If you want to temporarily modify container parameters for a running pod in a cluster that runs Kubernetes 1.27 or earlier, you must modify the PodSpec parameter and submit the change. Then, the pod is deleted and recreated. The feature provided by Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) allows you to use cgroup configuration files to modify the resource parameters of pods. This allows you to temporarily adjust the CPU parameters, memory parameters, and disk IOPS limits without the need to restart the pod.
This feature is suitable for scenarios in which temporary adjustment is required. For example, the memory usage of a pod increases. In this case, you need to increase the memory limit of the pod to avoid triggering the out of memory (OOM) killer. To perform common O&M operations, we recommend that you use the relevant features provided by ACK. For more information, see Enable CPU Burst, Enable topology-aware CPU scheduling, and Resource profiling.
Prerequisites
A kubectl client is connected to the ACK cluster. For more information, see Obtain the kubeconfig file of a cluster and use kubectl to connect to the cluster.
The ack-koordinator component whose version is 0.5.0 or later is installed. For more information, see ack-koordinator (FKA ack-slo-manager).
Billing
No fee is charged when you install or use the ack-koordinator component. However, fees may be charged in the following scenarios:
ack-koordinator is a non-managed component that occupies worker node resources after it is installed. You can specify the amount of resources requested by each module when you install the component.
By default, ack-koordinator exposes the monitoring metrics of features such as resource profiling and fine-grained scheduling as Prometheus metrics. If you enable Prometheus metrics for ack-koordinator and use Managed Service for Prometheus, these metrics are considered custom metrics and fees are charged for these metrics. The fee depends on factors such as the size of your cluster and the number of applications. Before you enable Prometheus metrics, we recommend that you read the Billing topic of Managed Service for Prometheus to learn about the free quota and billing rules of custom metrics. For more information about how to monitor and manage resource usage, see Query the amount of observable data and bills.
Modify the memory limit
When the memory usage of a pod increases, you can dynamically modify the memory limit of the pod by using cgroup configuration files to avoid triggering the OOM killer. In this example, a container with an original memory limit of 1 GB is created to verify that the memory limit of the container can be modified by using cgroup configuration files without the need to restart the pod.
If you use this feature in clusters that run Kubernetes 1.22 or later, make sure that the version of the ack-koordinator component is v1.5.0-ack1.14 or later. For other component versions, only clusters that run Kubernetes 1.22 or earlier are supported.
If you want to modify the CPU limit to meet common requirements, we recommend that you use the CPU Burst feature. This feature can automatically modify the CPU limit of the pod. For more information, see Enable CPU Burst. If you want to temporarily modify the CPU limit of the pod, perform the steps in Upgrade from resource-controller to ack-koordinator.
Create a pod-demo.yaml file with the following YAML template:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: pod-demo spec: containers: - name: pod-demo image: registry-cn-beijing.ack.aliyuncs.com/acs/stress:v1.0.4 resources: requests: cpu: 1 memory: "50Mi" limits: cpu: 1 memory: "1Gi" # Set the container memory limit to 1 GB. command: ["stress"] args: ["--vm", "1", "--vm-bytes", "256M", "-c", "2", "--vm-hang", "1"]Run the following command to deploy the pod-demo application in the cluster:
kubectl apply -f pod-demo.yamlRun the following command to query the original memory limit of the container:
