This topic introduces the basic concepts of Anti-DDoS Origin.
DDoS attack
Distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks include volumetric attacks and application-layer attacks.
Volumetric attacks target the network bandwidth of your service. In most cases, attackers manipulate multiple computers or attack simulators to send a large number of requests or data packets to the target server. This exhausts network bandwidths and causes your service to become unavailable.
Application-layer attacks target at servers. During application-layer attacks, the memory of the servers is exhausted by malicious requests or the CPUs of the servers are exhausted by kernels and application programs. As a result, servers cannot respond to normal requests.
Traffic scrubbing
If you want to perform traffic scrubbing, you can use an anti-DDoS device or service to analyze and filter traffic. The anti-DDoS device or service can distinguish service traffic from attack traffic and return only service traffic to your server. This reduces the pressure and risks on the server.
Blackhole filtering
If DDoS attacks exceed the mitigation capability that is provided for a service, blackhole filtering is triggered. Blackhole filtering is used to discard all inbound traffic that is destined for the service. This helps protect other services that are deployed in the same network as the attacked service. For more information, see Blackhole filtering policy of Alibaba Cloud.
Best-effort protection
Best-effort protection defends against DDoS attacks based on the network capacity of the cloud data center. The level of protection is dynamic and improves as Alibaba Cloud enhances its network infrastructure. However, during times of high demand on data center resources, the protection level may be reduced. For more information about the protection capabilities of various Anti-DDoS Origin instances, see Mitigation capabilities.
Mitigation sessions
The system records a traffic data point every 5 seconds (12 per minute). When attack traffic exceeds N Gbps, the system accumulates the attack duration, as shown by X+Y in the figure. One best-effort protection session is consumed for every 15 minutes of accumulated attack time, equivalent to 180 data points.
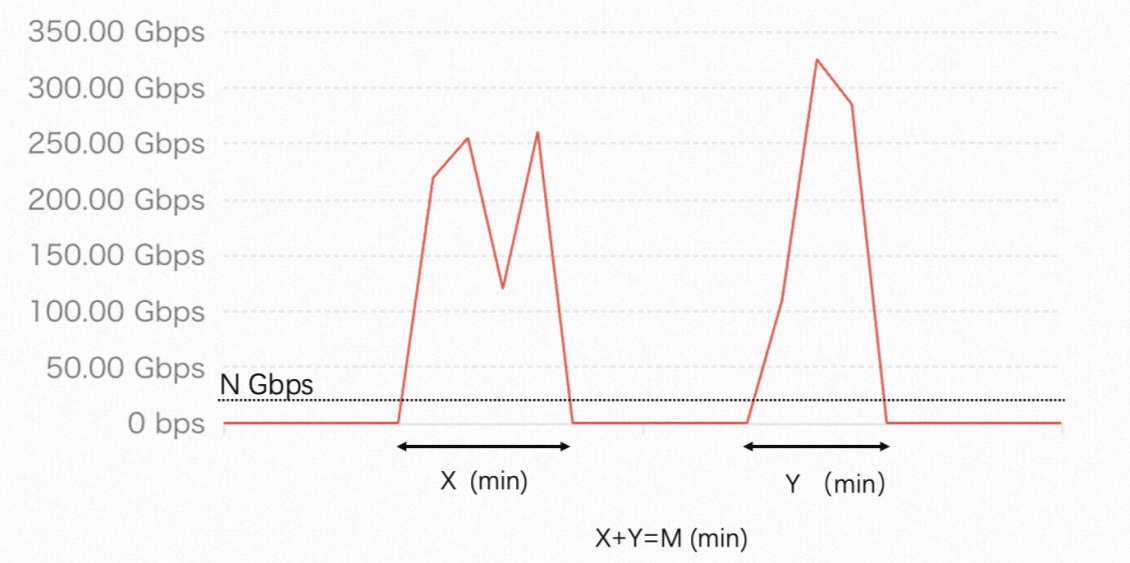
The red line represents the inbound traffic of a public IP-enabled asset.
For protected assets in the Chinese mainland, N is 20.
For protected assets outside the Chinese mainland, N is 10.
For example, a Chinese mainland asset under two attacks exceeding 20 Gbps, lasting 10 and 12 minutes (22 minutes total), consumes one session after the first 15 minutes; the remaining 7 minutes apply toward the second session. If additional attacks occur in the same month and the accumulated duration reaches 15 minutes, the second session is consumed.