To launch pods within seconds without worrying about node resources, you can use the ack-autoscaling-placeholder component. ack-autoscaling-placeholder provides a buffer for the auto scaling of pods in a Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) cluster. A placeholder pod with an extremely low priority (a negative value) is created to occupy a certain amount of computing resources for other pods with higher priorities. When the computing resources are insufficient, the placeholder pod is evicted to release the occupied computing resources for the workload. This way, pods can be launched within seconds. cluster-autoscaler is also used to scale nodes in the cluster. This topic describes how to use ack-autoscaling-placeholder to scale pods within seconds.
Prerequisites
Auto Scaling is enabled for your ACK cluster. For more information about how to enable auto scaling, see Enable node auto scaling.
Procedure
Step 1: Install ack-autoscaling-placeholder
Log on to the ACK console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the App Catalog tab, find and click ack-autoscaling-placeholder.
On the ack-autoscaling-placeholder page, click Deploy.
On the Basic Information wizard page, select a cluster from the Cluster drop-down list and a namespace from the Namespace drop-down list, and then click Next. Select a chart version from the Chart Version drop-down list, configure the parameters, and then click OK.
After ack-autoscaling-placeholder is deployed, go to the cluster details page. In the left-side navigation, choose . You can find that the application is in the Deployed state.
Step 2: Update and deploy
In the left-side navigation pane of the details page, choose .
On the Helm page, find ack-autoscaling-placeholder and click Update in the Actions column. In the Update Release panel, modify the YAML template based on your requirements, and then click OK.
nameOverride: "" fullnameOverride: "" ## priorityClassDefault: enabled: true name: default-priority-class value: -1 ## deployments: - name: ack-place-holder replicaCount: 1 containers: - name: placeholder image: registry-vpc.cn-shenzhen.aliyuncs.com/acs/pause:3.1 pullPolicy: IfNotPresent resources: requests: cpu: 4 # Occupy 4 vCPUs and 8 GiB of memory. memory: 8 imagePullSecrets: {} annotations: {} nodeSelector: # Specify rules that are used to select nodes. demo: "yes" tolerations: [] affinity: {} labels: {}Create a PriorityClass for the workload.
In this example, a PriorityClass that grants a high priority is created.
kubectl apply -f priorityClass.yamlapiVersion: scheduling.k8s.io/v1 kind: PriorityClass metadata: name: high-priority value: 1000000 # Specify the priority. globalDefault: false description: "This priority class should be used for XYZ service pods only."Deploy a workload.
kubectl apply -f workload.yamlapiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: placeholder-test labels: app: nginx spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: nginx template: metadata: labels: app: nginx spec: nodeSelector: # Specify rules that are used to select nodes. demo: "yes" priorityClassName: high-priority # Specify the name of the PriorityClass that you created in Step 8. containers: - name: nginx image: nginx:1.7.9 ports: - containerPort: 80 resources: requests: cpu: 3 # Specify the resource request of the workload. memory: 5A PriorityClass that grants a higher priority than other pods is created for the pod of the workload, as shown in the following figure. When node resources are insufficient, the placeholder pod named placeHolder is evicted and changes to the Pending state. After the placeholder pod changes to the Pending state, a scale-out activity is triggered in the cluster because Auto Scaling is enabled for the cluster. Consequently, a new pod is created within seconds for the workload.
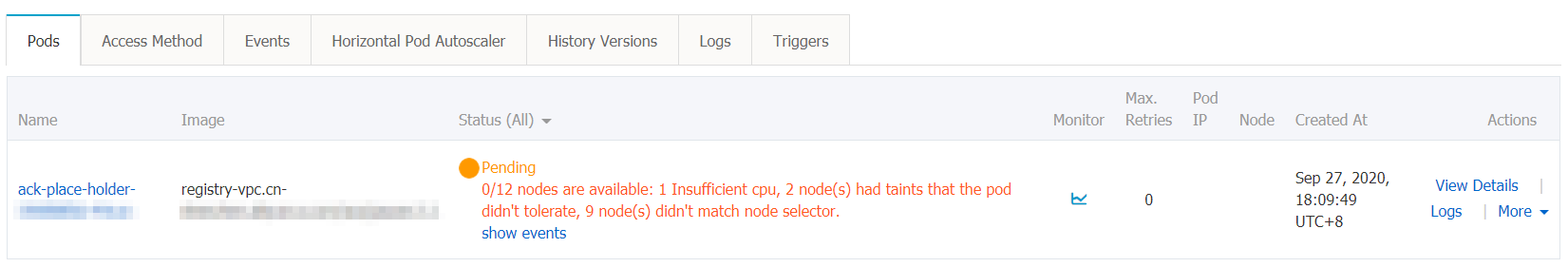
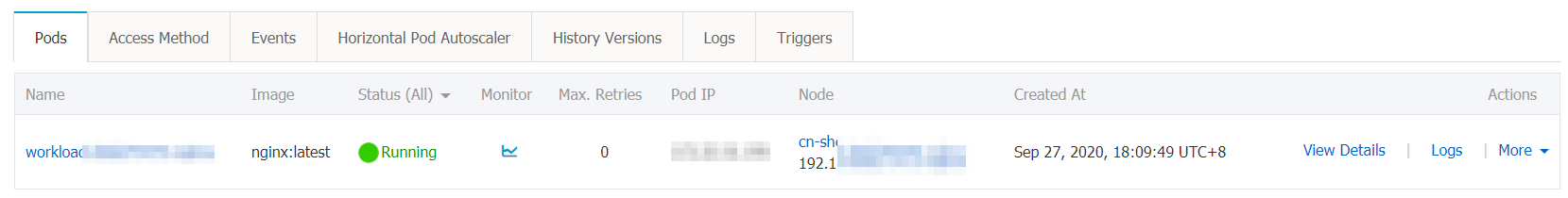
References
Multi-zone load balancing is a deployment solution commonly used in high availability scenarios. If an application that is deployed across zones does not have sufficient resources to handle heavy workloads, you may want ACK to create a specific number of nodes in each zone of the application. For more information, see Configure auto scaling for cross-zone deployment.