parameters.
Mount Source: Select the PVC that you created.
Container Path: Enter the path in the container where you want to mount the NAS file system.
Mount Source: nas-pvc
Container Path: /data
Check the application deployment status.
On the Deployments page, click the application name.
On the Pods tab, confirm that the status of the pods is Running.
Create a new NAS file system as a persistent volume
Step 1: Create a StorageClass
Modify the following YAML content based on the parameter descriptions and save it as a file named nas-sc.yaml.
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1 kind: StorageClass metadata: name: alicloud-nas-fs mountOptions: - nolock,tcp,noresvport - vers=3 parameters: volumeAs: filesystem fileSystemType: standard storageType: Performance regionId: cn-shanghai zoneId: cn-shanghai-e vpcId: "vpc-2ze2fxn6popm8c2mzm****" vSwitchId: "vsw-2zwdg25a2b4y5juy****" accessGroupName: DEFAULT_VPC_GROUP_NAME deleteVolume: "false" provisioner: nasplugin.csi.alibabacloud.com reclaimPolicy: RetainThe following table describes the parameters.
ImportantDifferent types and storage classes of NAS file systems are supported in different regions and zones. You must select an appropriate region, zone, VPC, and vSwitch for the NAS file system and mount target. The selection must be compatible with the region of your ACS cluster and the VPC and vSwitch information of the pods in the cluster. For more information, see the following topics:
For information about the storage specifications, performance, billing, and supported regions and zones of different types of NAS file systems, see General-purpose NAS file systems and Extreme NAS file systems.
General-purpose NAS file systems and Extreme NAS file systems have different limits on mount connectivity, the number of file systems, and protocol types. For more information, see Limits.
You can run the
kubectl get cm -n kube-system acs-profile -o yamlcommand to view the YAML file of acs-profile. Retrieve the VPC ID and vSwitch ID from thevpcIdandvSwitchIdsfields.
Parameter
Description
volumeAsOnly
filesystemis supported. This value indicates that a NAS file system is automatically created. Each NAS volume corresponds to a NAS file system.fileSystemTypeThe type of the NAS file system.
standard(default): General-purpose NAS file system. For more information, see General-purpose NAS file systems.extreme: Extreme NAS file system. For more information, see Extreme NAS file systems.
storageTypeThe storage class of the NAS file system.
For General-purpose NAS file systems, the following values are supported:
Performance(default): compute-optimized instanceCapacity: storage-optimized
For Extreme NAS file systems, the following values are supported:
standard(default): mediumadvanced: advanced
regionIdThe ID of the region where the NAS file system resides. The region ID must be the same as that of the ACS cluster.
zoneIdThe ID of the zone where the NAS file system resides. Select a zone based on the vSwitch used by the pod in the ACS cluster.
NoteIn the same VPC, a NAS file system can be mounted across zones. For better performance, we recommend that you select the same zone.
vpcId,vSwitchIdThe IDs of the VPC and vSwitch where the mount target of the NAS file system resides. Set these to the IDs of the VPC and vSwitch used by the pods in the ACS cluster.
accessGroupNameThe permission group of the mount target of the NAS file system. The default value is
DEFAULT_VPC_GROUP_NAME.provisionerThe driver type. This must be set to
nasplugin.csi.alibabacloud.com, which indicates that the Alibaba Cloud NAS Container Storage Interface (CSI) plug-in is used.reclaimPolicyThe reclaim policy of the PV. Currently, only
Retainis supported. This means that when the PV is deleted, the corresponding NAS file system and mount target are retained.Create the StorageClass.
kubectl create -f nas-sc.yamlView the StorageClass.
kubectl get scExpected output:
NAME PROVISIONER RECLAIMPOLICY VOLUMEBINDINGMODE ALLOWVOLUMEEXPANSION AGE alicloud-nas-fs nasplugin.csi.alibabacloud.com Retain Immediate false 13m ......
Step 2: Create a PVC
Save the following content as a file named nas-pvc-fs.yaml.
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: nas-pvc-fs spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteMany storageClassName: alicloud-nas-fs resources: requests: storage: 20GiThe following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Description
accessModesThe access mode.
storageThe storage capacity to allocate to the pod. This is the capacity of the NAS volume to create.
NoteExtreme NAS file systems have a minimum capacity of 100 GiB. If the NAS file system type defined in the StorageClass is Extreme NAS, the value of
storagemust be 100 GiB or greater. Otherwise, the corresponding PV cannot be created.storageClassNameThe name of the StorageClass to bind.
Create the PVC.
kubectl create -f nas-pvc-fs.yamlView the PVC.
kubectl get pvcThe output shows that the PVC is associated with the automatically created PersistentVolume (PV). You can go to the NAS console to view the corresponding NAS file system.
