This topic describes how to create a Tablestore sink connector to synchronize data from a topic on an ApsaraMQ for Kafka instance to a table on a Tablestore instance.
Prerequisites
ApsaraMQ for Kafka
The connector feature is enabled for the ApsaraMQ for Kafka instance. For more information, see Enable the connector feature.
A topic is created as the data source on the ApsaraMQ for Kafka instance. For more information, see Step 1: Create a topic.
Tablestore
Tablestore is activated and an instance is created. For more information, see Activate Tablestore and create an instance.
Usage notes
You can export data from a topic on an ApsaraMQ for Kafka instance only to a table on a Tablestore instance that resides in the same region as the ApsaraMQ for Kafka instance. For information about the limits on connectors, see Limits.
When you create a Tablestore sink connector, a service-linked role is required.
If the service-linked role is not created, ApsaraMQ for Kafka automatically creates the role for you. This way, you can export data from ApsaraMQ for Kafka to Tablestore as expected.
If the service-linked role is created, ApsaraMQ for Kafka does not create the role again.
For more information, see Service-linked roles.
Process
This section describes how to use a Tablestore sink connector to export data from a topic on an ApsaraMQ for Kafka instance to a table on a Tablestore instance.
(Optional) Create the topics and group that are required by a Tablestore sink connector.
If you do not want to manually create the topics and group, skip this step and set the Resource Creation Method parameter to Auto in the next step.
ImportantSpecific topics that are required by a Tablestore sink connector must use local storage. If the major version of your ApsaraMQ for Kafka instance is 0.10.2, you cannot manually create topics that use local storage. In major version 0.10.2, these topics must be automatically created.
Verify the result
Create the topics that are required by a Tablestore sink connector
You can manually create the following topics that are required by a Tablestore sink connector in the ApsaraMQ for Kafka console: task offset topic, task configuration topic, task status topic, dead-letter queue topic, and error data topic. The number of partitions and the storage engine required by each of the topics vary. For more information, see Parameters configured for the source service.
Log on to the ApsaraMQ for Kafka console.
In the Resource Distribution section of the Overview page, select the region where the ApsaraMQ for Kafka instance that you want to manage resides.
ImportantYou must create topics in the region where your Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance is deployed. A topic cannot be used across regions. For example, if the producers and consumers of messages run on an ECS instance that is deployed in the China (Beijing) region, the topic must also be created in the China (Beijing) region.
On the Instances page, click the name of the instance that you want to manage.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Topics.
On the Topics page, click Create Topic.
In the Create Topic panel, specify the properties of the topic and click OK.
Parameter
Description
Example
Name
The topic name.
demo
Description
The topic description.
demo test
Partitions
The number of partitions in the topic.
12
Storage Engine
NoteYou can specify the storage engine type only if you use a Professional Edition instance. If you use a Standard Edition instance, cloud storage is selected by default.
The type of the storage engine that is used to store messages in the topic.
ApsaraMQ for Kafka supports the following types of storage engines:
Cloud Storage: If you select this value, the system uses Alibaba Cloud disks for the topic and stores data in three replicas in distributed mode. This storage engine features low latency, high performance, long durability, and high reliability. If you set the Instance Edition parameter to Standard (High Write) when you created the instance, you can set this parameter only to Cloud Storage.
Local Storage: If you select this value, the system uses the in-sync replicas (ISR) algorithm of open source Apache Kafka and stores data in three replicas in distributed mode.
Cloud Storage
Message Type
The message type of the topic. Valid values:
Normal Message: By default, messages that have the same key are stored in the same partition in the order in which the messages are sent. If a broker in the cluster fails, the order of messages that are stored in the partitions may not be preserved. If you set the Storage Engine parameter to Cloud Storage, this parameter is automatically set to Normal Message.
Partitionally Ordered Message: By default, messages that have the same key are stored in the same partition in the order in which the messages are sent. If a broker in the cluster fails, messages are still stored in the partitions in the order in which the messages are sent. Messages in some partitions cannot be sent until the partitions are restored. If you set the Storage Engine parameter to Local Storage, this parameter is automatically set to Partitionally Ordered Message.
Normal Message
Log Cleanup Policy
The log cleanup policy that is used by the topic.
If you set the Storage Engine parameter to Local Storage, you must configure the Log Cleanup Policy parameter. You can set the Storage Engine parameter to Local Storage only if you use an ApsaraMQ for Kafka Professional Edition instance.
ApsaraMQ for Kafka provides the following log cleanup policies:
Delete: the default log cleanup policy. If sufficient storage space is available in the system, messages are retained based on the maximum retention period. After the storage usage exceeds 85%, the system deletes the earliest stored messages to ensure service availability.