# The actual path consists of the UID of the pod and the ID of the container. cat /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/kubepods.slice/kubepods-burstable.slice/kubepods-burstable-podaf44b779_41d8_43d5_a0d8_8a7a0b17****.slice/memory.limit_in_bytesExpected output:
# In this example, 1073741824 is returned, which is the result of 1 × 1024 × 1024 × 1024. This indicates that the original memory limit of the container is 1 GB. 1073741824The output shows that the original memory limit of the container is 1 GB, which is the same as the value of the
spec.containers.resources.limits.memoryparameter in the YAML file that you created in Step 1.Use the following YAML template to specify the memory limit of a container and create a cgroups-sample.yaml file:
apiVersion: resources.alibabacloud.com/v1alpha1 kind: Cgroups metadata: name: cgroups-sample spec: pod: name: pod-demo namespace: default containers: - name: pod-demo memory: 5Gi # Change the memory limit of the pod to 5 GB.Run the following command to deploy the cgroups-sample.yaml file in the cluster:
kubectl apply -f cgroups-sample.yamlRun the following command to query the new memory limit of the container after you submit the change:
# The specific path can be obtained based on the UID of the pod. cat /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/kubepods.slice/kubepods-burstable.slice/kubepods-burstable-podaf44b779_41d8_43d5_a0d8_8a7a0b17****.slice/memory.limit_in_bytesExpected output:
# In this example, 5368709120 is returned, which is the result of 5 × 1024 × 1024 × 1024. This indicates that the new memory limit of the container is 5 GB. 5368709120The output shows that the memory limit of the container is 5 GB, which is the same as the value of the
spec.pod.containers.memoryparameter in the YAML file that you created in Step 4. The modification is successful.Run the following command to query the status of the pod:
kubectl describe pod pod-demoExpected output:
Events: Type Reason Age From Message ---- ------ ---- ---- ------- Normal Scheduled 36m default-scheduler Successfully assigned default/pod-demo to cn-hangzhou.192.168.0.50 Normal AllocIPSucceed 36m terway-daemon Alloc IP 192.XX.XX.51/24 took 4.490542543s Normal Pulling 36m kubelet Pulling image "registry-cn-beijing.ack.aliyuncs.com/acs/stress:v1.0.4" Normal Pulled 36m kubelet Successfully pulled image "registry-cn-beijing.ack.aliyuncs.com/acs/stress:v1.0.4" in 2.204s (2.204s including waiting). Image size: 7755078 bytes. Normal Created 36m kubelet Created container pod-demo Normal Started 36m kubelet Started container pod-demoThe output shows that the pod runs as normal and no restart events are generated.
Change the vCores that are bound to a pod
If your application requires high CPU performance and you want to achieve better resource isolation, you can modify the vCores that are bound to the pod and specify the serial numbers of vCores that can be used by the pod.
In this example, a pod without bound vCores is created to verify that the bound vCores of the pod can be modified by using cgroup configuration files without the need to restart the pod.
In common cases, we recommend that you use topology-aware CPU scheduling to manage CPU resources for CPU-sensitive workloads. For more information, see Enable topology-aware CPU scheduling.
Create a pod-cpuset-demo.yaml file with the following YAML template:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: pod-cpuset-demo spec: containers: - name: pod-cpuset-demo image: registry-cn-beijing.ack.aliyuncs.com/acs/stress:v1.0.4 resources: requests: memory: "50Mi" limits: memory: "1000Mi" cpu: 0.5 command: ["stress"] args: ["--vm", "1", "--vm-bytes", "556M", "-c", "2", "--vm-hang", "1"]Run the following command to deploy the pod-cpuset-demo.yaml file in the cluster:
kubectl apply -f pod-cpuset-demo.yamlRun the following command to query the vCores that are bound to the container:
# The actual path consists of the UID of the pod and the ID of the container. cat /sys/fs/cgroup/cpuset/kubepods.slice/kubepods-burstable.slice/kubepods-burstable-podf9b79bee_eb2a_4b67_befe_51c270f8****.slice/cri-containerd-aba883f8b3ae696e99c3a920a578e3649fa957c51522f3fb00ca943dc2c7****.scope/cpuset.cpusExpected output:
0-31The output shows that the serial numbers of the vCores that can be used by the container range from 0 to 31 before you bind vCores to the container.
