Improper configurations of authorization policies may cause unexpected access to be denied or allowed. You can use Service Mesh (ASM) authorization policies in trial mode to verify the correctness and reliability of authorization policies without affecting production environments. This reduces the risk of issues arising in production environments and ensures the smooth deployment and operation of authorization policies.
Prerequisites
A cluster is added to an ASM instance, and the version of the ASM instance is 1.14 or later. For more information about how to update an ASM instance, see Update an ASM instance.
A sample namespace named foo is created and automatic sidecar proxy injection is enabled. For more information, see Manage global namespaces.
Background information
ASM allows you to configure authorization policies to implement access control for all workloads or only specific workloads in a namespace. Authorization policies control access traffic. If they are not configured properly, access requests may be allowed or denied unexpectedly. In this case, ASM administrators face great challenges. For example, some normal access requests are denied, whereas the access requests that should be denied are allowed. To solve this issue, ASM provides a trial mode for authorization policies. In trial mode, authorization policies are executed, but they do not allow or block traffic. Only execution logs are recorded. ASM administrators can check whether the execution results of authorization policies meet expectations based on these logs. If not, they can adjust authorization policies until the execution results meet expectations and then disable the trial mode to make the authorization policies take effect.
In this example, two test applications, sleep and HTTPBin, are deployed. The overall test process is as follows: Access the HTTPBin application by using a curl command in the pod where the sleep application resides, verify the connectivity, configure an authorization policy for the ASM instance to deny specific requests and enable the trial mode, and then initiate a request that meets the denial conditions of the authorization policy. In trial mode, the request is not denied and the sidecar proxy generates the execution logs of the authorization policy. After you confirm that the execution results of the authorization policy meet your expectations, disable the trial mode to make the authorization policy take effect.
Step 1: Deploy the sleep and HTTPbin applications and test their connectivity
Use the following content to create a sleep.yaml file:
Use kubectl to connect to the cluster and run the following command to deploy the sleep application in the foo namespace.
For more information about how to use kubectl to connect to the cluster, see Obtain the kubeconfig file of a cluster and use kubectl to connect to the cluster.
kubectl apply -f sleep.yaml -n fooUse the following content to create an httpbin.yaml file:
Run the following command to deploy the HTTPBin application in the foo namespace:
kubectl apply -f httpbin.yaml -n fooRun the following command to test the connectivity between the sleep application and the HTTPBin application:
for i in {1..20}; do kubectl exec "$(kubectl get pod -l app=sleep -n foo -o jsonpath={.items..metadata.name})" -c sleep -n foo -- curl http://httpbin.foo:8000/headers -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n"; doneExpected output:
200 200 200 ...The output shows that when you access the HTTPBin application 20 times by running a curl command in the pod where the sleep application resides, the status code returned is always 200. This indicates that the network connection is normal.
Step 2: Create an authorization policy and enable the trial mode
Log on to the ASM console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Mesh Management page, click the name of the ASM instance. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, click Create.
On the Create page, configure the following parameters and click Create.
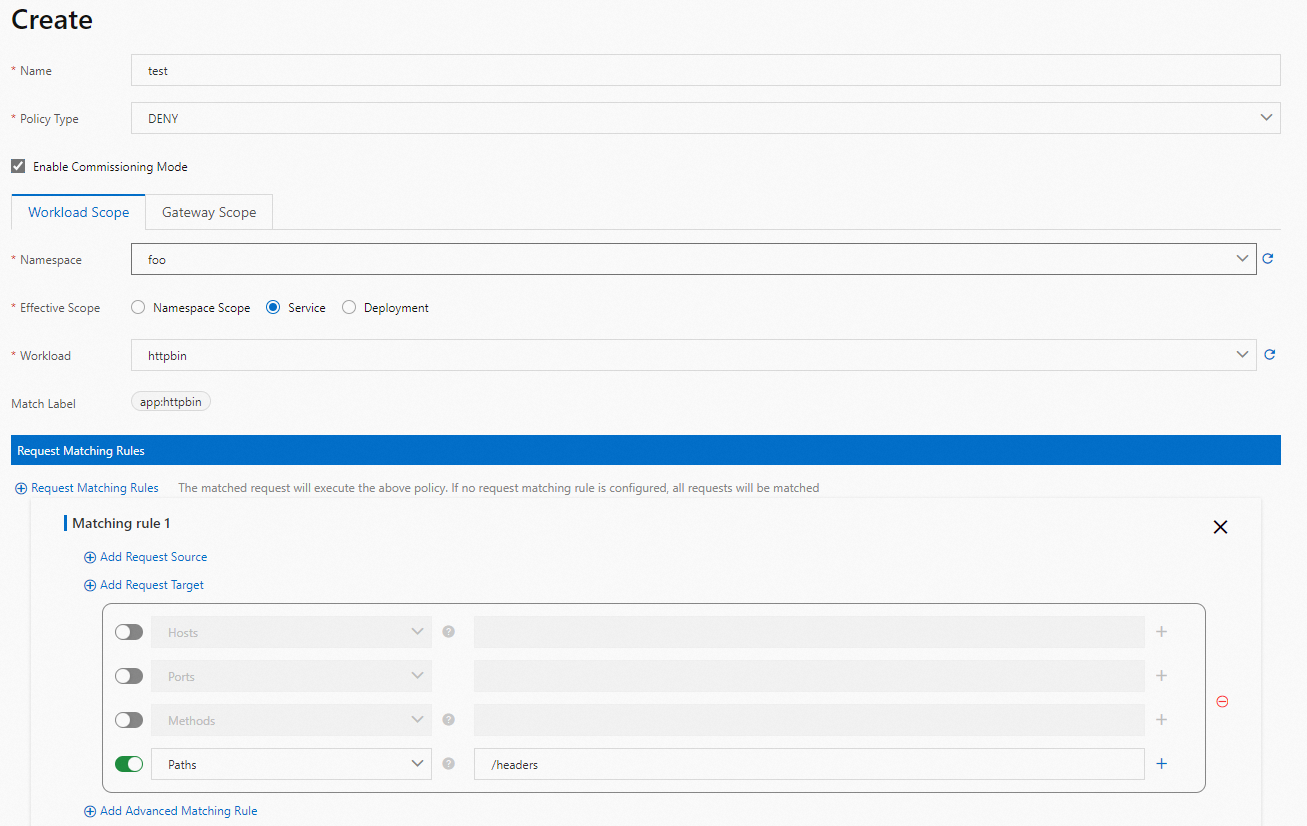
Step 3: Observe the execution results of the authorization policy
Run the following command again to access the HTTPBin application from the pod where the sleep application resides:
for i in {1..20}; do kubectl exec "$(kubectl get pod -l app=sleep -n foo -o jsonpath={.items..metadata.name})" -c sleep -n foo -- curl http://httpbin.foo:8000/headers -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n"; doneExpected output:
200 200 200 ...The output indicates that the access request is still allowed because the authorization policy is running in trial mode.
