This topic describes how to use Enterprise Edition transit routers to enable Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances that are deployed in virtual private clouds (VPCs) to access Object Storage Service (OSS) across regions over VPC connections.
You can run the sample code with one click.
Scenario

As shown in the figure above, a company has deployed VPC1 in the China (Shanghai) region with services running on ECS instances. The company has activated OSS in the China (Hangzhou) region and wants to enable ECS instances in VPC1 to access the OSS service in the China (Hangzhou) region.
To address this issue, the company can create a VPC (VPC2) in the China (Hangzhou) region, in which OSS is deployed, and connect VPC1 and VPC2 to the Enterprise Edition transit routers in the China (Shanghai) and China (Hangzhou) regions. The Enterprise Edition transit routers allow VPC1 and VPC2 to communicate with each other over inter-region connections. This way, the ECS instances in VPC1 can access OSS in VPC2.
To allow ECS instances in a VPC to access OSS in a different region by using Enterprise Edition transit routers, at least one VPC must be deployed in the region where OSS is activated. In this example, if a VPC exists in the China (Hangzhou) region, the company does not need to create VPC2 and can connect the existing VPC to the Enterprise Edition transit router. The ECS instances in the China (Shanghai) region can access OSS through any VPC in the China (Hangzhou) region.
Network planning
When you assign CIDR blocks, make sure that the CIDR blocks of the VPCs do not overlap.
Resource | VPC region | CIDR block and IP address |
VPC1 | China (Shanghai) | Primary CIDR block: 192.168.0.0/16
|
VPC2 | China (Hangzhou) | Primary CIDR block: 172.16.0.0/16
|
Procedure
This topic provides two configuration methods: console and Terraform. Choose the method that suits your needs.
Console
Preparations
Before you begin, ensure the following prerequisites are met:
OSS has been activated in the China (Hangzhou) region. For more information, see Get started with OSS.
VPC1 has been created in the China (Shanghai) region, with services deployed on the ECS instances. For more information, see Create an IPv4 VPC.
VPC2 has been established in the China (Hangzhou) region. For more information, see Create and manage a VPC.
Sufficient vSwitches are deployed in each VPC in the zones of the Enterprise Edition transit router. Each vSwitch has at least one idle IP address.
If the Enterprise Edition transit router is deployed in a region that supports only one zone, for example, China (Nanjing - Local Region), the VPC must have at least one vSwitch in the zone.
If the Enterprise Edition transit router is deployed in a region that supports multiple zones, for example, China (Shanghai), the VPC must have at least two vSwitches in the zones. The vSwitches must be in different zones.
For more information, see How a VPC connection works.
You have knowledge of the security group rules for VPC1 and VPC2. The security group rules allow the ECS instances in VPC1 to access OSS through VPC2. For more information, see Query security group rules and Add security group rules.
A Cloud Enterprise Network (CEN) instance has been created. For more information, see Create a CEN instance.
Enterprise Edition transit routers have been deployed in both the China (Shanghai) and China (Hangzhou) regions. For more information, see Create a transit router instance.
When you create Enterprise Edition transit routers, use the default settings.
Step 1: Create a VPC connection
Connect VPC1 to the Enterprise Edition transit router in the China (Shanghai) region, and VPC2 to the Enterprise Edition transit router in the China (Hangzhou) region.
Log on to the CEN console.
Navigate to the Instances page, find the target CEN instance, and click its ID.
In this example, the CEN instance mentioned in the Preparations section is used.
On the tab, find a transit router instance and click Create Connection in the Actions column.
On the Connect with Peer Network Instance page, set the following parameters, and click OK.
Configure the parameters to connect VPC1 to the Enterprise Edition transit router in the China (Shanghai) region and VPC2 to that in the China (Hangzhou) region by referring to the following table:
Parameter
Description
VPC1
VPC2
Network Type
Select the type of network instance that you want to connect.
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
Region
Select the region where the network instance is deployed.
China (Shanghai)
China (Hangzhou)
Transit Router
The ID of the transit router in the selected region is automatically displayed.