Use the following YAML template to specify the vCores and create a cgroups-sample-cpusetpod.yaml file:
apiVersion: resources.alibabacloud.com/v1alpha1 kind: Cgroups metadata: name: cgroups-sample-cpusetpod spec: pod: name: pod-cpuset-demo namespace: default containers: - name: pod-cpuset-demo cpuset-cpus: 2-3 # Bind vCore 2 and vCore 3 to the pod.Run the following command to deploy the cgroups-sample-cpusetpod.yaml file in the cluster:
kubectl apply -f cgroups-sample-cpusetpod.yamlRun the following command to query the vCores that are bound to the container after you submit the change:
# The actual path consists of the UID of the pod and the ID of the container. cat /sys/fs/cgroup/cpuset/kubepods.slice/kubepods-burstable.slice/kubepods-burstable-podf9b79bee_eb2a_4b67_befe_51c270f8****.slice/cri-containerd-aba883f8b3ae696e99c3a920a578e3649fa957c51522f3fb00ca943dc2c7****.scope/cpuset.cpusExpected output:
2-3The output shows that vCore 2 and vCore 3 are bound to the containers. The vCores that are bound to the containers are the same as the vCores that are specified in the
spec.pod.containers.cpuset-cpusparameter in the YAML file that you created in Step 4. The modification is successful.Run the following command to query the status of the pod:
kubectl describe pod pod-cpuset-demoExpected output:
Events: Type Reason Age From Message ---- ------ ---- ---- ------- Normal Scheduled 7m7s default-scheduler Successfully assigned default/pod-cpuset-demo to cn-hangzhou.192.XX.XX.50 Normal AllocIPSucceed 7m5s terway-daemon Alloc IP 192.XX.XX.56/24 took 2.060752512s Normal Pulled 7m5s kubelet Container image "registry-cn-beijing.ack.aliyuncs.com/acs/stress:v1.0.4" already present on machine Normal Created 7m5s kubelet Created container pod-cpuset-demo Normal Started 7m5s kubelet Started container pod-cpuset-demo Normal CPUSetBind 84s koordlet set cpuset 2-3 to container pod-cpuset-demo successThe output shows that the pod runs as normal and no restart events are generated.
Modify the disk IOPS
If you want to modify the disk IOPS for a pod, you must use Alibaba Cloud Linux as the operating system of the worker node that you want to manage.
In this example, an I/O-intensive application is created to verify that the disk IOPS of a pod can be modified by using cgroup configuration files without the need to restart the pod.
If you specify a blkio limit in cgroup v1, the OS kernel limits only the direct I/O of a pod. The OS kernel does not limit the buffered I/O of a pod. To limit the buffered I/O of a pod, use cgroup v2 or enable the cgroup writeback feature for Alibaba Cloud Linux. For more information, see Enable the cgroup writeback feature.
Create an I/O-intensive application with the following YAML template:
Mount the host directory /mnt to the pod. The device name of the corresponding disk is /dev/vda1.
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: fio-demo labels: app: fio-demo spec: selector: matchLabels: app: fio-demo template: metadata: labels: app: fio-demo spec: containers: - name: fio-demo image: registry.cn-zhangjiakou.aliyuncs.com/acs/fio-for-slo-test:v0.1 command: ["sh", "-c"] # Use Fio to perform write stress tests on the disk. args: ["fio -filename=/data/test -direct=1 -iodepth 1 -thread -rw=write -ioengine=psync -bs=16k -size=2G -numjobs=10 -runtime=12000 -group_reporting -name=mytest"] volumeMounts: - name: pvc mountPath: /data # The disk volume is mounted to the path /data. volumes: - name: pvc hostPath: path: /mntRun the following command to deploy the fio-demo Deployment in the cluster:
kubectl apply -f fio-demo.yamlCreate a cgroup configuration file that is used to control the disk IOPS to limit the throughput of the pod.
Use the following YAML file to specify the bytes per second (BPS) limit of the /dev/vda1 device and create a file named cgroups-sample-fio.yaml:
apiVersion: resources.alibabacloud.com/v1alpha1 kind: Cgroups metadata: name: cgroups-sample-fio spec: deployment: name: fio-demo namespace: default containers: - name: fio-demo blkio: # The I/O limit in bit/s. Example: 1048576, 2097152, or 3145728. device_write_bps: [{device: "/dev/vda1", value: "1048576"}]Run the following command to query the disk IOPS limit after you submit the change:
# The actual path consists of the UID of the pod and the ID of the container. cat /sys/fs/cgroup/blkio/kubepods.slice/kubepods-besteffort.slice/kubepods-besteffort-pod0840adda_bc26_4870_adba_f193cd00****.slice/cri-containerd-9ea6cc97a6de902d941199db2fcda872ddd543485f5f987498e40cd706dc****.scope/blkio.throttle.write_bps_deviceExpected output:
253:0 1048576The output shows that the IOPS limit of the disk is
1048576bit/s.
