This topic describes how to use the dynamic subset load balancing feature of Service Mesh (ASM) to route requests to correct runtime environments, thereby accelerating the inference process of Model Service Mesh.
Background information
Model Service Mesh provides a scalable, high-performance infrastructure for managing, deploying, and scheduling multiple model services.
When you run multiple different models in Model Service Mesh at the same time, a specific model is generally loaded to a specific model serving runtime. However, a Kubernetes service randomly sends an inference request to any model serving runtime. This inference request may be routed many times in Model Service Mesh before it can be sent to the correct model serving runtime.
Dynamic subset load balancing can identify the running models in each runtime workload in Model Service Mesh. ASM gateways identifies the model corresponding to an inference request and routes the request to the correct runtime workload. This way, the routing decision of Model Service Mesh is optimized to accelerate the response to the inference request. For more information about dynamic subset load balancing, see Dynamic subset load balancing.
Prerequisites
An ASM instance of V1.21.6.47 or later is created. For more information, see Create an ASM instance.
A Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) cluster is added to the ASM instance. For more information, see Add a cluster to an ASM instance.
Model Service Mesh is enabled and the sklearn-mnist model is deployed. For more information, see Use Model Service Mesh to roll out a multi-model inference service.
Step 1: Deploy the tf-mnist model in Model Service Mesh
The precise routing capability of dynamic subset load balancing is mainly used in multi-model scenarios. Therefore, an additional tf-mnist model is deployed in Model Service Mesh in this example. The tf-mnist model is an mnist model implemented by TensorFlow, and its runtime environment is provided by the Triton serving runtime.
The persistent volume claim (PVC) my-models-pvc created by performing the steps in Use Model Service Mesh to roll out a multi-model inference service is used to save the tf-mnist model. All the content in the mnist directory is the model content.
Store the tf-mnist model on a persistent volume.
Use kubectl to connect to the ACK cluster based on the information in the kubeconfig file. Then, run the following command to copy the mnist-svm.joblib model file to the /mnt/models folder of the pvc-access pod:
kubectl -n modelmesh-serving cp mnist pvc-access:/mnt/models/Run the following command to verify that the model exists on the persistent volume:
kubectl -n modelmesh-serving exec -it pvc-access -- ls -alr /mnt/models/Expected output:
-rw-r--r-- 1 502 staff 344817 Apr 23 08:17 mnist-svm.joblib drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Apr 23 08:23 mnist drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4096 Apr 23 08:17 .. drwxrwxrwx 3 root root 4096 Apr 23 08:23 .
Deploy an inference service.
Create a tf-mnist.yaml file with the following content:
apiVersion: serving.kserve.io/v1beta1 kind: InferenceService metadata: name: tf-mnist namespace: modelmesh-serving annotations: serving.kserve.io/deploymentMode: ModelMesh spec: predictor: model: modelFormat: name: tensorflow storage: parameters: type: pvc name: my-models-pvc path: mnistUse kubectl to connect to the ACK cluster based on the information in the kubeconfig file. Then, run the following command to deploy the tf-mnist inference service:
kubectl apply -f tf-mnist.yamlWait for a while (the waiting time depends on the image pulling speed). Then, run the following command to check whether the tf-mnist inference service is deployed:
kubectl get isvc -n modelmesh-servingExpected output:
NAME URL READY sklearn-mnist grpc://modelmesh-serving.modelmesh-serving:8033 True tf-mnist grpc://modelmesh-serving.modelmesh-serving:8033 TrueThe expected output shows that two models with different frameworks, sklearn-mnist and tf-mnist, have been deployed in Model Service Mesh.
(Optional) Step 2: Test the latency of processing inference requests in Model Service Mesh
Install the fortio stress testing tool. For more information, see the installation instructions for the fortio project.
Use the fortio stress testing tool to send an inference request to the tf-mnist model. For more information about how to obtain the IP address of an ASM ingress gateway, see Integrate KServe with ASM to implement inference services based on cloud-native AI models.
