When you use ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ, message accumulation can lead to high system loads. To prevent service interruptions and enhance system reliability and stability, you can use Kubernetes Event-Driven Autoscaling (KEDA) to automate horizontal pod autoscaling based on the message accumulation metrics of ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ.
Function description
As a distributed messaging middleware service featuring high performance, high reliability, and high scalability, ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ is widely adopted by enterprise-class applications. You may encounter message accumulation when you use ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ, especially when the loads are high. This may further increase the system loads and even cause application breakdown.
To resolve this issue, you can use KEDA to enable horizontal pod autoscaling for your applications based on the custom message accumulation metrics of ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ. KEDA can automatically scale applications based on the message accumulation metrics with high efficiency. This ensures the reliability and stability of the system. If you use open-source Apache RocketMQ, you can enable horizontal pod autoscaling based on the metrics collected by the Java Management Extensions (JMX) Prometheus exporter. For more information, see Apache RocketMQ.
This topic details the configuration of RocketMQ message docking scaling objects using Managed Service for Prometheus as the data source.
Prerequisites
The ack-keda component is deployed. For more information, see Event-driven autoscaling.
An ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ 5.x instance has been created. For more information, see Create an instance.
Serverless ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ 5.x instances support rapid resource scaling based on business workloads. To reduce costs, resources are allocated and computing fees are billed according to actual usage. For more information, see Overview of Serverless ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ 5.x instances.
Aliyun RocketMQ (5.0) Service is integrated in the ARMS console.
The Go runtime environment is configured.
Step 1: Deploy an application
In this example, an NGINX application named sample-app is created.
Log on to the ACK console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want to manage and click its name. In the left-side pane, choose .
On the Deployments page, click Create from YAML. On the Create page, set Sample Template to Custom, and use the following YAML template to create an NGINX application named sample-app:
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: sample-app namespace: default labels: app: sample-app spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: sample-app template: metadata: labels: app: sample-app spec: containers: - name: sample-app # Replace with the actual RocketMQ consumer image. image: alibaba-cloud-linux-3-registry.cn-hangzhou.cr.aliyuncs.com/alinux3/nginx_optimized:20240221-1.20.1-2.3.0 resources: limits: cpu: "500m"
Step 2: Configure scaling policies through ScaledObject
Configure KEDA scaling policies using the ScaledObject YAML file, which includes scaling objects, maximum and minimum replicas, and scaling thresholds such as message accumulation thresholds. Before configuring the ScaledObject, obtain the Prometheus address and other relevant information for the ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ instance metrics.
1. Obtain instance information from the ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ console
Log on to the ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Instances.
In the top navigation bar, select a region, such as China (Hangzhou). On the Instances page, click the name of the instance that you want to manage.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Topics, and record the Name and Instance ID in the upper right corner, such as keda and mq-cn-uax33****, respectively.
2. Obtain the Prometheus data source for the ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ instance in the Prometheus console
Log on to the ARMS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
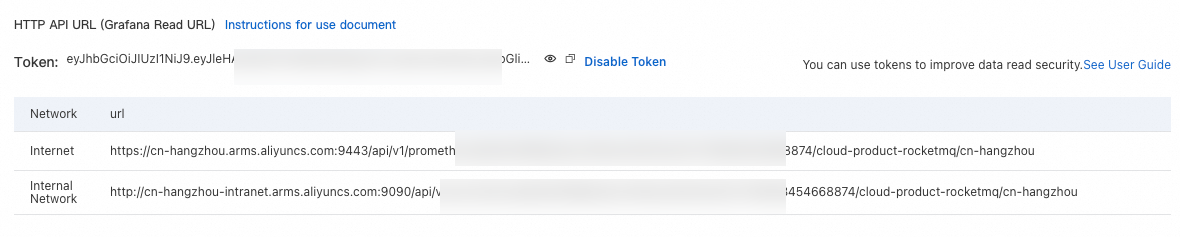
Find the instance named Cloud Services-{{RegionId}} and click its name. In the left-side pane, click Settings, and copy the endpoint in the HTTP API URL (Grafana Read URL) section.