View the monitoring data of the node.
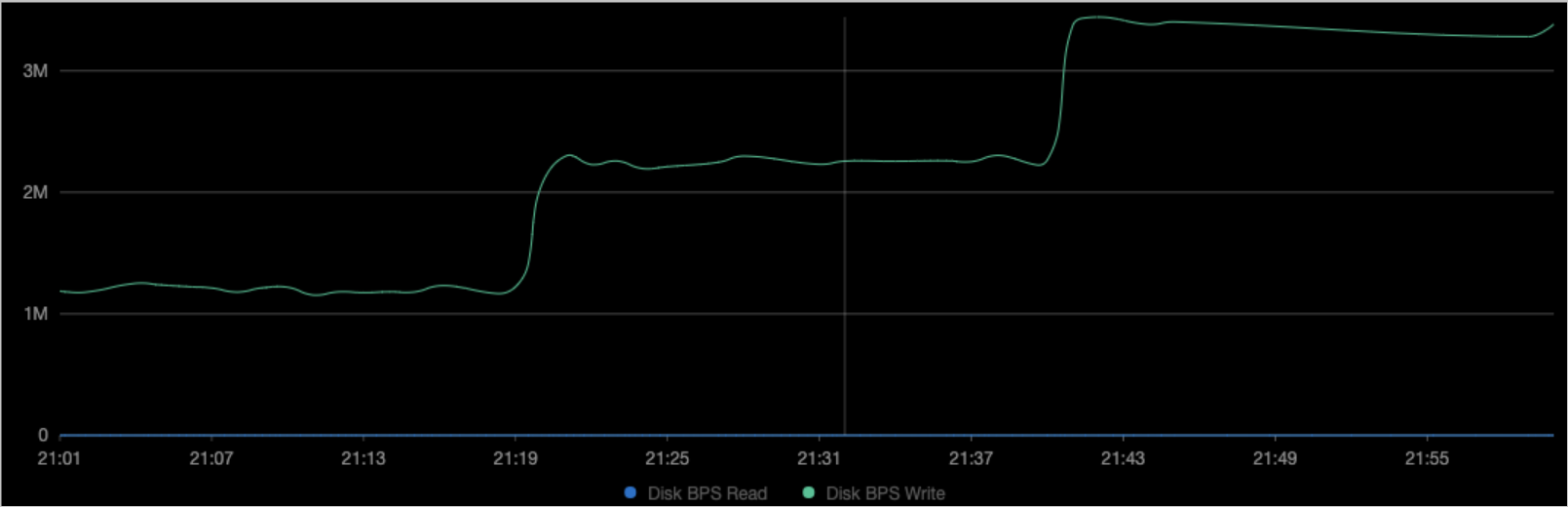
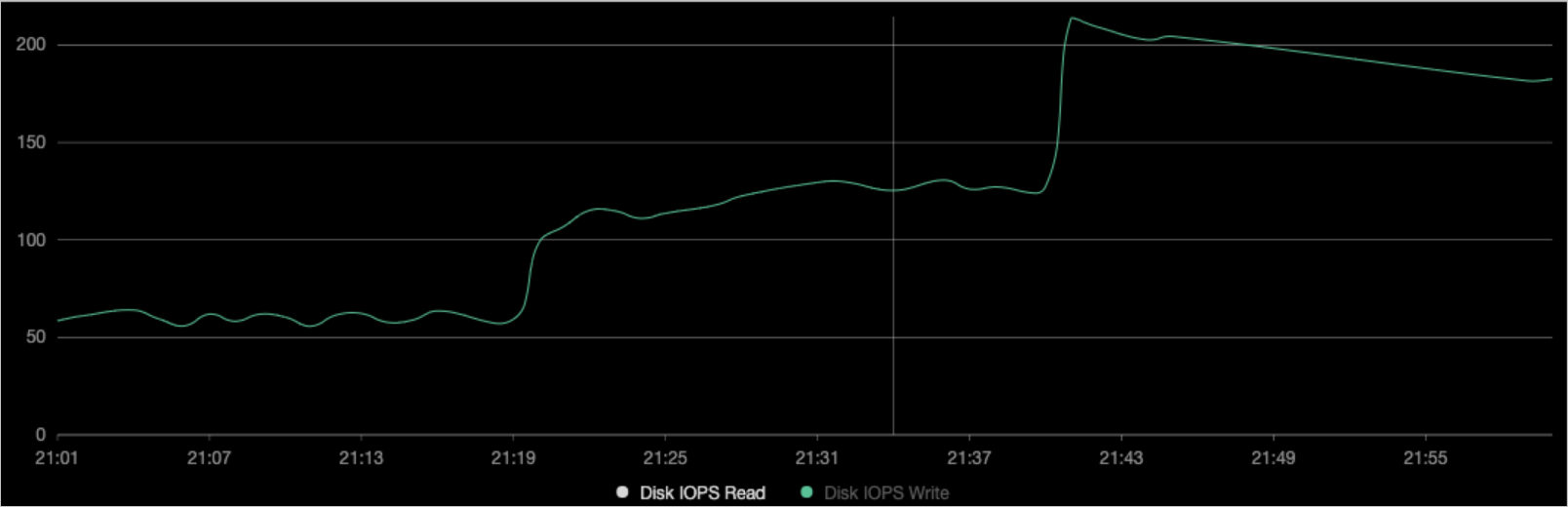
The figures show that the BPS of the container is the same as the value that is specified in the
device_write_bpsparameter of the YAML file that you created in Step 3. The pod is not restarted after you submit the change.NoteFor more information about how to enable Managed Service for Prometheus, see Managed Service for Prometheus. In the left-side navigation pane, choose Operations > Prometheus Monitoring. Click the Application Monitoring tab to view the disk data.
Dynamically modify Deployment-level resource parameters of a pod
The dynamic modification of pod-level resource parameters described in the preceding section also takes effect in the Deployment-level parameters. Pod-level resource parameters are modified by using the spec.pod field in the cgroups configuration files. Deployment-level resource parameters are modified by using the spec.deployment field. The following example describes how to modify the vCores in a Deployment. The operations in other scenarios are similar.
Create a go-demo.yaml file with the following YAML template:
The Deployment creates two pods that run a stress testing program. Each pod requests 0.5 vCores.
