HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) encryption uses the AES-128 algorithm. This method is compatible with all HLS players and uses key management and token services for access control. HLS encryption is widely used in scenarios with high security requirements, such as online education and exclusive content streaming. This topic describes how to use HLS encryption to encrypt videos and decrypt them for playback.
How it works
ApsaraVideo VOD uses envelope encryption. Your service uses Alibaba Cloud Key Management Service (KMS) to generate a data key (DK) and an enveloped data key (EDK). After you use the DK to encrypt a video, the encrypted video and the EDK are stored. During playback, the decryption service retrieves the DK to decrypt the video.
To perform security authentication on the decryption address, you can enable M3U8 encryption and rewrite to add another layer of protection to the HLS data access process. The default rewritten parameter is MtsHlsUriToken. For more information about how to enable M3U8 encryption and rewrite and how it works, see Configure M3U8 encryption and rewrite.
Prerequisites
Alibaba Cloud Video Encryption (HLS encryption) is a free service. However, video transcoding is required to use this feature. Transcoding operations incur service fees. For more information about billing, see Media transcoding billing.
ApsaraVideo VOD is activated. For more information, see Activate ApsaraVideo VOD.
You have granted ApsaraVideo VOD the required permissions to access KMS. You can grant the permissions on the Cloud Resource Access Authorization page.
An accelerated domain name is configured in ApsaraVideo VOD. For more information, see Add an accelerated domain name.
The ApsaraVideo VOD server-side software development kit (SDK) is installed. For more information, see Server-side SDKs. This topic uses the SDK for Java as an example.
Encryption and decryption process
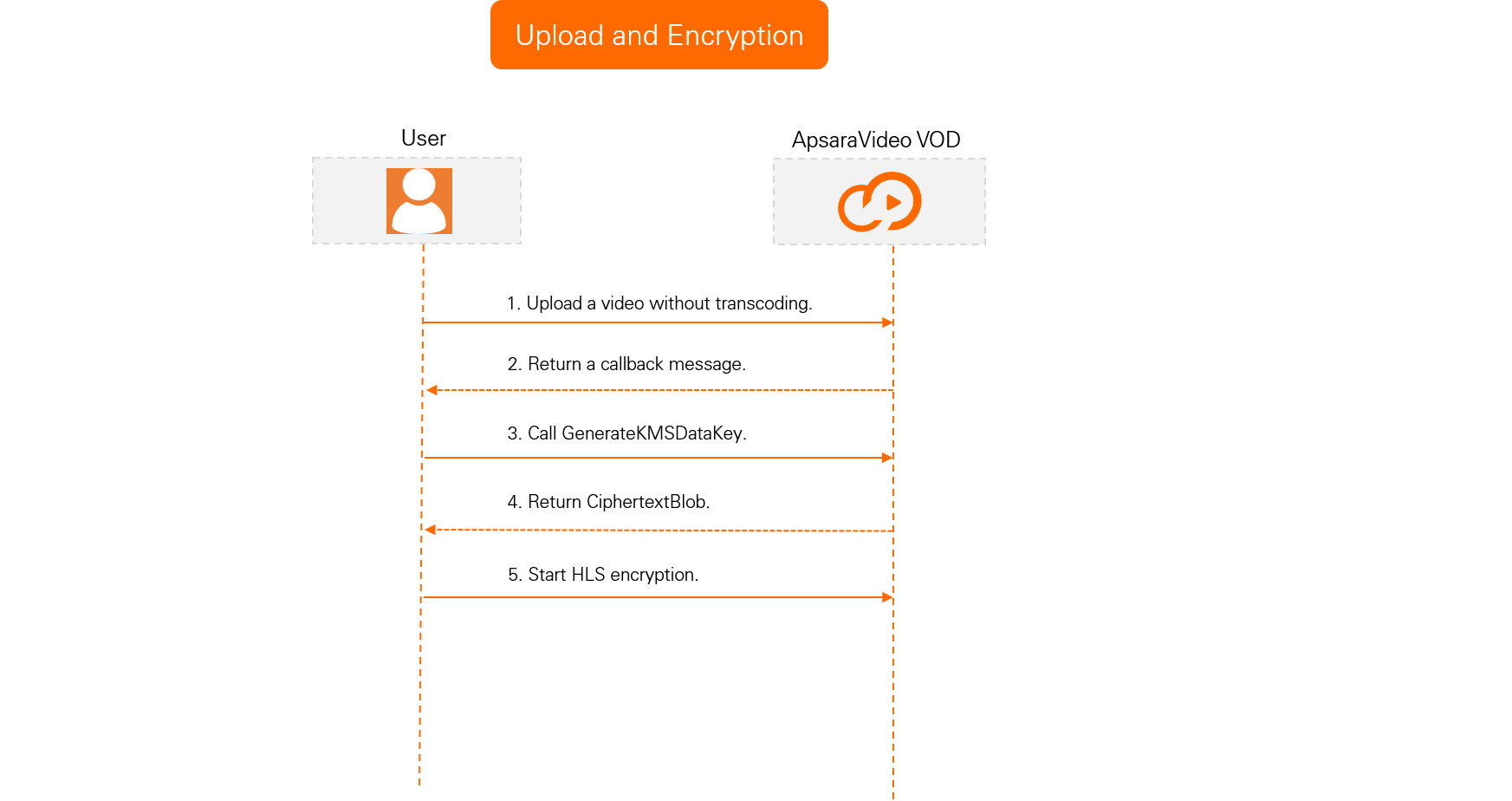
Upload and encryption process
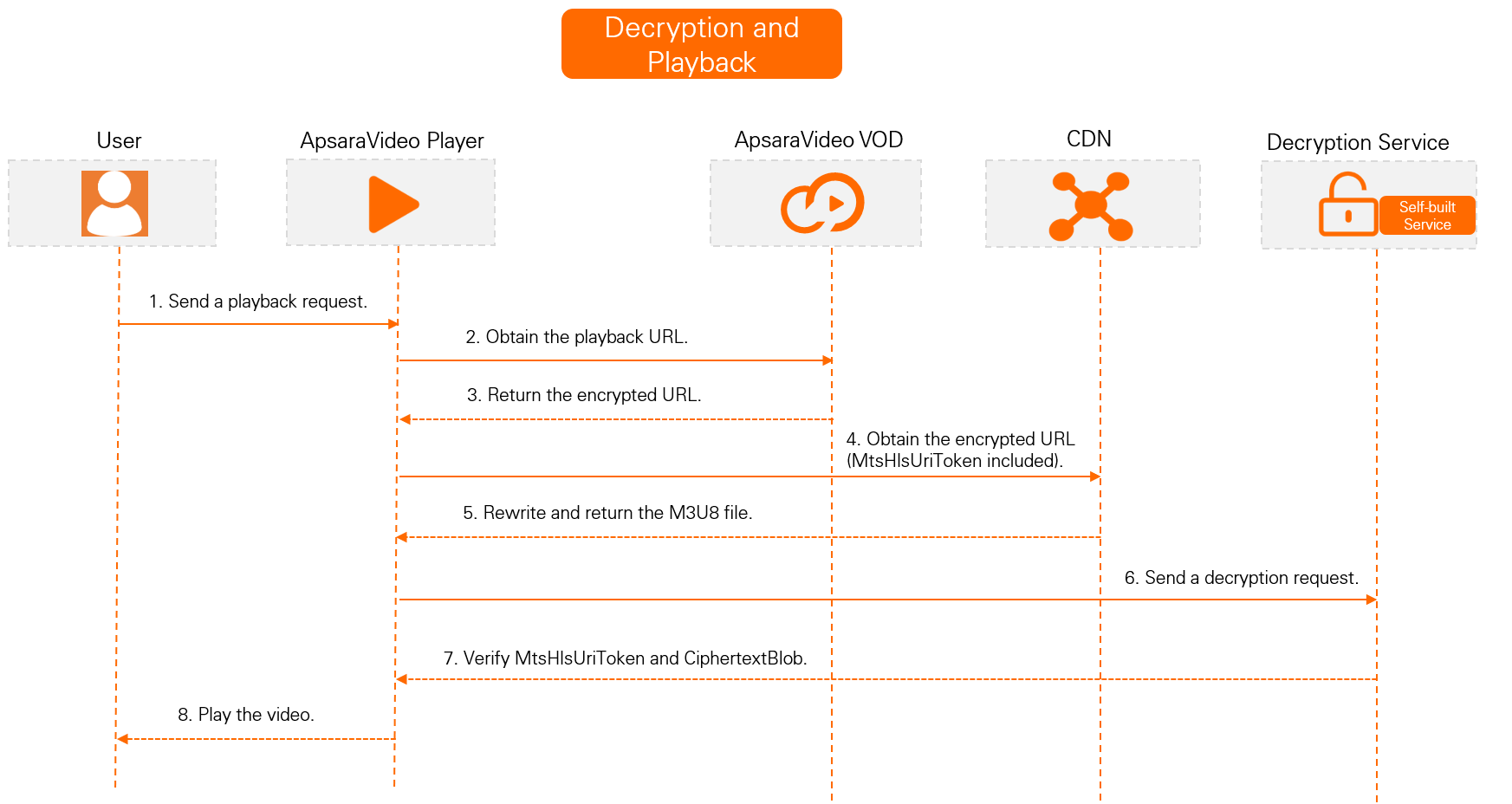
Decryption and playback process
M3U8 encryption and rewrite enabled (Recommended)
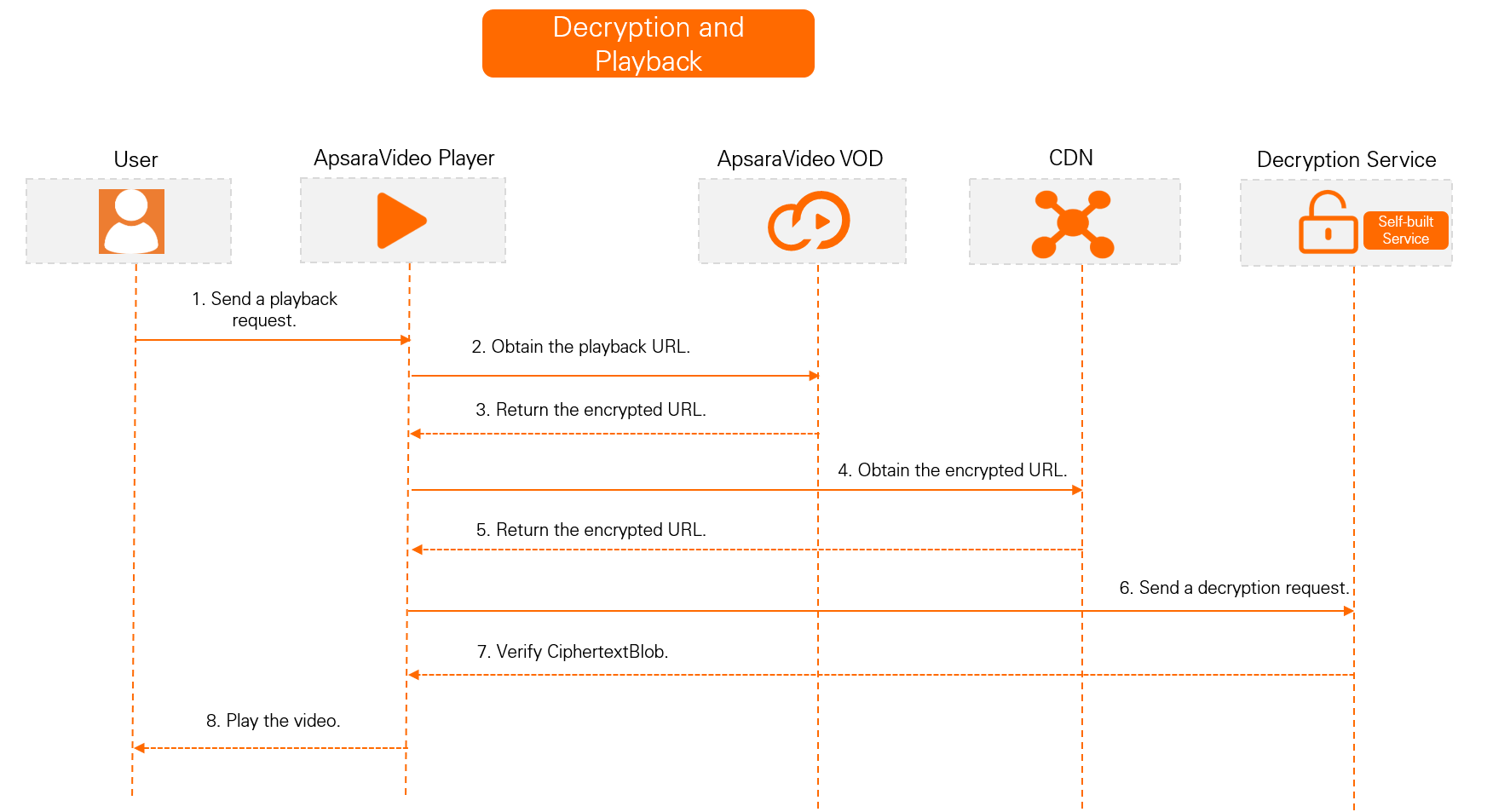
M3U8 encryption and rewrite not enabled
Encrypt a video
Upload a video and receive a callback.
To prevent HLS-encrypted videos from being automatically transcoded, use the built-in No Transcoding template group when you upload them to ApsaraVideo VOD.