ASM_GW_IP="IP address of the ASM ingress gateway" fortio load -jitter=False -H 'model: tf-mnist' -c 1 -qps 100 -t 60s -payload '{"inputs": [{ "name": "inputs", "shape": [1, 784], "datatype": "FP32", "contents": { "fp32_contents": [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.01176471, 0.07058824, 0.07058824, 0.07058824, 0.49411765, 0.53333336, 0.6862745, 0.10196079, 0.6509804, 1.0, 0.96862745, 0.49803922, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.11764706, 0.14117648, 0.36862746, 0.6039216, 0.6666667, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.88235295, 0.6745098, 0.99215686, 0.9490196, 0.7647059, 0.2509804, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.19215687, 0.93333334, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.9843137, 0.3647059, 0.32156864, 0.32156864, 0.21960784, 0.15294118, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.07058824, 0.85882354, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.7764706, 0.7137255, 0.96862745, 0.94509804, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.3137255, 0.6117647, 0.41960785, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.8039216, 0.04313726, 0.0, 0.16862746, 0.6039216, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.05490196, 0.00392157, 0.6039216, 0.99215686, 0.3529412, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.54509807, 0.99215686, 0.74509805, 0.00784314, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.04313726, 0.74509805, 0.99215686, 0.27450982, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.13725491, 0.94509804, 0.88235295, 0.627451, 0.42352942, 0.00392157, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.31764707, 0.9411765, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.46666667, 0.09803922, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.1764706, 0.7294118, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.5882353, 0.10588235, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0627451, 0.3647059, 0.9882353, 0.99215686, 0.73333335, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.9764706, 0.99215686, 0.9764706, 0.2509804, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.18039216, 0.50980395, 0.7176471, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.8117647, 0.00784314, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.15294118, 0.5803922, 0.8980392, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.98039216, 0.7137255, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.09411765, 0.44705883, 0.8666667, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.7882353, 0.30588236, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.09019608, 0.25882354, 0.8352941, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.7764706, 0.31764707, 0.00784314, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.07058824, 0.67058825, 0.85882354, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.7647059, 0.3137255, 0.03529412, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.21568628, 0.6745098, 0.8862745, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.95686275, 0.52156866, 0.04313726, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.53333336, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.99215686, 0.83137256, 0.5294118, 0.5176471, 0.0627451, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] }}]}' -a ${ASM_GW_IP}:8008/v2/models/tf-mnist/inferExpected output:
View the visual stress testing results of fortio.
Run the following command to open the local fortio server:
fortio serverUse a browser to access localhost:8080. Click
saved resultsin the interface, and select the JSON file on fortio server to view the visual results of the stress test.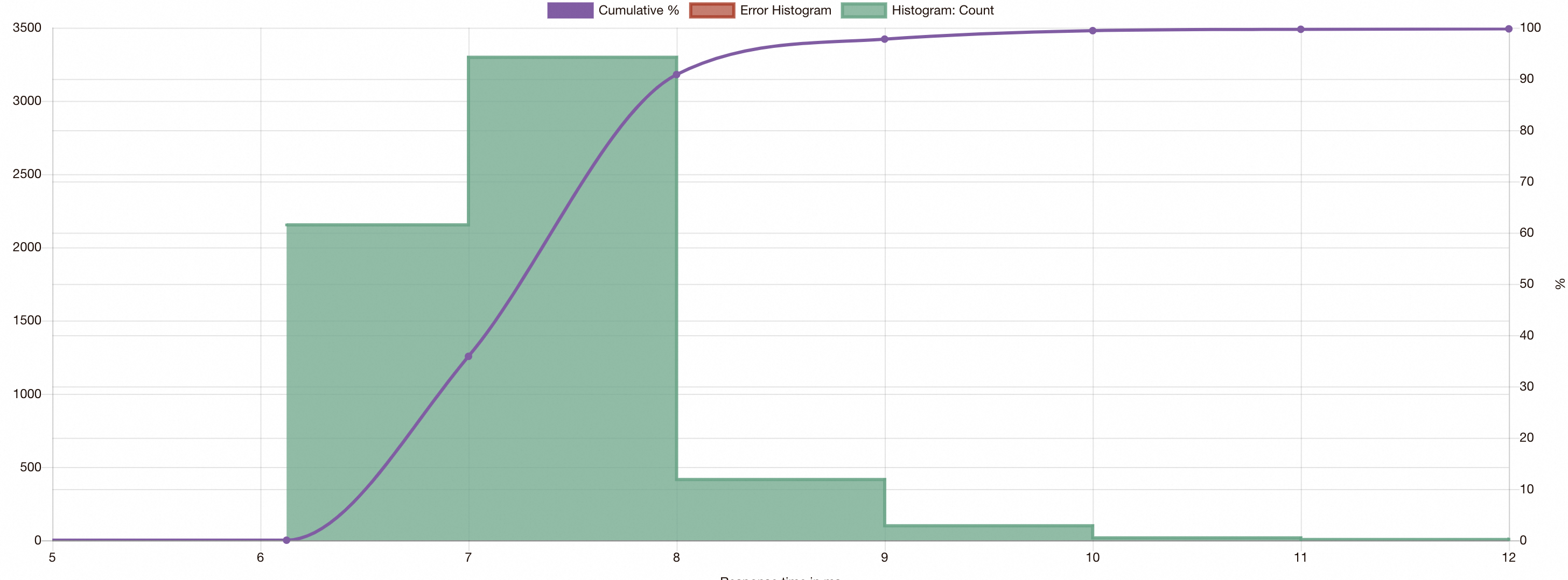
As shown in the preceding figure, the latency of some inference requests sent to Model Service Mesh increases. This is because the requests are rerouted in Model Service Mesh, and the response speed decreases.