Compact: the log compaction policy that is used in Apache Kafka. Log compaction ensures that the latest values are retained for messages that have the same key. This policy is suitable for scenarios such as restoring a failed system or reloading the cache after a system restarts. For example, when you use Kafka Connect or Confluent Schema Registry, you must store the information about the system status and configurations in a log-compacted topic.
ImportantYou can use log-compacted topics only in specific cloud-native components, such as Kafka Connect and Confluent Schema Registry. For more information, see aliware-kafka-demos.
Compact
Tag
The tags that you want to attach to the topic.
demo
After a topic is created, you can view the topic on the Topics page.
Create the group that is required by a Tablestore sink connector
You can manually create the group that is required by a Tablestore sink connector in the ApsaraMQ for Kafka console. The name of the group must be in the connect-Task name format. For more information, see Parameters configured for the source service.
Log on to the ApsaraMQ for Kafka console.
In the Resource Distribution section of the Overview page, select the region where the ApsaraMQ for Kafka instance that you want to manage resides.
On the Instances page, click the name of the instance that you want to manage.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Groups.
On the Groups page, click Create Group.
In the Create Group panel, enter a group name in the Group ID field and a group description in the Description field, attach tags to the group, and then click OK.
After a consumer group is created, you can view the consumer group on the Groups page.
Create and deploy a Tablestore sink connector
Perform the following steps to create and deploy a Tablestore sink connector that you can use to export data from ApsaraMQ for Kafka to Tablestore.
Log on to the ApsaraMQ for Kafka console.
In the Resource Distribution section of the Overview page, select the region where the ApsaraMQ for Kafka instance that you want to manage resides.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Connectors.
On the Connectors page, select the instance to which the connector belongs from the Select Instance drop-down list and click Create Connector.
On the Create Connector wizard, perform the following steps:
In the Configure Basic Information step, follow the on-screen instructions to configure the parameters and click Next. The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Description
Example
Name
The name of the connector. Specify a connector name based on the following rules:
The connector name must be 1 to 48 characters in length. It can contain digits, lowercase letters, and hyphens (-), but cannot start with a hyphen (-).
Each connector name must be unique within a ApsaraMQ for Kafka instance.
The data synchronization task of the connector must use a consumer group that is named in the connect-Task name format. If you have not created such a consumer group, Message Queue for Apache Kafka automatically creates one for you.
kafka-ts-sink
Instance
The information about the ApsaraMQ for Kafka instance. By default, the name and ID of the instance are displayed.
demo alikafka_post-cn-st21p8vj****
In the Configure Source Service step, select ApsaraMQ for Kafka as the source service, follow the on-screen instructions to configure other parameters, and then click Next. The following table describes the parameters.
NoteIf you have created the topics and group in advance, set the Resource Creation Method parameter to Manual and enter the names of the created resources. Otherwise, set the Resource Creation Method parameter to Auto.
Table 1. Parameters configured for the source service
Parameter
Description
Example
Data Source Topic
The name of the topic from which you want to synchronize data.
ts-test-input
Consumer Thread Concurrency
The number of concurrent consumer threads that are used to synchronize data from the source topic. Default value: 6. Valid values:
1
2
3
6
12
6
Consumer Offset
The offset from which you want to start message consumption. Valid values:
Earliest Offset: consumes messages from the earliest offset.
Latest Offset: consumes messages from the latest offset.
Earliest Offset
VPC ID
The ID of the virtual private cloud (VPC) in which the source instance is deployed. This parameter is displayed only after you click Configure Runtime Environment. By default, the VPC ID that you specified when you deployed the source ApsaraMQ for Kafka instance is displayed. You do not need to configure this parameter.
vpc-bp1xpdnd3l***
vSwitch ID
The ID of the vSwitch with which the source instance is associated. This parameter is displayed only after you click Configure Runtime Environment. The vSwitch must reside in the same VPC as the source ApsaraMQ for Kafka instance. By default, the vSwitch ID that you specified when you deployed the source ApsaraMQ for Kafka instance is displayed.
vsw-bp1d2jgg81***
Failure Handling Policy
Specifies whether to retain the subscription to the partition in which an error occurs after a message fails to be sent. This parameter is displayed only after you click Configure Runtime Environment. Valid values:
Continue Subscription: retains the subscription to the partition in which an error occurs and prints the logs.
Stop Subscription: stops the subscription to the partition in which an error occurs and prints the logs.
NoteFor information about how to view the connector logs, see Manage a connector.
For information about how to troubleshoot errors based on error codes, see Error codes.