Run the following command to adjust the role-based access control (RBAC) log level of the sidecar proxy of the HTTPBin application to Debug:
kubectl exec "$(kubectl get pod -l app=httpbin -n foo -o jsonpath={.items..metadata.name})" -c istio-proxy -n foo -- curl -X POST 127.0.0.1:15000/logging?rbac=debugExpected output:
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 0active loggers: ... rbac: debug ... 100 1028 0 1028 0 0 1003k 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 1003kRun the following command to filter the trial run logs of the authorization policy from the sidecar proxy of the HTTPBin application:
kubectl logs "$(kubectl -n foo -l app=httpbin get pods -o jsonpath={.items..metadata.name})" -c istio-proxy -n foo | grep "shadow denied"The following output shows blocking logs:
2023-12-20T03:58:47.107915Z debug envoy rbac external/envoy/source/extensions/filters/http/rbac/rbac_filter.cc:130 shadow denied, matched policy ns[foo]-policy[test]-rule[0] thread=32 2023-12-20T03:58:48.800098Z debug envoy rbac external/envoy/source/extensions/filters/http/rbac/rbac_filter.cc:130 shadow denied, matched policy ns[foo]-policy[test]-rule[0] thread=33 2023-12-20T03:58:50.420179Z debug envoy rbac external/envoy/source/extensions/filters/http/rbac/rbac_filter.cc:130 shadow denied, matched policy ns[foo]-policy[test]-rule[0] thread=32
Step 4: Disable the trial mode
After you determine that the execution results of the authorization policy meet expectations based on logs, you can disable the trial mode to make the authorization policy take effect.
Log on to the ASM console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Mesh Management page, click the name of the ASM instance. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the AuthorizationPolicy page, find the authorization policy that you created in Step 2, turn off the switch in the Commissioning mode column, and then click OK in the Submit message to disable the trial mode.
Run the following command to initiate an access request again:
for i in {1..20}; do kubectl exec "$(kubectl get pod -l app=sleep -n foo -o jsonpath={.items..metadata.name})" -c sleep -n foo -- curl http://httpbin.foo:8000/headers -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n"; doneExpected output:
403 403 403 ...The output indicates that the access request is denied and 403 is returned because the authorization policy takes effect.
Run the following command to restore the log level of the sidecar proxy to Warning:
kubectl exec "$(kubectl get pod -l app=httpbin -n foo -o jsonpath={.items..metadata.name})" -c istio-proxy -n foo -- curl -X POST 127.0.0.1:15000/logging?rbac=warningExpected output:
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 0active loggers: ... rbac: warning ... 100 1028 0 1028 0 0 1003k 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 1003k
References
If you need to perform RAM and permission management on workloads in a cluster, you can use authorization policies to set access conditions for the workloads, such as limiting request paths, request methods, and client IP addresses. This ensures that only requests that meet specific requirements can access the workloads. For more information, see Configure authorization policies for access control on workloads.
If you need to perform fine-grained RAM for service-to-service HTTP or TCP requests, you can configure authorization policies for the requests. For more information, see Configure authorization policies for HTTP requests and Configure authorization policies for TCP requests.
For more information about how to control access traffic from services in an ASM instance to external services, see Use an authorization policy to control access traffic from services in an ASM instance to an external website and Use an authorization policy to control access traffic from services in an ASM instance to an external database.
You can customize the content of access logs of an ASM gateway to detect potential security risks in a timely manner. For more information, see Configure the features of generating and collecting the access logs of an ASM gateway.
You can enable the mesh audit feature to record or trace the daily operations of different users. You can also configure audit alerts for operations on ASM resources and send alert notifications to alert contacts in a timely manner when important resources change. For more information, see Use the KubeAPI operation audit feature in ASM and Configure audit alerts for operations on ASM resources.