Upload the video using the ApsaraVideo VOD console or by calling an API operation. For more information, see Upload media files using the ApsaraVideo VOD console and Media upload.
Configure event notifications for ApsaraVideo VOD. When you receive a Video Upload Completed callback message, the video is uploaded to ApsaraVideo VOD. For more information about how to configure event notifications, see Event notifications.
Set up an encryption service.
Create a service key.
A service key is the primary encryption key in KMS and is required to generate standard encryption keys. If you do not create a service key, an error is reported when you call the GenerateDataKey operation to generate a key.
In the upper-left corner of the page, click the region ID to switch to the region where you want to create the service key.
NoteThe service key must be in the same region as the origin server where your video is stored. For example, if your video is stored in China (Shanghai), the service key must also be created in China (Shanghai).
Log on to the ApsaraVideo VOD console. In the navigation pane on the left, choose Configuration Management > Media Processing > HLS Standard Encryption.
On the Standard Encryption page, click Create Service Key.
After the service key is created, a message is displayed. You can view your service key in the Key Information section.
NoteIf a message indicates that the service key is created but you cannot view the service key, a service-linked role may be missing. You can re-grant the permissions to restore the role and then refresh the page to view the service key.
Call an API operation to generate a data key.
Call the GenerateDataKey operation to generate a DK and an EDK. You do not need to pass any parameters for this operation. After the call is successful, the `CiphertextBlob` in the response is the EDK in AES-128 format. You must cache this value for standard encryption and transcoding. The `Plaintext` in the response is the DK.
Create a transcoding template group for HLS encryption.
The HLS encryption process requires two transcoding template groups: the built-in No Transcoding template group and a custom HLS encryption transcoding template group. The following steps describe how to create the custom group:
Log in to the ApsaraVideo VOD console. In the navigation pane on the left, choose Configuration Management > Media Processing > Transcoding Template Groups.