Resource Owner ID
Select the Alibaba Cloud account to which the instance belongs.
Current Account
Current Account
Billing Method
The default value is Pay-As-You-Go.
Attachment Name
Enter a name for the network connection.
VPC1 connection
VPC2 connection
Network Instance
Select the ID of the network instance.
Select VPC1
Select VPC2
VSwitch
Select a vSwitch in a zone of the transit router.
If each zone of the transit router has a vSwitch, you can select multiple zones and select a vSwitch in each of the zones to enable zone-disaster recovery.
Shanghai Zone F: Select vSwitch 1
Shanghai Zone G: Select vSwitch 2
Hangzhou Zone H: Select vSwitch 1
Hangzhou Zone I: Select vSwitch 2
Advanced Settings
Use the default settings for VPC1 and VPC2. All advanced features are enabled for the VPCs.
Step 2: Create an inter-region connection
The Enterprise Edition transit routers for VPC1 and VPC2 are in different regions, so by default, VPC1 and VPC2 cannot communicate. Create an inter-region connection between the China (Hangzhou) and China (Shanghai) regions to enable cross-region communication between VPC1 and VPC2.
Log on to the CEN console.
On the Instances page, click the ID of the CEN instance that you want to manage.
Navigate to the tab, select a transit router instance, and click Create Connection in the Actions column.
On the Connection with Peer Network Instance page, configure the following parameters, and then click OK.
The table below lists the parameters that are closely related to the example. Other parameters are kept at their default values. For more information, see Create an inter-region connection using Enterprise Edition transit routers.
Parameter
Description
Instance Type
Select Inter-region Connection.
Region
Select one of the regions to be connected.
In this example, China (Shanghai) is selected.
Peer Region
Select the peer region that you want to connect.
In this example, China (Hangzhou) is selected.
Bandwidth Allocation Mode
Select the method that is used to allocate bandwidth to the inter-region connection.
In this example, Pay-By-Data-Transfer is selected. The system charges you based on the actual traffic of the inter-region connection.
Bandwidth
Specify a bandwidth value for the inter-region connection. Unit: Mbps.
In the Pay-By-Data-Transfer bandwidth allocation mode, this parameter specifies the maximum bandwidth value for the inter-region connection.
Default Line Type
Select a line type for the inter-region connection.
In this example, the default value is used. For more information, see Line types.
Advanced Settings
In this example, the default settings are retained with all three advanced features enabled.
Step 3: Add routes that point to OSS in the VPC
With the inter-region connection established, VPC1 and VPC2 can now communicate using the Enterprise Edition transit router. However, ECS instances in VPC1 still cannot access OSS in VPC2. You must routes that point to OSS in the route table of VPC1 to direct traffic from VPC1 to the transit router.
Log on to the VPC console.
In the top navigation bar, select the region where VPC1 is deployed.
For this example, choose China (Shanghai).
Click Route Tables in the left-side navigation pane.
On the Route Tables page, find the route table for VPC1 and click its ID.
In this example, VPC1 has only one system route table. If your VPC has multiple route tables, select the one that is associated with the vSwitch in which the ECS instances are deployed.
Navigate to the Route Entry List tab, choose the Custom Route tab, and then click Add Route Entry.
In the Add Route Entry panel, configure the following parameters and click OK:
Add routes that point to all CIDR blocks of OSS in the China (Hangzhou) region to the route table of VPC1. The following table describes the parameters.
For more information about the CIDR blocks of the OSS service in the China (Hangzhou) region, see Internal OSS endpoints and VIP ranges.
Parameter
Description
Route 1
Route 2
Route 3
Route 4
Name
Enter a name for the custom route.
OSS CIDR block 1
OSS CIDR block 2
OSS CIDR block 3
OSS CIDR block 4
Destination CIDR Block
Enter the destination CIDR block.
100.118.28.0/24
100.114.102.0/24
100.98.170.0/24
100.118.31.0/24
Next Hop Type
Select a next hop type and select a next hop for the custom route.