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS VOLUMEATTRIBUTESCLASS AGE nas-pvc-fs Bound nas-04a730ba-010d-4fb1-9043-476d8c38**** 20Gi RWX alicloud-nas-fs <unset> 14s
Step 3: Create an application and mount the NAS volume
Create a file named nas-test-fs.yaml with the following content.
The following YAML file creates a deployment that contains two pods. Both pods request storage from the PVC named
nas-pvc-fsand mount the volume to the/datapath.apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: nas-test labels: app: nginx spec: replicas: 2 selector: matchLabels: app: nginx template: metadata: labels: app: nginx spec: containers: - name: nginx image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/acs-sample/nginx:latest ports: - containerPort: 80 volumeMounts: - name: pvc-nas mountPath: /data volumes: - name: pvc-nas persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: nas-pvc-fsCreate the deployment and mount the NAS volume.
kubectl create -f nas-test-fs.yamlCheck the status of the pods in the deployment.
kubectl get pod | grep nas-testThe following output shows that two pods are created.
nas-test-****-***a 1/1 Running 0 40s nas-test-****-***b 1/1 Running 0 40sCheck the mount path.
kubectl exec nas-test-****-***a -- df -h /dataExpected output:
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on 350514*****-mw***.cn-shanghai.nas.aliyuncs.com:/ 10P 0 10P 0% /dataIf a similar output is returned, the file system is mounted.
Mount an existing NAS file system using an NFS volume
Step 1: Get NAS file system information
For more information about how to obtain the NAS mount target address, see Obtain NAS file system information.
Step 2: Create an application and mount the NAS volume
Create a file named
nas-test-nfs.yamlwith the following content.The following YAML creates a deployment with two pods. Both pods mount the NAS file system to the
/datapath using a volume namednfs-nas.apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: nas-test labels: app: nginx spec: replicas: 2 selector: matchLabels: app: nginx template: metadata: labels: app: nginx spec: containers: - name: nginx image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/acs-sample/nginx:latest ports: - containerPort: 80 volumeMounts: - name: nfs-nas mountPath: /data volumes: - name: nfs-nas nfs: server: file-system-id.region.nas.aliyuncs.com # The mount target address of the Alibaba Cloud NAS file system. Replace this with your actual value. Example: 7bexxxxxx-xxxx.ap-southeast-1.nas.aliyuncs.com. path: / # The path of the directory in the NAS file system. The directory must be an existing directory or the root directory. The root directory for a General-purpose NAS file system is "/". The root directory for an Extreme NAS file system is "/share".Create the deployment and mount the NAS volume.
kubectl create -f nas-test-nfs.yamlCheck the status of the pods in the deployment.
kubectl get pod | grep nas-testThe following output shows that two pods are created.
nas-test-****-***a 1/1 Running 0 40s nas-test-****-***b 1/1 Running 0 40sCheck the mount path.
kubectl exec nas-test-****-***a -- df -h /dataExpected output:
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on 350514*****-mw***.cn-shanghai.nas.aliyuncs.com:/ 10P 0 10P 0% /dataIf a similar output is returned, the file system is mounted.
Verify the shared storage and data persistence of NAS
The deployment created in the previous examples contains two pods that mount the same NAS file system. You can perform the following steps to verify the deployment:
Create a file in one pod and then view the file from the other pod to verify shared storage.
Recreate the deployment. Then, from a new pod, check whether the data in the file system still exists to verify persistent storage.
View the pod information.
kubectl get pod | grep nas-testThe following is a sample output:
nas-test-****-***a 1/1 Running 0 40s nas-test-****-***b 1/1 Running 0 40sVerify shared storage.
Create a file in one pod.
This example uses the pod named
nas-test-****-***a:kubectl exec nas-test-****-***a -- touch /data/test.txtView the file from the other pod.
This example uses the pod named
nas-test-****-***b:kubectl exec nas-test-****-***b -- ls /dataThe output shows that the new file
test.txtis shared.test.txt
Verify persistent storage.
Recreate the deployment.
kubectl rollout restart deploy nas-testView the pods and wait for the new pods to be created.
kubectl get pod | grep nas-testThe following is a sample output:
nas-test-****-***c 1/1 Running 0 67s nas-test-****-***d 1/1 Running 0 49sFrom a new pod, check whether the data in the file system still exists.
This example uses the pod named
nas-test-c***:kubectl exec nas-test-****-***c -- ls /dataThe output shows that the data in the NAS file system persists and can be retrieved from the mount directory of the new pod.
test.txt