On the Transcoding Template Groups page, create a template group for HLS encryption.
Set the Encapsulation Format to hls. In the Advanced Parameters section, enable Video Encryption and select Alibaba Cloud Encryption. You can configure the other parameters as needed. For more information, see Transcoding templates.
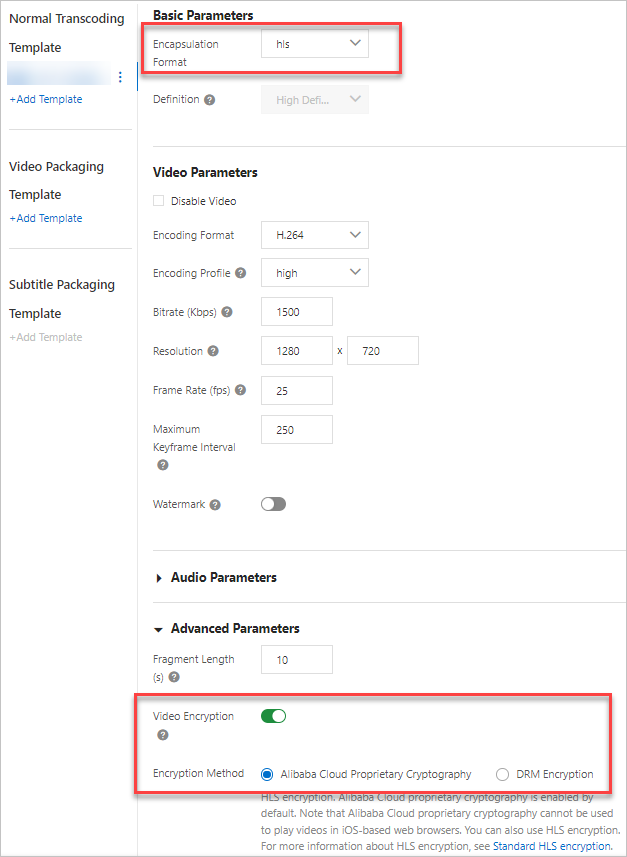
After the template is created, you can view the ID of the transcoding template group on the Transcoding Template Groups page. Save the ID. You will need it later when you initiate HLS encryption and transcoding.
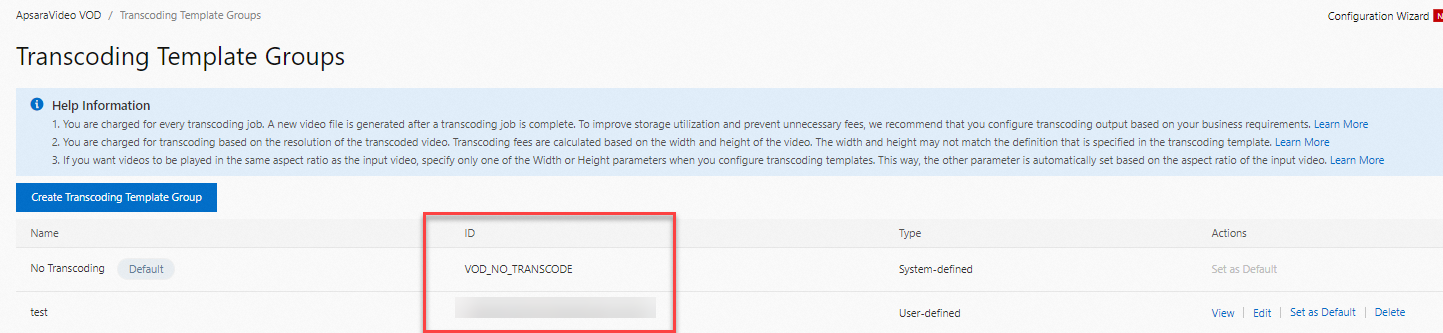
Initiate HLS encryption and transcoding.
Call the SubmitTranscodeJobs operation to initiate HLS encryption and transcoding.