Select Transit Router and then select VPC1 connection.
Select Transit Router and then select VPC1 connection.
Select Transit Router and then select VPC1 connection.
Select Transit Router and then select VPC1 connection.
Step 4: Add routes that point to OSS in the transit router
You need to add routes that point to OSS to the route table of the Enterprise Edition transit router in the China (Hangzhou) region. When requests from the ECS instances in VPC1 reach the Enterprise Edition transit router, the Enterprise Edition transit router forwards the requests to VPC2 based on the routing policy of OSS. Then, the ECS instances can access OSS through VPC2.
Log on to the CEN console.
Go to the CEN Instance page, find the target CEN instance, and click its ID.
On the tab, find the transit router instance in the China (Hangzhou) region, and click its ID.
On the details page of the transit router instance, click the Route Table tab. In the left-side navigation pane, select the target route table.
By default, VPC1 and VPC2 are associated with the default tables of the Enterprise Edition transit routers because they have advanced settings enabled. Therefore, the default route table (system route table) of the transit router is selected in this example.
On the Route Entry tab, click Add Route Entry.
In the Add Route Entry dialog box, enter the following parameters and click Confirm.
Add routes that point to the CIDR blocks of OSS in the China (Hangzhou) region to the route table of the transit router.
Parameter
Description
Route 1
Route 2
Route 3
Route 4
Name
Enter a name for the route.
OSS CIDR block 1
OSS CIDR block 2
OSS CIDR block 3
OSS CIDR block 4
Destination CIDR Block
Enter a destination CIDR block for the route.
100.118.28.0/24
100.114.102.0/24
100.98.170.0/24
100.118.31.0/24
Blackhole Route
Specify whether the route is a blackhole route.
Yes: specifies that the route is a blackhole route. All traffic destined for this route is dropped.
No: specifies that the route is not a blackhole route. In this case, you must specify a next hop for the route.
Select No
Select No
Select No
Select No
Next Hop
Select a next hop for the route.
Select VPC2 connection
Select VPC2 connection
Select VPC2 connection
Select VPC2 connection
Step 5: Test network connectivity
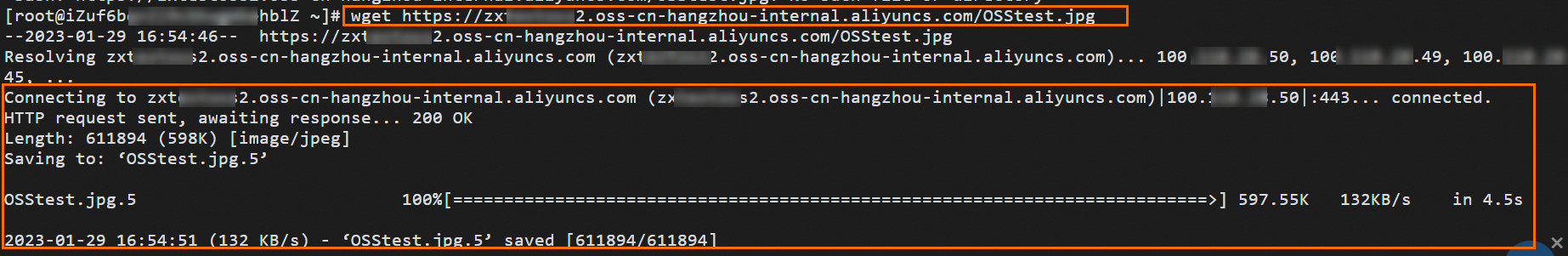
After you complete these steps, the ECS instances in VPC1 can access OSS across regions over VPC connections. In this example, ECS1 is used to download an image from OSS to check whether the ECS instances in VPC1 can access OSS.
Log on to ECS1 in VPC1. For more information, see ECS remote connection guide.
Use ECS1 to download an image named OSStest.jpg from OSS.
