The ack-kubernetes-elastic-workload component monitors a Kubernetes workload, and replicates and generates workloads based on the predefined scheduling policies of elastic units. If the number of replicas in an elastic workload reaches the threshold, the numbers of replicas scheduled on the source workload and on the elastic unit are dynamically adjusted. This topic describes how to install and use ack-kubernetes-elastic-workload in a Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) cluster.
You can still use Elastic Workload. However, Elastic Workload has been in the inactive development state since June 2024. We recommend that you use UnitedDeployment instead.
For more information about the virtual node scheduling solutions, comparisons, and selection recommendations, see Schedule a pod to a virtual node.
Prerequisites
The ack-virtual-node component is deployed in the cluster, and the version is v2.0.0.102-045a06eb4-aliyun or later. For more information, see Schedule pods to elastic container instances through virtual nodes.
Limits
ack-kubernetes-elastic-workload does not support OpenKruise workloads. We recommend that you use the UnitdDeployment controller.
Deploy ack-kubernetes-elastic-workload
Log on to the ACK console.
In the left-side navigation pane of the ACK console, choose .
On the Marketplace page, click the App Catalog tab. Find and click ack-kubernetes-elastic-workload.
On the ack-kubernetes-elastic-workload page, click Deploy.
In the Deploy panel, select a cluster and namespace, and then click Next.
In the Parameters step, set the parameters and click OK.
After you deploy ack-kubernetes-elastic-workload, go to the details page of the cluster. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . You can find that ack-kubernetes-elastic-workload is deployed in the cluster.
Use an elastic workload
For example, capacity is planned for an application and that the application is expected to have up to four replicas to run on Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances. Two replicas are retained during off-peak hours. If the number of replicas is greater than four, the extra replicas are scheduled to the virtual node. This prevents other applications on the ECS instances from being affected.
You must resolve the following issues when you use Kubernetes to schedule pods and manage the lifecycle of pods: To implement the preceding scenario, you must perform the following operations:
Control how the scheduling policy changes when the number of replicas reaches a specific value.
How to prioritize specific pods when Kubernetes manages the lifecycle of pods.
This section describes how to use ack-kubernetes-elastic-workload to perform the preceding operations for an elastic workload.
Create a Deployment.
apiVersion: apps/v1 # for versions before 1.8.0 use apps/v1beta1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: nginx-deployment-basic labels: app: nginx spec: replicas: 2 selector: matchLabels: app: nginx template: metadata: labels: app: nginx spec: # nodeSelector: # env: test-team containers: - name: nginx image: anolis-registry.cn-zhangjiakou.cr.aliyuncs.com/openanolis/nginx:1.14.1-8.6 ports: - containerPort: 80 resources: limits: cpu: "500m"Define an elastic workload.
apiVersion: autoscaling.alibabacloud.com/v1beta1 kind: ElasticWorkload metadata: name: elasticworkload-sample spec: sourceTarget: name: nginx-deployment-basic kind: Deployment apiVersion: apps/v1 min: 2 # The minimum number of replicas. max: 4 # The maximum number of replicas. replicas: 6 elasticUnit: - name: virtual-kubelet labels: alibabacloud.com/eci: "true"ack-kubernetes-elastic-workload is used similarly to an HPA. ack-kubernetes-elastic-workload is deployed as an external add-on and does not affect your existing business.
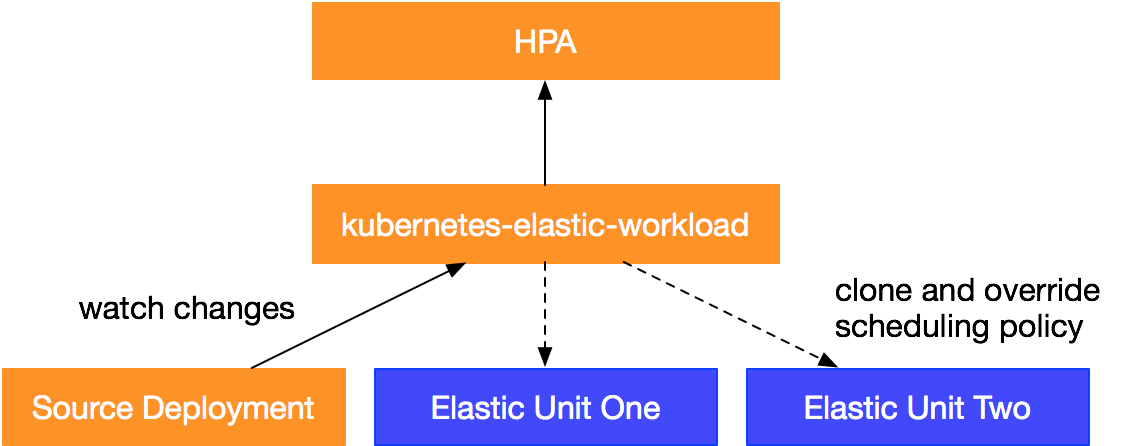
The ack-kubernetes-elastic-workload component monitors a Kubernetes workload, and replicates and generates workloads based on the predefined scheduling policies of elastic units. If the number of replicas in an elastic workload reaches the threshold, the numbers of replicas scheduled on the source workload and on the elastic unit are dynamically adjusted.
Typically, an elastic workload consists of the following two parts:
sourceTarget: defines the type of the source workload and the range for the number of replicas.
elasticUnit: an array that defines the scheduling policy for an elastic unit. To define scheduling policies for multiple elastic units, specify related parameters in the order shown in the template.