If you have configured event notifications for ApsaraVideo VOD, video transcoding is complete when you receive a Transcoding of a Single-definition Video Completed or Transcoding of All-definition Videos Completed callback message.
View the HLS encryption result.
After transcoding is complete, you can use the following three methods to determine whether standard encryption was successful.
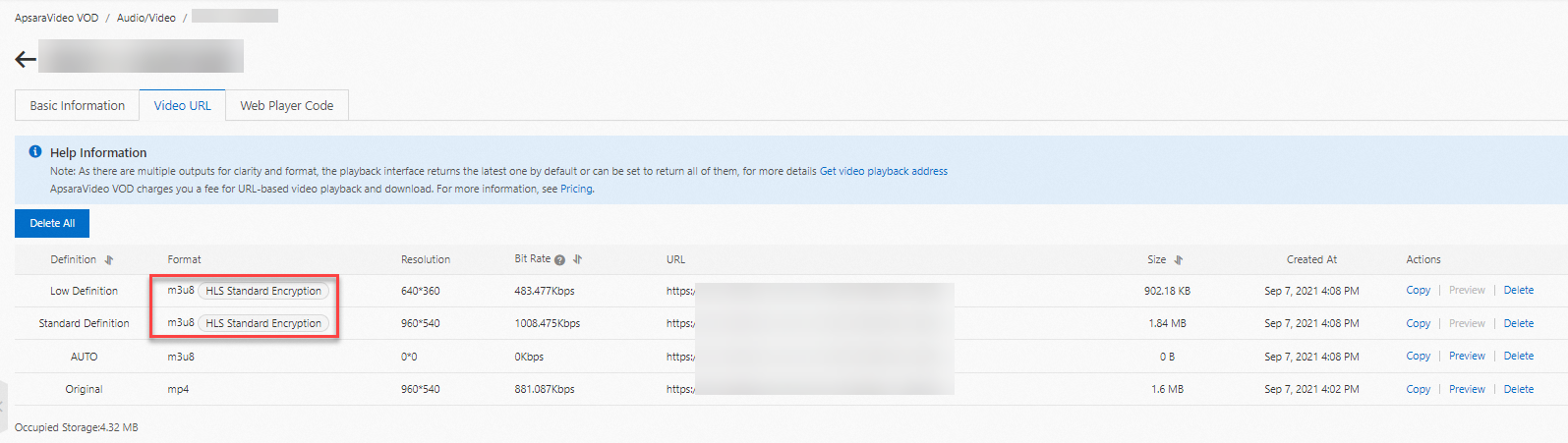
Method 1: Log on to the ApsaraVideo VOD console and choose Media Files > Audio/Video > Manage > Video URL. On the Video URL page, if the video has outputs in multiple formats, such as an original MP4 file, check whether the m3u8 video stream is labeled with HLS Standard Encryption. If the label is present, HLS encryption is successful.
Method 2: Copy the URL of an M3U8 file that uses HLS Standard Encryption. Run the
curl -v "URL of the M3U8 file"command to check the M3U8 content. If the content contains the keyURI="<The decryption URI that you pass for standard encryption, which is the value of the DecryptKeyUri parameter>", the video is protected by HLS encryption.Method 3: Call the GetTranscodeTask operation. Pass the value of the JobId parameter that is returned in Step 4. If the returned TranscodeTemplateId parameter is the ID of the transcoding template group that you created in Step 3 and the TranscodeJobStatus parameter is TranscodeSuccess, HLS encryption is successful.
HLS (M3U8) encryption and rewrite (Recommended)
After you enable the M3U8 encryption and rewrite feature, the system automatically adds encryption parameters, such as the encryption algorithm, key URI, and authentication parameters, to the #EXT-X-KEY tag in the Media Playlist (M3U8 file) of the HLS protocol. When the client parses the rewritten M3U8 file, it uses the key URI with authentication parameters to request the decryption key. The client then uses the key and the specified algorithm to decrypt the TS shards. This process provides encrypted access protection for HLS streaming media.
