ACK clusters are integrated with Managed Service for Prometheus, which provides visualized Prometheus dashboards. After you enable dynamic resource overcommitment for a cluster, you can use the colocation monitoring feature provided by ACK to view the data of colocated resources, such as the total CPU and memory resources for colocation and the ratio of allocated CPU and memory resources.
Prerequisites
The ack-koordinator component is installed and the version of the component is v1.1.1-ack.1 or later. For more information, see ack-koordinator (FKA ack-slo-manager).
Dynamic resource overcommitment is enabled. For more information, see Enable dynamic resource overcommitment.
Entry point for the dashboard
Log on to the ACK console. In the navigation pane on the left, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want and click its name. In the left-side pane, choose .
On the Prometheus Monitoring page, click the tab.
Description of the dashboard
You can view the following information on the colocation monitoring dashboard:
Resource benefits: provides panels that display statistics about resource benefits in colocation scenarios.
Observability: provides insights into the resources and workloads in colocation scenarios. You can view the resource statistics by cluster, node pool, node, and pod.
The following content shows an example of the colocation monitoring dashboard. The dashboards are periodically updated. Refer to the actual interface as the standard.
Resource benefits overview
This section displays information about resource benefits and resource usage trends.
Information about the total amount of colocated resources and the amount of colocated resources allocated
Term | Description |
Non-colocated resources | All allocatable physical resources on the node. The total amount of non-colocated resources depends on the node specification and remains unchanged after you enable colocation. |
Colocated resources | You can enable the dynamic resource overcommitment feature to find idle physical resources in a cluster, which are available colocated resources. The total amount of colocated resources varies based on the resource utilization of the node and dynamically changes with the idle resources of the node. Colocated resources are schedulable resources used in colocation scenarios. The amount of colocated resources is a key metric used to evaluate resource benefits in colocation scenarios. |
Total amount of colocated resources | Colocated resources include vCPUs and memory resources that can be used for colocation in the cluster. The preceding figure shows that the cluster has 118 vCPUs and 487 GiB of memory available for colocation of latency-sensitive (LS) workloads and best-effort (BE) workloads. If the amount of colocated resources increases, the cluster can provide more schedulable idle resources. In this case, more applications can be deployed and more resource benefits can be generated in colocation scenarios. |
Total amount of allocated colocated resources | Allocated colocated resources include vCPUs and memory resources that are allocated for colocation. The preceding figure shows that 2 vCPUs and 1 GiB of memory are allocated in colocation scenarios. If the amount of allocated colocated resources increases, more colocated resources are allocated. In this case, more applications can be deployed and more resource benefits can be generated in colocation scenarios. |