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: go-demo labels: app: go-demo spec: replicas: 2 selector: matchLabels: app: go-demo template: metadata: labels: app: go-demo spec: containers: - name: go-demo image: polinux/stress command: ["stress"] args: ["--vm", "1", "--vm-bytes", "556M", "-c", "1", "--vm-hang", "1"] imagePullPolicy: Always resources: requests: cpu: 0.5 limits: cpu: 0.5Run the following command to deploy the go-demo Deployment in the cluster:
kubectl apply -f go-demo.yamlUse the following YAML template to specify the CPU binding information and create a file named cgroups-cpuset-sample.yaml:
apiVersion: resources.alibabacloud.com/v1alpha1 kind: Cgroups metadata: name: cgroups-cpuset-sample spec: deployment: # This is a Deployment. name: go-demo namespace: default containers: - name: go-demo cpuset-cpus: 2,3 # Bind vCore 2 and vCore 3 to the pod.Run the following command to deploy the cgroups-cpuset-sample Deployment in the cluster:
kubectl apply -f cgroups-cpuset-sample.yamlRun the following command to query the vCores that are bound to the container after you submit the change:
# The actual path consists of the UID of the pod and the ID of the container. cat /sys/fs/cgroup/cpuset/kubepods.slice/kubepods-burstable.slice/kubepods-burstable-pod06de7408_346a_4d00_ba25_02833b6c****.slice/cri-containerd-733a0dc93480eb47ac6c5abfade5c22ed41639958e3d304ca1f85959edc3****.scope/cpuset.cpusExpected output:
2-3The output shows that vCore 2 and vCore 3 are bound to the containers. The vCores that are bound to the containers are the same as the vCores that are specified in the
spec.deployment.containers.cpuset-cpusparameter in the cgroup configuration file.