Step 3: Enable dynamic subset load balancing for Model Service Mesh
Inference requests access all running models in Model Service Mesh through the modelmesh-serving service in the modelmesh-serving namespace. This section demonstrates how to configure dynamic subset load balancing for the modelmesh-serving service to precisely route inference requests to different model serving runtimes.
Use the following content to configure a dynamic subset for the modelmesh-serving service in Model Service Mesh. For more information, see Manage destination rules.
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1 kind: DestinationRule metadata: name: modelmesh-serving namespace: modelmesh-serving spec: host: modelmesh-serving trafficPolicy: loadBalancer: dynamicSubset: subsetSelectors: - fallbackPolicy: ANY_ENDPOINT keys: - modelmesh.asm.alibabacloud.comThe preceding destination rule dynamically groups model serving runtimes based on the
modelmesh.asm.alibabacloud.comlabel. Model Service Mesh dynamically updates the runtime labels according to the models loaded in the serving runtimes.Use the following content to change the content of the virtual service named
vs-modelmesh-serving-service. For more information, see Manage virtual services.apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1 kind: VirtualService metadata: name: vs-modelmesh-serving-service namespace: modelmesh-serving spec: gateways: - grpc-gateway hosts: - '*' http: - headerToDynamicSubsetKey: - header: model key: modelmesh.asm.alibabacloud.com match: - port: 8008 name: default route: - destination: host: modelmesh-serving port: number: 8033The
headerToDynamicSubsetKeyfield is added to the preceding virtual service based on the requirements of dynamic subset load balancing. The ASM gateway converts themodelrequest header in an inference request into a request metadata to match the dynamic subset of Model Service Mesh.
(Optional) Step 4: Test the latency of processing inference requests in Model Service Mesh after optimization
Use fortio to run the test again and view the visual results. For more information, see Step 2.
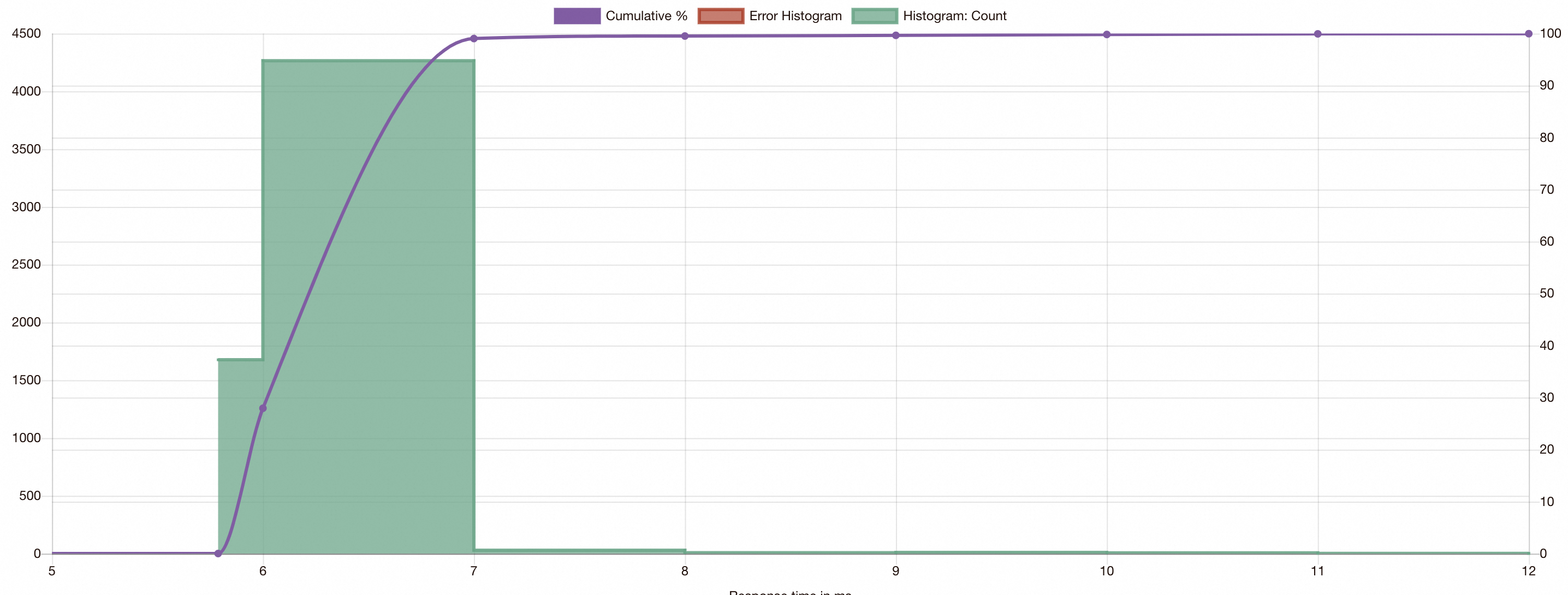
The expected results show that after dynamic subset load balancing of ASM is enabled for optimization, the access latency of all inference requests falls within a small range, and the latency of processing inference requests is greatly reduced.