NoteEnsure the ECS instance has read/write permissions for the image file before testing. For more information, see Access control.
wget https://zxtXXXXX.oss-cn-hangzhou-internal.aliyuncs.com/OSStest.jpg # "zxtXXXXX.oss-cn-hangzhou-internal.aliyuncs.com" is the domain name of OSS. # "OSStest.jpg" is the name of the image file.For information about OSS domain names, see OSS domain name usage rules.
The following response indicates that ECS1 can access OSS over VPC connections.
Terraform
You can use Terraform to set up the environment in this topic. For details on installing and configuring Terraform, see Install Terraform.
The steps below show how to run Terraform v1.9.8 on a Linux host. Make sure you have completed the Authentication.
Note that specific resources in this example may incur costs. Release or unsubscribe from the resources when they are no longer needed.
Step 1: Create resources
Create a directory for the scenario and navigate to it.
mkdir tf-cen-oss && cd tf-cen-ossCreate a
main.tffile to define the required resources.touch main.tfOpen the
main.tffile, paste the following code into the file, and save the changes. This file includes all the necessary resources and configurations.variable "pname" { description = "The prefix name for resources" type = string default = "tf-cen-oss" } variable "region_id_hangzhou" { description = "The region id of hangzhou" type = string default = "cn-hangzhou" } variable "region_id_shanghai" { # description = "The region id of shanghai" type = string default = "cn-shanghai" } variable "az_hangzhou" { description = "List of availability zones to use" type = list(string) default = ["cn-hangzhou-j", "cn-hangzhou-k"] } variable "az_shanghai" { description = "List of availability zones to use" type = list(string) default = ["cn-shanghai-m", "cn-shanghai-n"] } variable "cidr_list" { description = "List of VPC CIDR block" type = list(string) default = ["10.0.0.0/8", "172.16.0.0/12", "192.168.0.0/16"] } # --- provider --- provider "alicloud" { # default region hangzhou region = var.region_id_hangzhou } provider "alicloud" { alias = "hangzhou" region = var.region_id_hangzhou } provider "alicloud" { alias = "shanghai" region = var.region_id_shanghai } # --- oss --- resource "random_uuid" "default" { } resource "alicloud_oss_bucket" "bucket1" { provider = alicloud.hangzhou bucket = substr("${var.pname}-${replace(random_uuid.default.result, "-", "")}", 0, 32) } resource "alicloud_oss_bucket_policy" "default" { provider = alicloud.hangzhou policy = jsonencode({ "Version" : "1", "Statement" : [{ "Action" : ["oss:GetObject"], "Effect" : "Allow", "Resource" : ["acs:oss:*:*:${alicloud_oss_bucket.bucket1.bucket}"] }] }) bucket = alicloud_oss_bucket.bucket1.bucket } resource "alicloud_oss_bucket_object" "obj1" { provider = alicloud.hangzhou bucket = alicloud_oss_bucket.bucket1.bucket key = "example.txt" # Name of the file in the bucket content = "this is example text content \n" # Content of the file acl = "public-read" } # --- vpc --- resource "alicloud_vpc" "vpc1" { provider = alicloud.shanghai vpc_name = "${var.pname}-1" cidr_block = "192.168.0.0/16" } resource "alicloud_vpc" "vpc2" { provider = alicloud.hangzhou vpc_name = "${var.pname}-2" cidr_block = "172.16.0.0/16" } resource "alicloud_vswitch" "vsw1-1" { provider = alicloud.shanghai vpc_id = alicloud_vpc.vpc1.id cidr_block = "192.168.0.0/24" zone_id = var.az_shanghai[0] vswitch_name = "${var.pname}-vsw1-1" } resource "alicloud_vswitch" "vsw1-2" { provider = alicloud.shanghai vpc_id = alicloud_vpc.vpc1.id cidr_block = "192.168.1.0/24" zone_id = var.az_shanghai[1] vswitch_name = "${var.pname}-vsw1-2" } resource "alicloud_vswitch" "vsw2-1" { provider = alicloud.hangzhou vpc_id = alicloud_vpc.vpc2.id cidr_block = "172.16.0.0/24" zone_id = var.az_hangzhou[0] vswitch_name = "${var.pname}-vsw2-1" } resource "alicloud_vswitch" "vsw2-2" { provider = alicloud.hangzhou vpc_id = alicloud_vpc.vpc2.id cidr_block = "172.16.1.0/24" zone_id = var.az_hangzhou[1] vswitch_name = "${var.pname}-vsw2-2" } # --- cen --- # cen resource "alicloud_cen_instance" "cen1" { cen_instance_name = "${var.pname}-cen1" } # tr resource "alicloud_cen_transit_router" "tr1" { provider = alicloud.shanghai transit_router_name = "${var.pname}-tr1" cen_id = alicloud_cen_instance.cen1.id } resource "alicloud_cen_transit_router" "tr2" { provider = alicloud.hangzhou transit_router_name = "${var.pname}-tr2" cen_id = alicloud_cen_instance.cen1.id } data "alicloud_cen_transit_router_route_tables" "tr1" { # get tr sys table transit_router_id = alicloud_cen_transit_router.tr1.transit_router_id transit_router_route_table_type = "System" } data "alicloud_cen_transit_router_route_tables" "tr2" { transit_router_id = alicloud_cen_transit_router.tr2.transit_router_id transit_router_route_table_type = "System" } # tr-peer resource "alicloud_cen_transit_router_peer_attachment" "peer" { provider = alicloud.shanghai cen_id = alicloud_cen_instance.cen1.id transit_router_id = alicloud_cen_transit_router.tr1.transit_router_id peer_transit_router_region_id = var.region_id_hangzhou peer_transit_router_id = alicloud_cen_transit_router.tr2.transit_router_id bandwidth_type = "DataTransfer" bandwidth = 1 auto_publish_route_enabled = true # default is false } resource "alicloud_cen_transit_router_route_table_association" "ass_peer1" { transit_router_route_table_id = data.alicloud_cen_transit_router_route_tables.tr1.tables[0].id transit_router_attachment_id = alicloud_cen_transit_router_peer_attachment.peer.transit_router_attachment_id } resource "alicloud_cen_transit_router_route_table_propagation" "propa_peer1" { transit_router_route_table_id = data.alicloud_cen_transit_router_route_tables.tr1.tables[0].id transit_router_attachment_id = alicloud_cen_transit_router_peer_attachment.peer.transit_router_attachment_id } resource "alicloud_cen_transit_router_route_table_association" "ass_peer2" { transit_router_route_table_id = data.alicloud_cen_transit_router_route_tables.tr2.tables[0].id transit_router_attachment_id = alicloud_cen_transit_router_peer_attachment.peer.transit_router_attachment_id } resource "alicloud_cen_transit_router_route_table_propagation" "propa_peer2" { transit_router_route_table_id = data.alicloud_cen_transit_router_route_tables.tr2.tables[0].id transit_router_attachment_id = alicloud_cen_transit_router_peer_attachment.peer.transit_router_attachment_id } # attach1 resource "alicloud_cen_transit_router_vpc_attachment" "attach1" { provider = alicloud.shanghai cen_id = alicloud_cen_instance.cen1.id transit_router_id = alicloud_cen_transit_router.tr1.transit_router_id vpc_id = alicloud_vpc.vpc1.id zone_mappings { zone_id = var.az_shanghai[0] vswitch_id = alicloud_vswitch.vsw1-1.id } zone_mappings { zone_id = var.az_shanghai[1] vswitch_id = alicloud_vswitch.vsw1-2.id } transit_router_vpc_attachment_name = "attach1" } resource "alicloud_cen_transit_router_route_table_association" "ass1" { transit_router_route_table_id = data.alicloud_cen_transit_router_route_tables.tr1.tables[0].id transit_router_attachment_id = alicloud_cen_transit_router_vpc_attachment.attach1.transit_router_attachment_id } resource "alicloud_cen_transit_router_route_table_propagation" "propa1" { transit_router_route_table_id = data.alicloud_cen_transit_router_route_tables.tr1.tables[0].id transit_router_attachment_id = alicloud_cen_transit_router_vpc_attachment.attach1.transit_router_attachment_id } resource "alicloud_route_entry" "vpc1_to_tr1" { provider = alicloud.shanghai count = 3 route_table_id = alicloud_vpc.vpc1.route_table_id destination_cidrblock = var.cidr_list[count.index] nexthop_type = "Attachment" nexthop_id = alicloud_cen_transit_router_vpc_attachment.attach1.transit_router_attachment_id } # attach2 resource "alicloud_cen_transit_router_vpc_attachment" "attach2" { provider = alicloud.hangzhou cen_id = alicloud_cen_instance.cen1.id transit_router_id = alicloud_cen_transit_router.tr2.transit_router_id vpc_id = alicloud_vpc.vpc2.id zone_mappings { zone_id = var.az_hangzhou[0] vswitch_id = alicloud_vswitch.vsw2-1.id } zone_mappings { zone_id = var.az_hangzhou[1] vswitch_id = alicloud_vswitch.vsw2-2.id } transit_router_vpc_attachment_name = "attach2" } resource "alicloud_cen_transit_router_route_table_association" "ass2" { transit_router_route_table_id = data.alicloud_cen_transit_router_route_tables.tr2.tables[0].id transit_router_attachment_id = alicloud_cen_transit_router_vpc_attachment.attach2.transit_router_attachment_id } resource "alicloud_cen_transit_router_route_table_propagation" "propa2" { transit_router_route_table_id = data.alicloud_cen_transit_router_route_tables.tr2.tables[0].id transit_router_attachment_id = alicloud_cen_transit_router_vpc_attachment.attach2.transit_router_attachment_id } resource "alicloud_route_entry" "vpc2_to_tr2" { provider = alicloud.hangzhou count = 3 route_table_id = alicloud_vpc.vpc2.route_table_id destination_cidrblock = var.cidr_list[count.index] nexthop_type = "Attachment" nexthop_id = alicloud_cen_transit_router_vpc_attachment.attach2.transit_router_attachment_id } # oss_cidr variable "oss_cidr" { description = "The OSS CIDR block" type = list(string) default = ["100.118.28.0/24", "100.114.102.0/24", "100.98.170.0/24", "100.118.31.0/24"] } # vpc entry resource "alicloud_route_entry" "entry" { provider = alicloud.shanghai count = 4 route_table_id = alicloud_vpc.vpc1.route_table_id destination_cidrblock = var.oss_cidr[count.index] nexthop_type = "Attachment" nexthop_id = alicloud_cen_transit_router_vpc_attachment.attach1.transit_router_attachment_id } # tr entry resource "alicloud_cen_transit_router_route_entry" "tr2_rt1_entry1" { count = 4 transit_router_route_table_id = data.alicloud_cen_transit_router_route_tables.tr2.tables[0].id transit_router_route_entry_destination_cidr_block = var.oss_cidr[count.index] transit_router_route_entry_next_hop_type = "Attachment" transit_router_route_entry_next_hop_id = alicloud_cen_transit_router_vpc_attachment.attach2.transit_router_attachment_id } # --- ecs --- resource "alicloud_instance" "main" { provider = alicloud.shanghai depends_on = [alicloud_cen_transit_router_route_entry.tr2_rt1_entry1] instance_name = "${var.pname}-ecs" instance_type = "ecs.e-c1m1.large" security_groups = [alicloud_security_group.default.id] vswitch_id = alicloud_vswitch.vsw1-1.id image_id = "aliyun_3_x64_20G_qboot_alibase_20230727.vhd" system_disk_category = "cloud_essd" private_ip = "192.168.0.1" instance_charge_type = "PostPaid" user_data = base64encode(<<-EOT #!/bin/bash curl https://${alicloud_oss_bucket.bucket1.bucket}.${alicloud_oss_bucket.bucket1.intranet_endpoint}/${alicloud_oss_bucket_object.obj1.key} > /root/curl.txt EOT ) } # sg resource "alicloud_security_group" "default" { provider = alicloud.shanghai name = var.pname vpc_id = alicloud_vpc.vpc1.id } resource "alicloud_security_group_rule" "allow_inbound_ssh" { provider = alicloud.shanghai type = "ingress" ip_protocol = "tcp" nic_type = "intranet" policy = "accept" port_range = "22/22" priority = 1 security_group_id = alicloud_security_group.default.id cidr_ip = "0.0.0.0/0" } resource "alicloud_security_group_rule" "allow_inbound_icmp" { provider = alicloud.shanghai type = "ingress" ip_protocol = "icmp" nic_type = "intranet" policy = "accept" port_range = "-1/-1" priority = 1 security_group_id = alicloud_security_group.default.id cidr_ip = "0.0.0.0/0" } # --- output --- output "ecs_login_address" { value = "https://ecs-workbench.aliyun.com/?from=EcsConsole&instanceType=ecs®ionId=${var.region_id_shanghai}&instanceId=${alicloud_instance.main.id}" } output "test_command" { value = "curl ${alicloud_oss_bucket.bucket1.bucket}.${alicloud_oss_bucket.bucket1.intranet_endpoint}/${alicloud_oss_bucket_object.obj1.key}" }Initialize the folder to complete Terraform setup.