In this example:
As defined in sourceTarget, the number of replicas for the source workload ranges from two to four. In this case, if the elastic workload has two to four replicas, replicas are scheduled to the source workload. If the number of replicas is greater than four, the extra replicas are scheduled to the elastic unit (Virtual Node virtual-kubelet).
In elasticUnit, the elastic unit is defined as the virtual-kubelet virtual node, which corresponds to the
labels: alibabacloud.com/eci=truescheduling policy.
View the deployment result.
View the status of the elastic workload.
kubectl describe ew elasticworkload-sample # same as kubectl get elasticworkloadA command output similar to the following one is returned. The value of Desired Replicas in the Status section indicates the number of replicas scheduled to the elastic unit:
Name: elasticworkload-sample Namespace: default Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> API Version: autoscaling.alibabacloud.com/v1beta1 Kind: ElasticWorkload Metadata: Creation Timestamp: 2021-05-21T01:53:58Z Generation: 4 Managed Fields: API Version: autoscaling.alibabacloud.com/v1beta1 Fields Type: FieldsV1 fieldsV1: f:spec: .: f:elasticUnit: f:replicas: f:sourceTarget: .: f:apiVersion: f:kind: f:max: f:min: f:name: Manager: Apache-HttpClient Operation: Update Time: 2021-05-21T01:53:58Z API Version: autoscaling.alibabacloud.com/v1beta1 Fields Type: FieldsV1 fieldsV1: f:status: .: f:elasticUnitsStatus: f:replicas: f:selector: f:sourceTarget: .: f:apiVersion: f:desiredReplicas: f:kind: f:name: f:updateTimestamp: Manager: manager Operation: Update Time: 2021-05-21T01:56:45Z Resource Version: 8727 Self Link: /apis/autoscaling.alibabacloud.com/v1beta1/namespaces/default/elasticworkloads/elasticworkload-sample UID: c4a508aa-2702-4d17-ac25-e6a207c0761a Spec: Elastic Unit: Labels: alibabacloud.com/eci: true Name: virtual-kubelet Replicas: 6 Source Target: API Version: apps/v1 Kind: Deployment Max: 4 Min: 2 Name: nginx-deployment-basic Status: Elastic Units Status: Desired Replicas: 2 Name: nginx-deployment-basic-unit-virtual-kubelet Update Timestamp: 2021-05-21T01:56:45Z Replicas: 6 Selector: app=nginx Source Target: API Version: apps/v1 Desired Replicas: 4 Kind: Deployment Name: nginx-deployment-basic Update Timestamp: 2021-05-21T01:56:45Z Events: Type Reason Age From Message ---- ------ ---- ---- ------- Normal SourceUpdate 12m ElasticWorkload Source Target scale from 2 to 4 Normal UnitCreation 12m ElasticWorkload ElasticWorkloadUnit nginx-deployment-basic-unit-virtual-kubelet created Normal ElasticWorkloadUpdate 9m27s (x9 over 12m) ElasticWorkload ElasticWorkload update Normal UnitUpdate 9m27s (x8 over 12m) ElasticWorkload ElasticWorkloadUnit virtual-kubelet has been updatedView the status of pods.
kubectl get pod -o wideA command output similar to the following one is returned. The output indicates that the elastic workload has cloned Deployments and pods, and that pod replicas in these Deployments are dynamically scheduled based on the predefined scheduling policy.
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES nginx-deployment-basic-5bf87f5f59-22jnw 1/1 Running 0 16m 10.34.0.131 cn-beijing.172.16.0.1 <none> <none> nginx-deployment-basic-5bf87f5f59-gfp24 1/1 Running 0 13m 10.34.0.133 cn-beijing.172.16.0.1 <none> <none> nginx-deployment-basic-5bf87f5f59-pw2zx 1/1 Running 0 13m 10.34.0.134 cn-beijing.172.16.0.1 <none> <none> nginx-deployment-basic-5bf87f5f59-qvh7m 1/1 Running 0 16m 10.34.0.132 cn-beijing.172.16.0.1 <none> <none> nginx-deployment-basic-unit-virtual-kubelet-65fb6f4cd7-48ssb 1/1 Running 0 13m 172.16.22.157 virtual-kubelet-cn-beijing-e <none> <none> nginx-deployment-basic-unit-virtual-kubelet-65fb6f4cd7-gjqhm 1/1 Running 0 13m 172.16.22.158 virtual-kubelet-cn-beijing-e <none> <none>
In addition, HPAs can be used for elastic workloads. Elastic workloads can dynamically adjust the number of replicas scheduled to each elastic unit based on the status of HPAs. For example, if the number of replicas in a Deployment changes from six to four for an elastic workload, the elastic workload preferentially reduces the replicas on elastic units.
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2beta2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: elastic-workload-demo
namespace: default
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: autoscaling.alibabacloud.com/v1beta1
kind: ElasticWorkload
name: elasticworkload-sample
minReplicas: 2
maxReplicas: 10
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 50In conclusion, elastic workloads can generate Deployments by cloning and overriding scheduling policies. This allows you to manage scheduling policies. Elastic workloads can also adjust the number of replicas scheduled to source workloads and adjust the number of replicas scheduled to elastic units within the specified ranges. This allows you to prioritize specific pods for lifecycle management.