Ratio of allocated colocated resources | The ratio of allocated colocated resources is calculated based on vCPUs and memory for colocation, respectively. The ratio is calculated by using the following formula: A higher ratio indicates that more resource benefits can be generated in colocation scenarios. |
Usage trend of colocated resources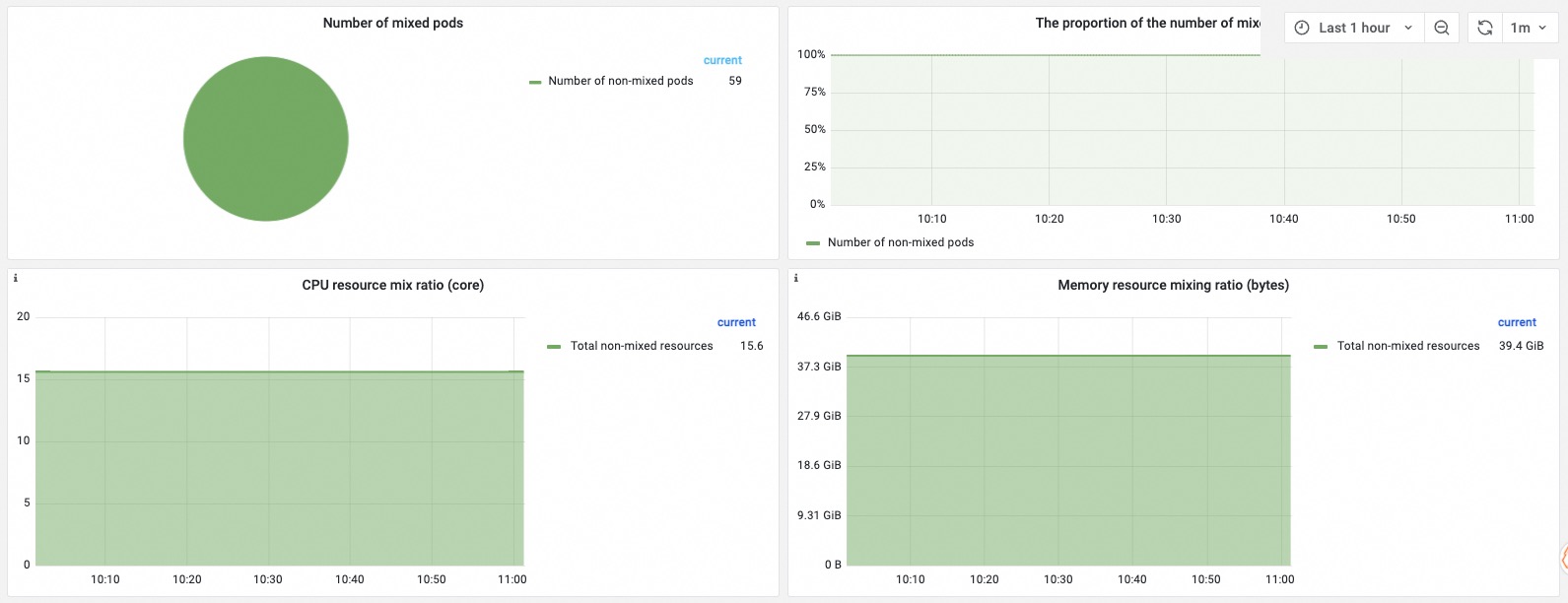
Term | Description |
Number of colocated pods | The number of colocated pods includes the number of pods that use non-colocated resources and the number of pods that use colocated resources. The ratio of pods that use non-colocated resources and the ratio of pods that use colocated resources are also displayed. |
Ratio of colocated resources | The ratio of vCPUs for colocation and the ratio of memory for colocation are displayed. The ratios indicate the amount of colocated resources and the amount of non-colocated resources. If the cluster has a large amount of idle resources and the ratio of colocated resources is high, a large amount of resources can be used for colocation. |
Colocated resources overview
The Cluster Dimension, Node Dimension, and Pod Dimension sections display the resource usage and resource requests by cluster, node, and pod.
Cluster Dimension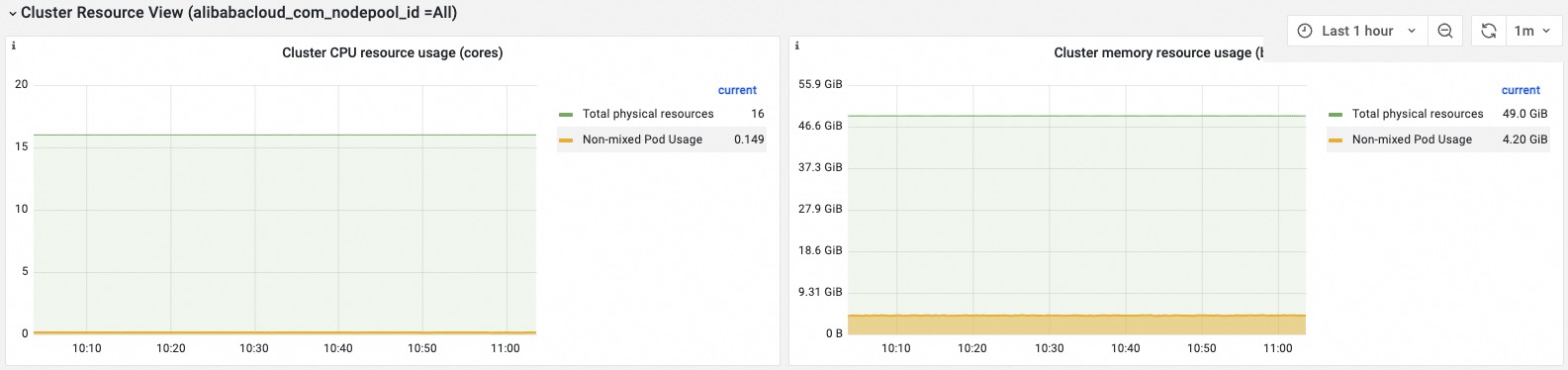
Term | Description |
Resource usage in the cluster | Information about the consumed CPU and memory resources is displayed. The information includes the total vCPUs and total memory capacity of the cluster, the vCPUs and memory used by non-colocated pods, the vCPUs and memory used by colocated pods, and the vCPUs and memory used by system components. If the vCPUs or memory used by non-colocated pods, colocated pods, and system components is much lower than the total vCPUs or memory capacity of the cluster, the CPU utilization and the memory utilization of the cluster are low and a large amount of CPU or memory resources is idle in the cluster. |
Requests for colocated resources in the cluster | Information about the requests for colocated resources is displayed. The information includes the total allocatable vCPUs and memory for colocation, and the requested vCPUs and memory for colocation. If the amount of requested colocated resources is close to the total amount of colocated resources, the ratio of allocated colocated resources is high. |
Requests for non-colocated resources in the cluster | Information about the requests for non-colocated resources is displayed. The information includes allocatable vCPUs and allocatable memory for non-colocation scenarios, and the requested vCPUs and memory for non-colocation scenarios. If the amount of requested non-colocated resources is close to the total amount of non-colocated resources, the ratio of allocated non-colocated resources is high. |
Node Dimension
In the upper part of the Kubernetes Reclaimed Resource tab, configure the node_label and node_label_value parameters to view the standalone resource dashboards of different nodes.

