DeepSeek-R1 is an large language model (LLM) that focus on complex inference tasks. Compared with other LLMs, DeepSeek-R1 has advantages in terms of understanding of complex instructions, accuracy of inference results, and performance stability. OpenSearch LLM-Based Conversational Search Edition is integrated with DeepSeek-R1 to further improve the enterprise-level Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) performance. This topic describes how to build a RAG-based system.
Create and configure an instance
Create an OpenSearch LLM-Based Conversational Search Edition instance. Only Standard Edition and Professional Edition instances of OpenSearch LLM-Based Conversational Search Edition in the China (Shanghai) region support DeepSeek-R1. For more information about how to create an instance, see Create an OpenSearch LLM-Based Conversational Search Edition instance. For more information about the billing rules, see Billing methods and billable items.
NoteStandard Edition instances do not support custom training of LLMs. Professional Edition instances support training of specific LLMs. DeepSeek-R1 does not support training.
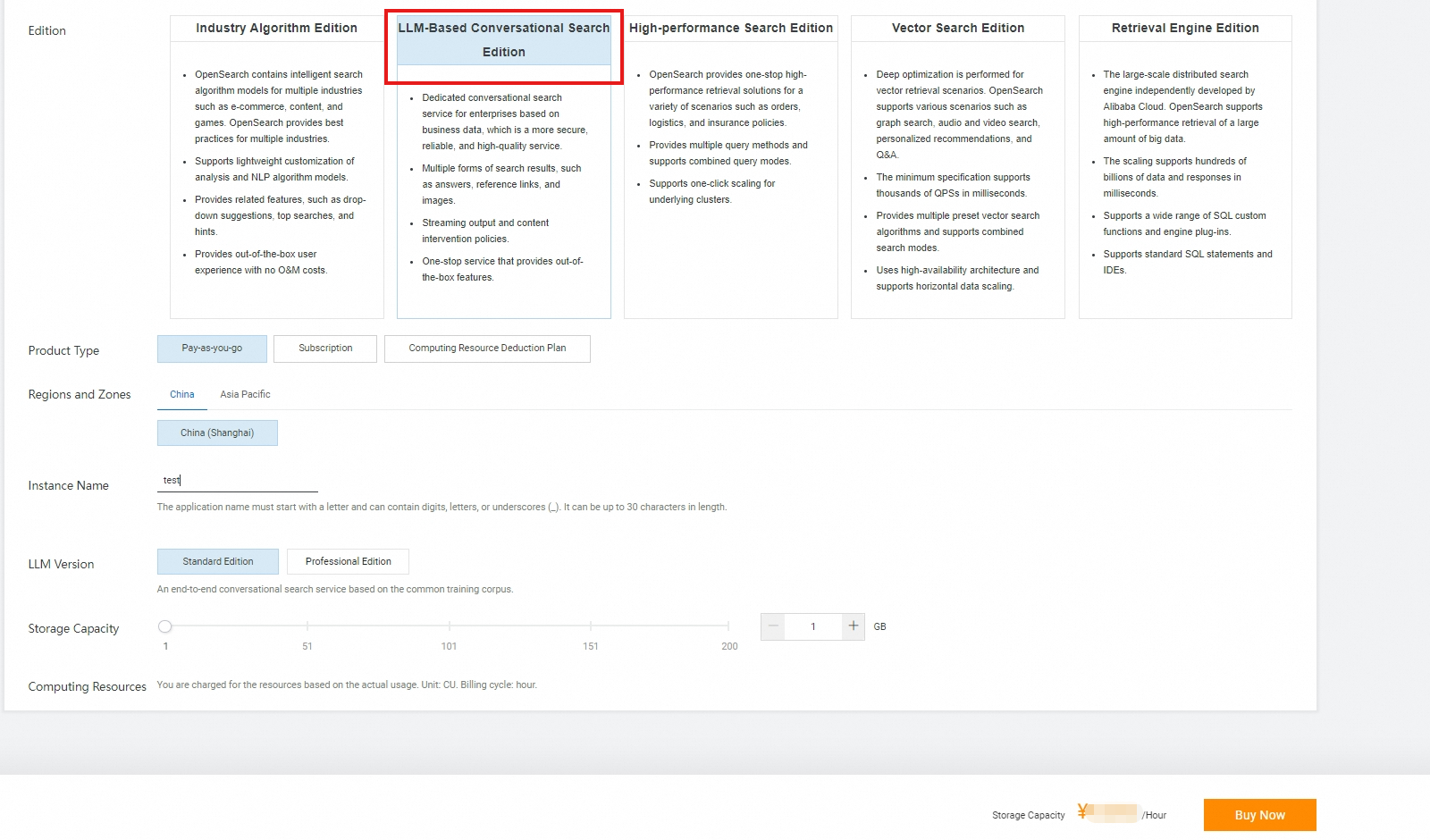
Import data of a knowledge base.