Continue Subscription
Resource Creation Method
The method that is used to create the topics and group that are required by the Tablestore sink connector. This parameter is displayed only after you click Configure Runtime Environment. Valid values:
Auto
Manual
Auto
Connector Consumer Group
The group that is used by the data synchronization task of the connector. This parameter is displayed only after you click Configure Runtime Environment. The name of the group must be in the connect-Task name format.
connect-cluster-kafka-ots-sink
Task Offset Topic
The topic that is used to store consumer offsets. This parameter is displayed only after you click Configure Runtime Environment.
Topic: the topic name. We recommend that you start the topic name with connect-offset.
Partitions: the number of partitions in the topic. This parameter must be set to a value greater than 1.
Storage Engine: the storage engine that is used by the topic. This parameter must be set to Local Storage.
cleanup.policy: the log cleanup policy that is used by the topic. This parameter must be set to Compact.
connect-offset-kafka-ots-sink
Task Configuration Topic
The topic that is used to store task configurations. This parameter is displayed only after you click Configure Runtime Environment.
Topic: the topic name. We recommend that you start the topic name with connect-config.
Partitions: the number of partitions in the topic. This parameter must be set to 1.
Storage Engine: the storage engine that is used by the topic. This parameter must be set to Local Storage.
cleanup.policy: the log cleanup policy that is used by the topic. This parameter must be set to Compact.
connect-config-kafka-ots-sink
Task Status Topic
The topic that is used to store the task status. This parameter is displayed only after you click Configure Runtime Environment.
Topic: the topic name. We recommend that you start the topic name with connect-status.
Partitions: the number of partitions in the topic. We recommend that you set this parameter to 6.
Storage Engine: the storage engine that is used by the topic. This parameter must be set to Local Storage.
cleanup.policy: the log cleanup policy that is used by the topic. This parameter must be set to Compact.
connect-status-kafka-ots-sink
Dead-letter Queue Topic
The topic that is used to store the error data of the Kafka Connect framework. This parameter is displayed only after you click Configure Runtime Environment. To save topic resources, you can create a topic and use the topic as both the dead-letter queue topic and the error data topic.
Topic: the topic name. We recommend that you start the topic name with connect-error.
Partitions: the number of partitions in the topic. We recommend that you set this parameter to 6.
Storage Engine: the storage engine that is used by the topic. This parameter can be set to Local Storage or Cloud Storage.
connect-error-kafka-ots-sink
Error Data Topic
The topic that is used to store the error data of the connector. This parameter is displayed only after you click Configure Runtime Environment. To save topic resources, you can create a topic and use the topic as both the dead-letter queue topic and the error data topic.
Topic: the topic name. We recommend that you start the topic name with connect-error.
Partitions: the number of partitions in the topic. We recommend that you set this parameter to 6.
Storage Engine: the storage engine that is used by the topic. This parameter can be set to Local Storage or Cloud Storage.
connect-error-kafka-ots-sink
In the Configure Destination Service step, select Tablestore as the destination service, follow the on-screen instructions to configure other parameters, and then click Create. The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Description
Example
Instance Name
The name of the Tablestore instance.
k00eny67****
Automatically Create Destination Table
Specifies whether to automatically create a destination table in Tablestore. Valid values:
Yes: automatically creates a table in Tablestore to store synchronized data. You can specify a custom name for the table.
No: uses an existing table to store synchronized data.
Yes
Destination Table Name
The name of the table that stores the synchronized data. If you set the Automatically Create Destination Table parameter to No, make sure that the table name you enter is the same as that of an existing table in the Tablestore instance.
kafka_table
Tablestore
The type of the table that stores the synchronized data. Valid values:
Wide Column Model
TimeSeries Model
Wide Column Model
Message Key Format
The format of the message key. Valid values: String and JSON. Default value: JSON. This parameter is displayed only if you set the Tablestore parameter to Wide Column Model.
String: The message key is parsed as a string.
JSON: The message key must be in the JSON format.
String
Message Value Format
The format of the message value. Valid values: String and JSON. Default value: JSON. This parameter is displayed only if you set the Tablestore parameter to Wide Column Model.
String: The message value is parsed as a string.
JSON: The message value must be in the JSON format.
String
JSON Message Field Conversion
The field processing method of JSON messages. This parameter is displayed only if you set the Message Key Format or Message Value Format parameter to JSON. Valid values:
Write All as String: All fields are converted into strings in Tablestore.
Automatically Identify Field Types: String and boolean fields in message bodies in JSON format are converted into string and boolean fields in Tablestore, respectively. Data of the integer and float types in message bodies in JSON format is converted into data of the double type in Tablestore.