The following table describes the filters that are provided on the page.
Filter | Description |
node_label_value | Default value: All. When the default value is used, the Resource Benefits Overview and Cluster Dimension sections display statistics about all cluster nodes. You can select a node pool ID from the drop-down list to display information about the node pool in the Resource Benefits Overview and Cluster Dimension sections. |
node_label | You can specify a node label to select a node. For more information, see Notes in the upper part of the page. |
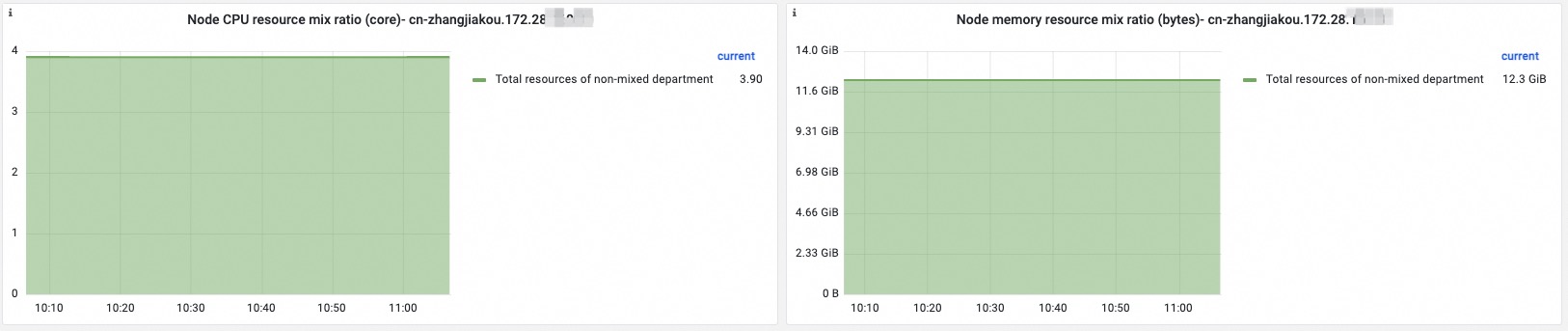
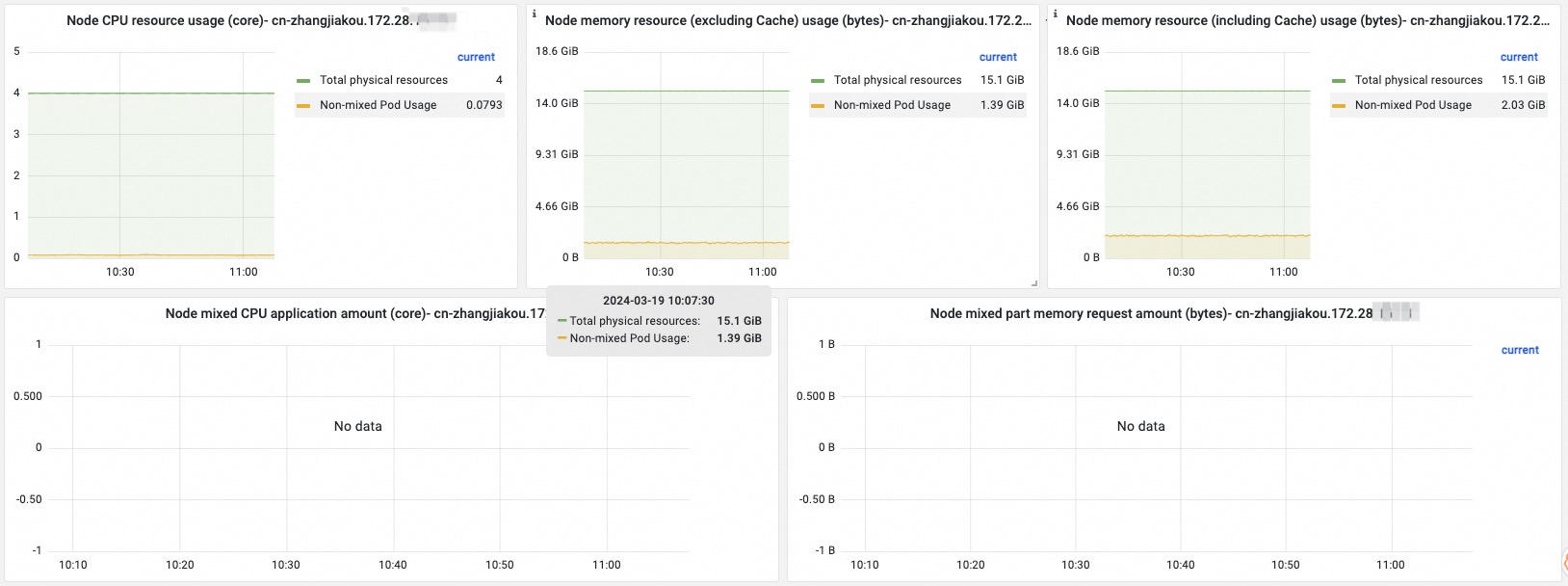

Term | Description |
Ratio of colocated resources on the node | Information about the ratio of colocated resources on the node is displayed. The information includes the ratio of vCPUs for non-colocation scenarios, the ratio of memory for non-colocation scenarios, the ratio of vCPUs for colocation, and the ratio of memory for colocation. The total amount of non-colocated resources is stacked on the total amount of colocated resources so you can compare the statistics. |
Resource usage on the node | Information about the CPU usage, memory usage (including cache), and memory usage (excluding cache) on the node is displayed. The information includes the total vCPUs and total memory of the node, the vCPUs and memory used by non-colocated pods, the vCPUs and memory used by colocated pods, and the vCPUs and memory used by system components. If the amount of vCPUs or memory resources used by non-colocated pods, colocated pods, and system components is much lower than the total vCPUs or memory capacity of the node, the CPU utilization or memory utilization of the node is low and a large amount of CPU or memory resources is idle on the node. |
Requested colocated resources on the node | Information about the requested vCPUs and memory for colocation is displayed. The information includes the total vCPUs, requested vCPUs, total memory, and requested memory for colocation on the node. If the amount of requested colocated resources is close to the total amount of colocated resources, the ratio of allocated colocated resources is high. |
Requests for colocated resources by each pod | Information about the requests for vCPUs and memory for colocation by each pod on the node is displayed. |