After you create an instance, the system automatically generates a knowledge base data table. You can import structured and unstructured data from documents or batch import data from multiple URLs.
On the Instance Management page, find the desired instance and click Manage in the Actions column. In the left-side navigation pane of the page that appears, choose . On the page that appears, click Import File or Web Page URL Import based on your business requirements. For more information, see Import data.
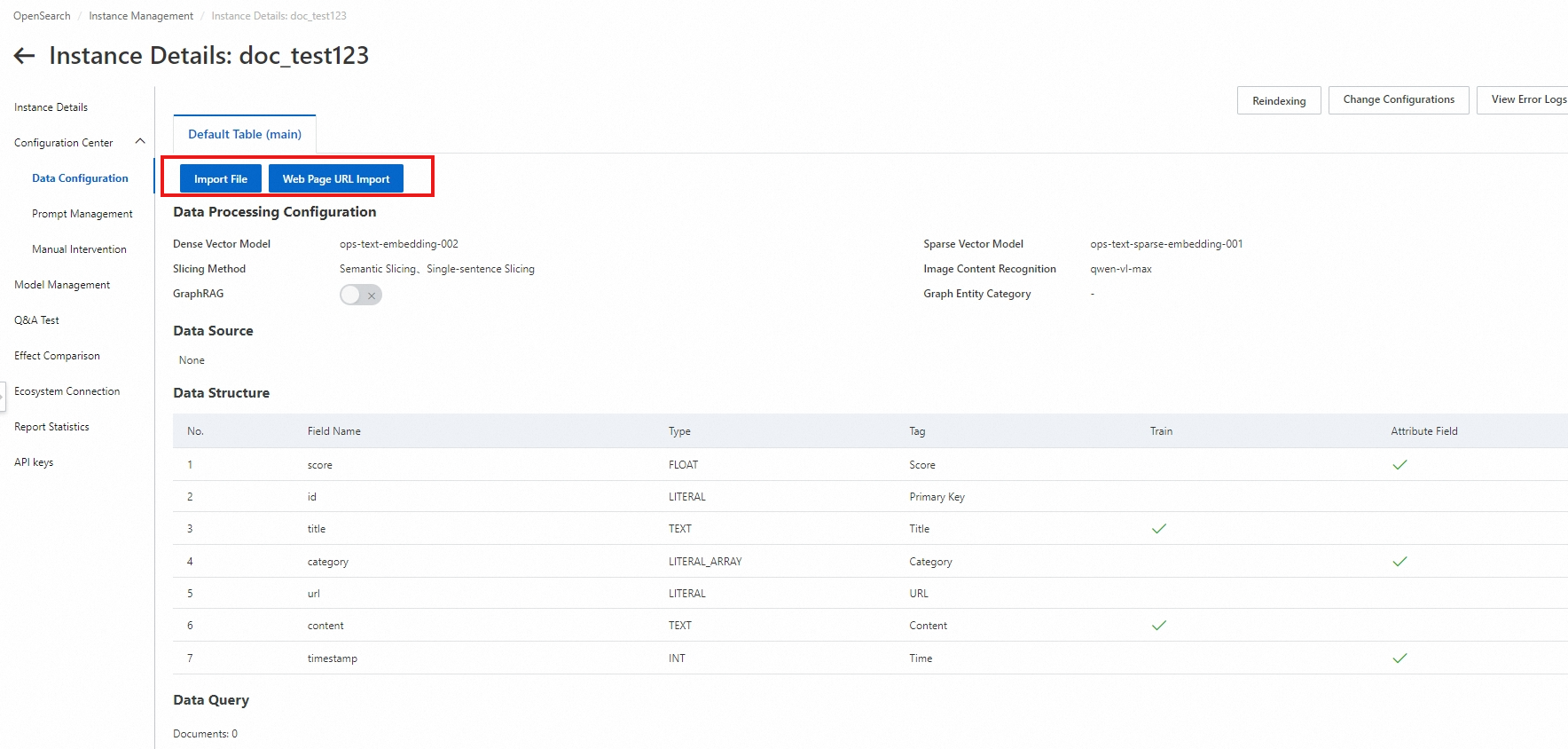
If the data import status is Uploaded, the data is vectorized and stored. You can click View Content in the Actions column of the desired document to view the parsed document. |
You can also call SDKs to upload structured or unstructured documents.