Write All as String
Primary Key Mode
The primary key mode. The primary keys for a data table can be extracted from different parts of ApsaraMQ for Kafka message records, including the coordinates (topic, partition, and offset), key, and value of the message records. This parameter is displayed only if you set the Tablestore parameter to Wide Column Model. Default value: kafka. Valid values:
kafka: uses <connect_topic>_<connect_partition> and <connect_offset> as the primary keys of the data table.
record_key: uses fields in the message key as the primary keys of the data table.
record_value: uses fields in the message value as the primary keys of the data table.
kafka
Primary Key Column Names
The names of the primary key columns and the corresponding data types. A column name specifies the field extracted from the message key or message value. You can set the data type of the field to String or Integer.
This parameter is displayed if you set the Message Key Format parameter to JSON and the Primary Key Mode parameter to record_key. This parameter is also displayed if you set the Message Value Format parameter to JSON and the Primary Key Mode parameter to record_value.
You can click Create to add a column name. You can configure a maximum of four column names.
None
Write Mode
The write mode. Valid values: put and update. Default value: put. This parameter is displayed only if you set the Tablestore parameter to Wide Column Model.
put: New data overwrites the original data in the table.
update: New data is added to the table and the original data is retained.
put
Delete Mode
Specifies whether to delete rows or attribute columns if ApsaraMQ for Kafka message records contain empty values. This parameter is displayed only if you set the Primary Key Mode parameter to record_key. Valid values:
none: does not allow you to delete rows or attribute columns. This is the default value.
row: allows you to delete rows.
column: allows you to delete attribute columns.
row_and_column: allows you to delete rows and attribute columns.
The deletion operation depends on the write mode.
If you set the Write Mode parameter to put, set the Delete Mode parameter to any value. Even if a message record contains empty values, the data of the message record is exported to the Tablestore table in the overwrite mode.
If you set the Write Mode parameter to update, set the Delete Mode parameter to none or row. If all fields in a message record are empty, the message record is processed as dirty data. If specific fields in a message record are empty, the empty values are automatically skipped and other non-empty values are added to the Tablestore table. If you set the Delete Mode parameter to column or row_and_column and a message record contains empty values, the system deletes the attribute columns or both rows and attribute columns corresponding to the empty values. Then, the remaining data is added to the Tablestore table.
None
Metric Name Field
Maps the field as the metric name field (_m_name) in the Tablestore TimeSeries model. The metric name field indicates a physical quantity or a monitoring metric that is measured by time series data, such as temperature or speed. Empty values are not supported. This parameter is displayed only if you set the Tablestore parameter to Wide Column Model.
measurement
Data Source Field
Maps the field as the data source field (_data_source) in the Tablestore TimeSeries model. The data source field indicates the source of specific time series data, such as a server name or a device ID. Empty values are supported. This parameter is displayed only if you set the Tablestore parameter to Wide Column Model.
source
Tag Field
Uses one or more fields as the tag fields (_tags) in the TimeSeries model in Tablestore. Each tag is a key-value pair of the string type. The key is the configured field name, and the value is the field value. A tag is a part of timeline metadata. A timeline consists of metric names, data sources, and tags. Empty values are supported. This parameter is displayed only if you set the Tablestore parameter to Wide Column Model.
tag1, tag2
Timestamp Field
Maps the field as the timestamp field (_time) in the Tablestore TimeSeries model. The timestamp field indicates the point in time corresponding to the time series data of the row, such as the time when the physical quantity is generated. When data is written to Tablestore, the timestamp field is converted into a value in microseconds. This parameter is displayed only if you set the Tablestore parameter to Wide Column Model.
time
Timestamp Unit
Configure this parameter based on the timestamp configuration. This parameter is displayed only if you set the Tablestore parameter to TimeSeries Model. Valid values:
SECONDS
MILLISECONDS
MICROSECONDS
NANOSECONDS
MILLISECONDS
Whether to Map All Non-primary Key Fields
Specifies whether to map all non-primary key fields as data fields. Primary key fields are fields that have been mapped as metric names, data sources, tags, or timestamps. This parameter is displayed only if you set the Tablestore parameter to TimeSeries Model. Valid values:
Yes: The fields are automatically mapped and the data types are automatically determined. Numbers are all converted into double data.
No: You must specify the fields to be mapped and the data types.
Yes
Configure Mapping for All Non-primary Key Fields
The field types corresponding to the names of non-primary key fields in the Tablestore TimeSeries model. The following data types are supported: double, integer, string, binary, and boolean. This parameter is displayed only if you set the Whether to Map All Non-primary Key Fields parameter to No.