Step 1: Enable standard encryption parameter pass-through
In the ApsaraVideo VOD console, enable Parameter Pass-through for HLS Encryption.
Enabling Parameter Pass-through for HLS Encryption lets you modify the M3U8 file for HLS. This feature modifies the URI in the #EXT-X-KEY tag by appending parameters from a client request. The default parameter name is MtsHlsUriToken.
Prerequisites
Cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) is configured. For more information, see Configure cross-origin resource sharing.
This feature is not currently supported in Alibaba Gov Cloud.
Procedure
Log on to the ApsaraVideo VOD console.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Configuration Management.
Click CDN Configuration > Domain Names to go to the Domain Names page.
Find the target domain name and click Configure in the Actions column.
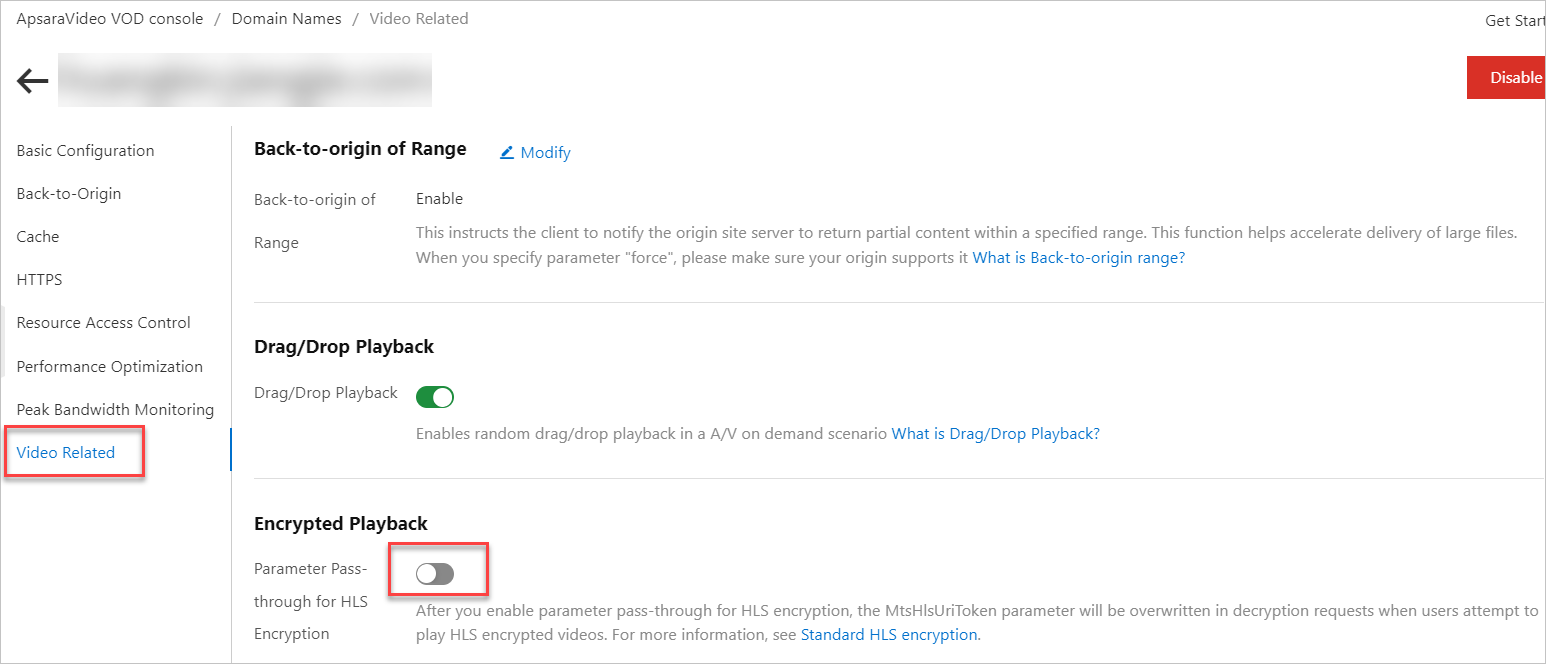
In the navigation pane on the left of the domain name's page, click Video Related.