Test the Q&A performance
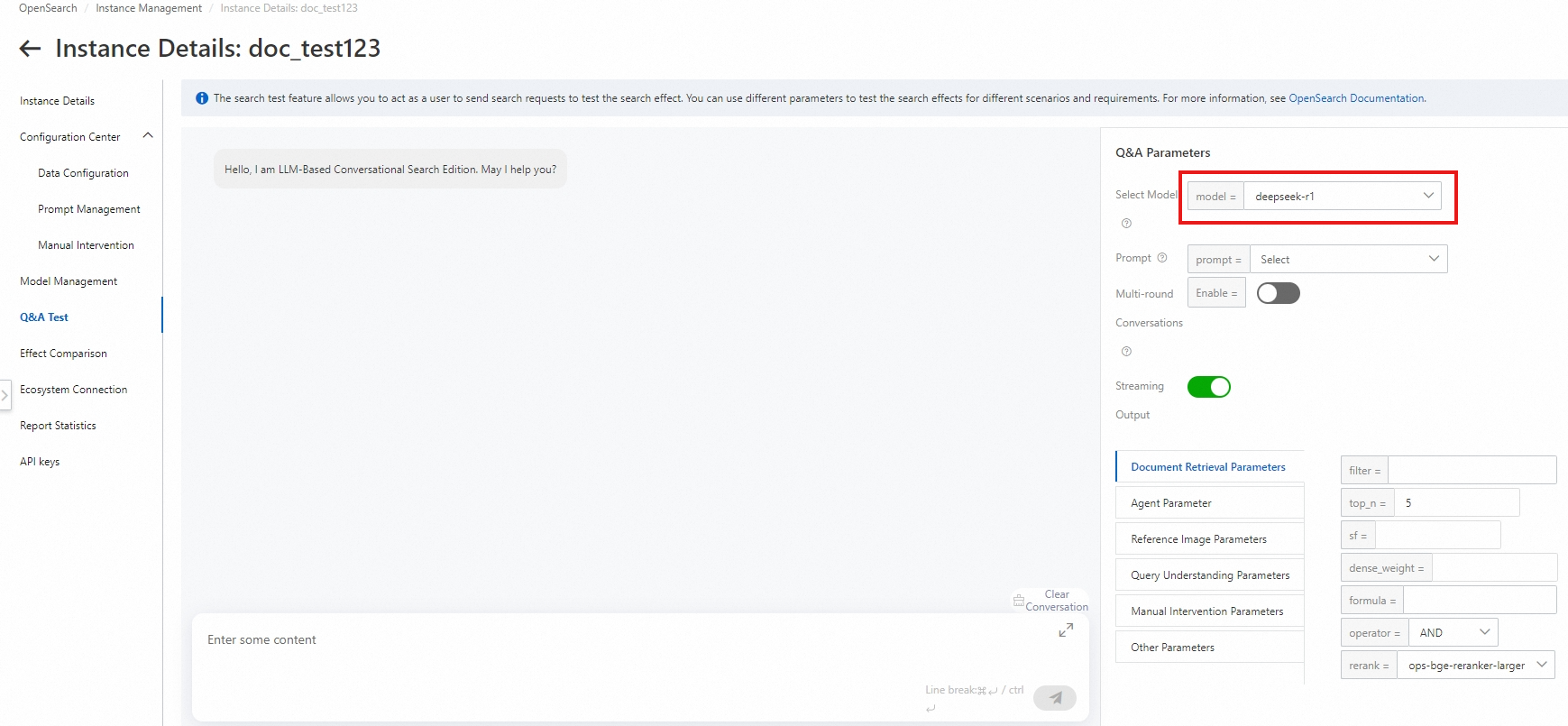
In the left-side navigation pane, click Q&A Test. In the Q&A Parameters section of the page that appears, set Select Model to deepseek-r1 and configure different values for Prompt and Document Retrieval Parameters, including filter, top_n, and rerank, to test the Q&A performance.