3. Create the ScaledObject YAML file
Use the following YAML template to create a file named ScaledObject.yaml for scaling policy configurations:
apiVersion: keda.sh/v1alpha1 kind: ScaledObject metadata: name: prometheus-scaledobject namespace: default spec: scaleTargetRef: name: sample-app maxReplicaCount: 10 minReplicaCount: 2 triggers: - type: prometheus metadata: serverAddress: http://cn-beijing.arms.aliyuncs.com:9090/api/v1/prometheus/8cba801fff65546a3012e9a684****/****538168824185/cloud-product-rocketmq/cn-beijing metricName: rocketmq_consumer_inflight_messages query: sum({__name__=~"rocketmq_consumer_ready_messages|rocketmq_consumer_inflight_messages",instance_id="rmq-cn-uax3xxxxxx",topic=~"keda"}) by (consumer_group) threshold: '30'The following table describes the parameters:
Parameter
Description
scaleTargetRef.nameThe object that you want to scale. In this example, the value is set to sample-app, which is the name of the application that you created in Step 1: Deploy an application.
maxReplicaCountThe maximum number of replicas to maintain during scale-out operations.
minReplicaCountThe minimum number of replicas to maintain during scale-in operations.
serverAddressThe endpoint of the Prometheus instance that stores the metrics of the ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ instance. In this example, the value is set to the endpoint that you copied from HTTP API Address (Grafana Read Address) in the preceding step.
metricNameThe Prometheus Query Language (PromQL) query data.
queryAggregates the PromQL query data specified in the metricName parameter. In this example, the statistics of the number of accumulated messages are aggregated.
thresholdThe scaling threshold. In this example, the scaling threshold is 30, which indicates that the application is scaled out if the number of accumulated messages exceeds 30.
Run the following commands to deploy the ScaledObject.yaml file, and verify the created resources:
# Apply the scaling configuration. kubectl apply -f ScaledObject.yaml # The following output indicates successful creation. scaledobject.keda.sh/prometheus-scaledobject created # Retrieve the status of the scaling configuration. kubectl get ScaledObject # Output showing the ScaledObject details. NAME SCALETARGETKIND SCALETARGETNAME MIN MAX TRIGGERS AUTHENTICATION READY ACTIVE FALLBACK AGE prometheus-scaledobject apps/v1.Deployment sample-app 2 10 prometheus True False False 105s # Check whether a Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) is created to scale the application. kubectl get hpa # Output showing the HPA status. NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE keda-hpa-prometheus-scaledobject Deployment/sample-app 0/30 (avg) 2 10 2 28m(Optional) To improve data security for read operations, use the Prometheus token for authentication.
Step 3: Produce and consume data
This example uses the rocketmq-keda-sample project to produce and consume data. In the project code, specify the endpoint, username, and password of the ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ instance obtained in Step 2.
Step 4: Use produced and consumed data to trigger application scaling
Log on to the ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Instances.
In the top navigation bar, select a region, such as China (Hangzhou). On the Instances page, click the name of the instance that you want to manage, and record the Endpoint and Network Information.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Access Control, then click the Intelligent Authentication tab, and record the username and password.
Run a producer program to produce data, then run the following command to query information about the HPA:
kubectl get hpaExpected output:
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE keda-hpa-prometheus-scaledobject Deployment/sample-app 32700m/30 (avg) 2 10 10 47mThe output indicates that the number of replicated pods for the sample-app application is scaled to the maximum value specified in KEDA.
Stop the producer program and run a consumer program. Then, run the following command to check the HPA scaling status:
kubectl get hpa -wExpected output:
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE keda-hpa-prometheus-scaledobject Deployment/sample-app 222500m/30 (avg) 2 10 10 50m keda-hpa-prometheus-scaledobject Deployment/sample-app 232400m/30 (avg) 2 10 10 51m keda-hpa-prometheus-scaledobject Deployment/sample-app 0/30 (avg) 2 10 10 52m keda-hpa-prometheus-scaledobject Deployment/sample-app 0/30 (avg) 2 10 2 57mThe output indicates that the number of replicated pods for the sample-app application scales down to the minimum value specified in KEDA a short time after data consumption has ended.
Reference
You can use KEDA with ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ metrics to automate horizontal pod autoscaling, and to monitor queue length and messaging rate. For more information, see Horizontal pod autoscaling based on the metrics of ApsaraMQ for RabbitMQ.