In the Encrypted Playback section, turn on the Parameter Pass-through for HLS Encryption switch.
After you enable this feature, when HLS encryption parameters are passed through, the system authenticates your request by rewriting the token authentication parameter. The rewritten parameter name is
MtsHlsUriToken, and its value istest. When Alibaba Cloud CDN decrypts the video for playback,MtsHlsUriToken=testis appended to the end of the URI in the#EXT-X-KEYtag of the M3U8 file.
Step 2: Send a request that includes the MtsHlsUriToken parameter
The client sends a request that includes the MtsHlsUriToken parameter to a CDN point of presence (POP) to access the M3U8 file.
To obtain the MtsHlsUriToken, you must build a token service to issue user tokens. This service generates the MtsHlsUriToken.
The token generated by the following code is the MtsHlsUriToken. The following parameters in the sample code must be changed based on your requirements:
Step 3: Decrypt and play the file
After a CDN POP receives a request from the client, it decrypts and plays the video if authentication is successful.
If the value of the MtsHlsUriToken parameter generated in Step 2 is test, MtsHlsUriToken=test is appended to the end of the URI in the #EXT-X-KEY tag of the M3U8 file when CDN decrypts the video for playback.
You must implement the authentication logic. For more information, see the sample code for the decryption service when M3U8 encryption and rewrite is enabled in Play videos.
Play videos
M3U8 encryption and rewrite enabled (Recommended)
Set up a decryption service.
Set up a local HTTP service to decrypt the video.
Call the Decrypt operation to decrypt the key. The
PlainTextin the response is the data key (DK). This DK is the Base64-decoded data of thePlainTextthat is returned by the GenerateDataKey operation.To perform security authentication on the decryption address, you can enable M3U8 encryption and rewrite. This adds another layer of protection to the HLS data access process. The default rewritten parameter is
MtsHlsUriToken. The code for setting up the decryption service varies depending on whether you enable M3U8 encryption and rewrite.Obtain the video playback URL and credential.
Call the GetVideoPlayAuth operation to obtain the playback credential or call the GetPlayInfo operation to obtain the playback URL.
Play the encrypted video.
HLS encryption is compatible with all HLS players. You can use a self-developed player or ApsaraVideo Player to play the encrypted video.
If you use ApsaraVideo Player, you must obtain the token and authentication information as required by ApsaraVideo Player before playback. For more information, see Play encrypted videos. If you use a player other than ApsaraVideo Player, you must implement the playback logic.
The following section describes the internal process of using ApsaraVideo Player for test playback:
M3U8 encryption and rewrite enabled (Recommended)
M3U8 encryption and rewrite disabled
Set up a decryption service.
Set up a local HTTP service to decrypt the video.
Call the Decrypt operation to decrypt the key. The
PlainTextin the response is the data key (DK). This DK is the Base64-decoded data of thePlainTextthat is returned by the GenerateDataKey operation.The following is an example:
Obtain the video playback URL and credential.
Call the GetVideoPlayAuth operation to obtain the playback credential or call the GetPlayInfo operation to obtain the playback URL.
Play the encrypted video.
HLS encryption is compatible with all HLS players. You can use a self-developed player or ApsaraVideo Player to play the encrypted video.
If you use ApsaraVideo Player, you must obtain the token and authentication information as required by ApsaraVideo Player before playback. For more information, see Play encrypted videos. If you use a player other than ApsaraVideo Player, you must implement the playback logic.
The following section describes the internal process of using ApsaraVideo Player for test playback:
M3U8 encryption and rewrite disabled