terraform initCreate resources. Terraform will preview the resources to be created. After verification, enter
yesto initiate the creation process.terraform apply
Step 2: Test the connectivity
Log on to the ECS instance named
tf-cen-oss-ecs.The logon address for the ECS instance can be found in the Terraform Outputs. Copy this address to a browser and select Temporary SSH Key-based as the authentication method.

In the Outputs section, copy the curl command:

Run the curl command in the ECS instance.
curl tf-cen-oss-xxxxxx.oss-cn-hangzhou-internal.aliyuncs.com/example.txt
If the text content can be retrieved as shown in the figure, it indicates a successful access.
Step 3: Release resources
When verification is complete and you no longer need the resources, run the command below to release them and stop billing.
terraform destroy --auto-approveRoutes
In this topic, the default routing configuration is used to create the VPC and inter-region connections. When the default routing configuration is used, CEN automatically learns and advertises routes for VPC1 and VPC2 to communicate with each other. The following sections describe the default routing configuration:
VPC instance
If you use the default routing configuration (with all advanced features enabled) when you create a VPC connection, the system automatically applies the following routing configuration to the VPC:
Associate with Default Route Table of Transit Router
After this feature is enabled, the VPC connection is automatically associated with the default route table of the transit router. The transit router forwards the traffic of the VPC based on the default route table.
Propagate System Routes to Default Route Table of Transit Router
After this feature is enabled, the system routes of the VPC are advertised to the default route table of the transit router. This way, the VPC can communicate with other network instances that are connected to the transit router.
Automatically Create Route That Points to Transit Router and Adds to All Route Tables of Current VPC
After this feature is enabled, the system automatically adds the following routes to all route tables of the VPC: 10.0.0.0/8, 172.16.0.0/12, and 192.168.0.0/16. The routes point to the VPC connection.
Inter-region connection
If you use the default routing configuration (with all advanced features enabled) when you create an inter-region connection, the system automatically applies the following routing configuration to the inter-region connection:
Associate with Default Route Table of Transit Router
After this feature is enabled, the inter-region connection is automatically associated with the default route table of the transit router. The transit router uses the default route table to forward network traffic across regions.
Propagate System Routes to Default Route Table of Transit Router
After this feature is enabled, the inter-region connection is associated with the default route tables of the transit routers in the connected regions.
Automatically Advertise Routes to Peer Region
After this feature is enabled, the routes in the route table of the transit router in the current region are automatically advertised to the route table of the peer transit router for cross-region communication. The route tables of the transit routers refer to the route tables that are associated with the inter-region connection.
View routes
You can check the routes within the Alibaba Cloud Management Console:
For more information about routes of transit routers, see Manage custom routes of a transit router.
For more information about routes of VPCs, see Create and manage a route table.