The following table describes the key parameters. For more information, see Parameters.
Parameter | Description |
Prompt | The instruction that you provide to the LLM to clarify requirements and guide the LLM to generate accurate and relevant answers or content. For more information, see Manage prompts. |
Multi-round conversation | Specifies whether to enable the multi-round conversation feature. If you enable the multi-round conversation feature, you must configure the request ID to check whether the questions are asked by the same user. This way, questions from the same user can be identified for multi-round conversations. |
Streaming output | We recommend that you enable streaming output to return intermediate results in real time. This reduces the waiting time. |
filter | The field specified to filter data when documents are retrieved. For example, if you set this parameter to timestamp>1356969600, documents whose timestamps are later than January 1, 2013 are queried. |
top_n | The number of documents to be retrieved. Default value: 5. |
Perform RAG-based Q&A by using SDKs
After you complete the performance test, perform RAG-based Q&A by using SDKs in application systems. To update a knowledge base, you can import documents in the OpenSearch console or import structured documents and unstructured documents by using SDKs.
Obtain an AccessKey Pair
Before you install and use an SDK, make sure that you obtain an AccessKey pair. For more information, see Create an AccessKey pair. When you use an SDK to access an Alibaba Cloud service, the initiated request includes the AccessKey ID and the signature that is generated to encrypt the request by using the AccessKey secret. In this case, the AccessKey pair is used for identity verification and request validity verification.
Move the pointer over the profile icon in the upper-right corner of the OpenSearch console and click AccessKey.
On the AccessKey page, view the AccessKey pair.

If the AccessKey list is empty or no AccessKey pair is enabled, create an AccessKey pair. For more information, see Create an AccessKey pair.
If you use a RAM user to access the Alibaba Cloud service, make sure that the AliyunOpenSearchFullAccess policy is attached to the RAM user.
Select a development language
Java
Step 1: Configure the Java environment
Step 2: Obtain the parameters
Callling API operations by using SDKs depends on the following key parameters:
AppName: the name of the application.
host: the endpoint of the application API.
Step 3: Call the API operations
Run the following sample code:
package com.aliyun.opensearch;
import com.aliyun.opensearch.OpenSearchClient;
import com.aliyun.opensearch.sdk.generated.OpenSearch;
import com.aliyun.opensearch.sdk.generated.commons.OpenSearchClientException;
import com.aliyun.opensearch.sdk.generated.commons.OpenSearchException;
import com.aliyun.opensearch.sdk.generated.commons.OpenSearchResult;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class LLMSearch {
private static String appName = "Your application name";
private static String host = "Your API";
private static String accesskey = "Your AccessKey ID";
private static String secret = "Your AccessKey Secret";
private static String path = "/apps/%s/actions/knowledge-search";
public static void main(String[] args) {
String appPath = String.format(path, appName);
//ApiReadTimeOut
OpenSearch openSearch = new OpenSearch(accesskey, secret, host);
openSearch.setTimeout(90000);
OpenSearchClient openSearchClient = new OpenSearchClient(openSearch);
Map<String, String> params = new HashMap<String, String>() {{
put("format", "full_json");
put("_POST_BODY", "{\"question\":{\"text\":\"怎么充电\",\"type\":\"TEXT\",\"session\":\"\"},\"options\":{\"retrieve\":{\"doc\":{\"filter\":\"\",\"top_n\":5,\"sf\":\"\",\"dense_weight\":\"0.7\",\"formula\":\"\",\"operator\":\"AND\"},\"entry\":{\"sf\":\"\"},\"image\":{\"sf\":\"\",\"dense_weight\":\"0.7\"},\"qp\":{\"query_extend\":false,\"query_extend_num\":5},\"return_hits\":false,\"rerank\":{\"enable\":true,\"model\":\"ops-bge-reranker-larger\"}},\"chat\":{\"stream\":true,\"prompt_config\":{\"attitude\":\"normal\",\"rule\":\"detailed\",\"noanswer\":\"sorry\",\"language\":\"Chinese\",\"role\":false,\"role_name\":\"AI小助手\",\"out_format\":\"text\"},\"agent\":{\"tools\":[]},\"csi_level\":\"strict\",\"history_max\":\"\",\"link\":\"false\",\"model\":\"deepseek-r1\",\"model_generation\":\"\"}}}");