String
After you create the connector, you can view the connector on the Connectors page.
Go to the Connectors page, find the connector that you created, and then click Deploy in the Actions column.
Click OK.
Send a test message
After you deploy a Tablestore sink connector, you can send a message to the ApsaraMQ for Kafka topic to test whether the message can be synchronized to the Tablestore table.
On the Connectors page, find the connector that you want to manage and click Test in the Actions column.
In the Send Message panel, configure the parameters to send a message for testing.
If you set the Sending Method parameter to Console, perform the following steps:
In the Message Key field, enter the message key. Example: demo.
In the Message Content field, enter the message content. Example: {"key": "test"}.
Configure the Send to Specified Partition parameter to specify whether to send the test message to a specific partition.
If you want to send the test message to a specific partition, click Yes and enter the partition ID in the Partition ID field. Example: 0. For information about how to query partition IDs, see View partition status.
If you do not want to send the test message to a specific partition, click No.
If you set the Sending Method parameter to Docker, run the Docker command in the Run the Docker container to produce a sample message section to send the test message.
If you set the Sending Method parameter to SDK, select an SDK for the required programming language or framework and an access method to send and subscribe to the test message.
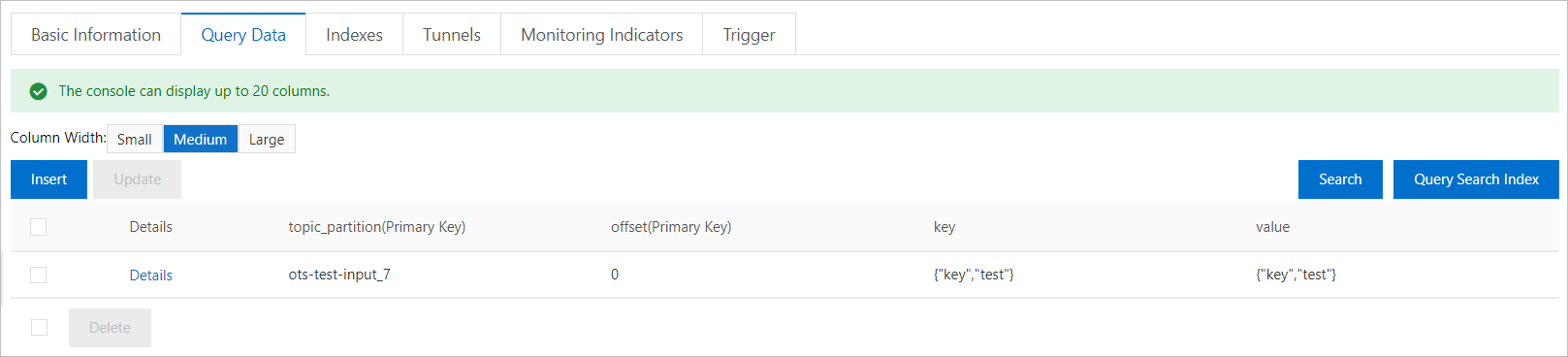
View data in the table
After you send a message to the ApsaraMQ for Kafka topic, you can check whether the message is received in the Tablestore console. To view data in the Tablestore table, perform the following steps:
Log on to the Tablestore console.
On the Overview page, click the name of the required instance or click Manage Instance in the Actions column of the required instance.
In the Tables section of the Instance Details tab, find the table that you want to manage.
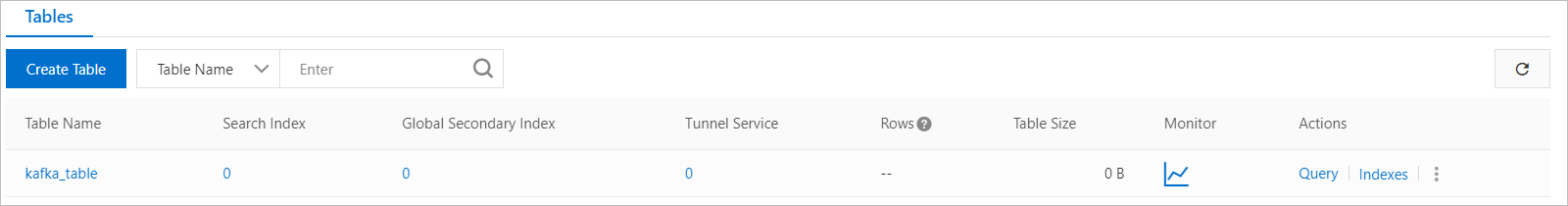
Click the name of the table. On the Query Data tab of the Manage Table page, view data in the table.