Colocated resource utilization of each pod | Information about the utilization of vCPUs for colocation and utilization of memory for colocation of each pod on the node is displayed. |
Pod Dimension
On the k8s-reclaimed-resource tab, you can change the values of the pod_namespace and pod_name parameters to view the panels of each pod.
Term | Description |
Amount of colocated resources used by the pod | Information about the amount of CPU and memory resources for colocation used by the pod. The information includes the CPU limit and memory limit, CPU request and memory request, and the actual CPU usage and memory usage. |
Colocated resource utilization of the pod | Information about the utilization of vCPUs for colocation and utilization of memory for colocation of the pod on the node is displayed. |
Amount of colocated resources used by each container | Information about the amount of CPU and memory resources for colocation used by each container in the pod. The information includes the CPU limit and memory limit, CPU request and memory request, and the actual CPU usage and memory usage. |
FAQ
How do I resolve the issue that no data is displayed in the Resource Benefits Overview section on the Kubernetes Reclaimed Resource tab?
Check whether ack-koordinator is installed.
Log on to the ACK console. In the navigation pane on the left, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the one you want to manage and click its name. In the navigation pane on the left, click Add-ons.
On the Add-ons page, check whether the ack-koordinator component is installed.
If the version of ack-koordinator you are using is earlier than 0.7, ack-koordinator is installed from the Marketplace page. Refer to Migrate ack-koordinator from the Marketplace page to the Add-ons page for migration.
If ack-koordinator is not installed, install ack-koordinator as prompted.
If the component is installed, proceed to Step 2.
Check whether data is displayed in the colocation monitoring dashboard.
If no data is displayed, perform the following steps:
Log on to the ARMS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
In the upper-left corner of the page, select the region in which the Prometheus instance you want to manage is deployed and click the Prometheus instance. In the left-side navigation pane of the Prometheus instance details page, click Metric Management.
In the Index exploration tab, click Metrics Explore, search and select kube_node_labels, then view the data details of the metric as prompted.