}};
try {
OpenSearchResult openSearchResult = openSearchClient
.callAndDecodeResult(appPath, params, "POST");
System.out.println("RequestID=" + openSearchResult.getTraceInfo().getRequestId());
System.out.println(openSearchResult.getResult());
} catch (
OpenSearchException e) {
System.out.println("RequestID=" + e.getRequestId());
System.out.println("ErrorCode=" + e.getCode());
System.out.println("ErrorMessage=" + e.getMessage());
} catch (
OpenSearchClientException e) {
System.out.println("ErrorMessage=" + e.getMessage());
}
}
}Python
Step 1: Configure the Python environment
(Optional) Configure a virtual environment
Step 2: Obtain the parameters
Calling API operations by using SDKs depends on the following key parameters:
app_name: the name of the application.
endpoint: the endpoint of the application API.
Step 3: Call the API operations
For more information about BaseRequest, see Sample code for the Python client.
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import time, os
from typing import Dict, Any
from Tea.exceptions import TeaException
from Tea.request import TeaRequest
from alibabacloud_tea_util import models as util_models
from BaseRequest import Config, Client
class LLMSearch:
def __init__(self, config: Config):
self.Clients = Client(config=config)
self.runtime = util_models.RuntimeOptions(
connect_timeout=10000,
read_timeout=90000,
autoretry=False,
ignore_ssl=False,
max_idle_conns=50,
max_attempts=3
)
self.header = {}
def searchDoc(self, app_name: str,body:Dict, query_params: dict={}) -> Dict[str, Any]:
try:
response = self.Clients._request(method="POST", pathname=f'/v3/openapi/apps/{app_name}/actions/knowledge-search',
query=query_params, headers=self.header, body=body, runtime=self.runtime)
return response
except TeaException as e:
print(e)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Specify the endpoint of the application API. Remove the http:// prefix from the value.
endpoint = "<endpoint>"
# Specify the request protocol. Valid values: HTTPS and HTTP.
endpoint_protocol = "HTTP"
# Specify your AccessKey pair.
# Obtain the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret from environment variables.
# You must configure environment variables before you run this code. For more information, see the "Configure an AccessKey pair as environment variables" section of this topic.
access_key_id = os.environ.get("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID")
access_key_secret = os.environ.get("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET")
# Specify the authentication method. Default value: access_key. The value sts indicates authentication based on RAM and Security Token Service (STS).
# Valid values: sts and access_key.
auth_type = "access_key"
# If you use authentication based on RAM and STS, you must configure the security_token parameter. You can call the AssumeRole operation of Alibaba Cloud RAM to obtain an STS token.
security_token = "<security_token>"
# Configure common request parameters.
# The type and security_token parameters are required only if you use the SDK as a RAM user.
Configs = Config(endpoint=endpoint, access_key_id=access_key_id, access_key_secret=access_key_secret,
security_token=security_token, type=auth_type, protocol=endpoint_protocol)
# Create an OpenSearch LLM-Based Conversational Search Edition instance.
# Replace <Application name> with the name of your OpenSearch LLM-Based Conversational Search Edition instance.
ops = LLMSearch(Configs)
app_name = "<Application name>"
# --------------- Search for documents ---------------
docQuery = {"question": {"text": "Search", "type": "TEXT"}, "options": {"chat": {"model": "deepseek-r1"}}}
res1 = ops.searchDoc(app_name=app_name, body=docQuery)
print(res1)