Container Registry Enterprise Edition provides a secure and efficient automated continuous integration process from source code to container images. Container Registry Enterprise Edition also provides the abilities to automatically build images and commit the images to image repositories based on Dockerfile rules. This topic describes how to use a Container Registry Enterprise Edition instance to build a container image.
Prerequisites
A Container Registry Enterprise Edition instance is created. For more information, see the "Step 1: Create a Container Registry Enterprise Edition instance" section of the Push an image to a Container Registry Enterprise Edition instance and pull an image from the instance topic.
A Dockerfile that is used to build images is created.
Background information
The image building service of Container Registry features security, stability, and intelligent acceleration:
Security: To ensure security, the system distributes each image building task to an environment that is exclusive to an Alibaba Cloud account.
Stability: If you use a source code repository to build multiple images, the time used for each image building task is stable because the image building tasks are run on the environment that is exclusive to your Alibaba Cloud account.
Intelligent acceleration:
By default, the system uses the efficient building tool BuildKit. BuildKit has robust building capabilities, especially for multi-stage building scenarios, and supports rich building features.
The system hosts common base images. During image building, the system can use the base images without the need to pull images. The base images help reduce the building time period.
The system can use remote caches to accelerate image building.
Container Registry supports multiple code hosting platforms and accelerated image generation.
Code hosting platforms: The following table lists the supported code hosting platforms.
Code hosting platform
Version of the code hosting platform
Authentication method for binding
Limit on triggering image building
Gitee
All
Gitee OAuth authentication
None
GitHub
GitHub developer version
GitHub OAuth authentication
None
GitLab
All
Personal access token
None
Bitbucket
All
Gitee OAuth authentication
None
Accelerated image generation: The system allows you to load resources of a container image on demand. The accelerated version of the container image is automatically generated after the container image is pushed. For more information, see Load resources of a container image on demand.
Step 1: Bind your instance to a source code hosting platform
Before you build images, you must bind your instance to a source code hosting platform. For more information, see Bind a source code hosting platform.
You cannot build images from an on-premises code repository.
For information about how to bind a private GitLab code repository in a virtual private cloud (VPC), see Build a container image in a VPC.
Step 2: Create a namespace
Log on to the Container Registry console.
In the top navigation bar, select a region.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Instances.
On the Instances page, click the Container Registry Enterprise Edition instance for which you want to create a namespace.
In the left-side navigation pane of the management page of the Enterprise Edition instance, choose .
On the Namespace page, click Create Namespace.
In the Create Namespace dialog box, configure Namespace, Automatically Create Repository, and Default Repository Type. Then, click Confirm.
Step 3: Create an image repository
Accelerated images can only be built on Container Registry Advanced Edition instances. We recommend that you upgrade Basic Edition instances to Advanced Edition instances.
Create an image repository and bind it to a code repository. All images that are generated from the code repository are pushed to the image repository.
Log on to the Container Registry console.
In the top navigation bar, select a region.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Instances.
On the Instances page, click the Enterprise Edition instance that you want to manage.
In the left-side navigation pane of the management page of the Enterprise Edition instance, choose .
- On the Repositories page, click Create Repository.
In the Repository Info step, configure the Namespace, Repository Name, Repository Type, Tags, Accelerated Images, Summary, and Description parameters. Then, click Next.
In the Code Source step, configure Code Source, Build Settings, and Build Rules, and then click Create Repository.
Parameter
description
Code Source
The code source.
Build Settings
Automatically Build Images When Code Changes: The building rule is automatically triggered when code is committed from a branch.
Build With Servers Deployed Outside Chinese Mainland: Images are built on servers outside the Chinese mainland and then pushed to a repository in the specified region. If the Dockerfile used in your project must be downloaded from a site outside the Chinese mainland but the cross-border network connection is unstable, you can enable Build With Servers Deployed Outside Chinese Mainland.
Build Without Cache: The system pulls the base image from the source code repository each time an image is built. This may slow down the building process. You can disable Build Without Cache to accelerate the image building.
On the Repositories page, click the created image repository. If Build is displayed in the left-side navigation pane of the repository management page, the image repository is bound to the source code repository.
Step 4: Build an image
If you cannot find Build on the repository management page, the Enterprise Edition instance fails to be bound to the code source hosting platform. You can refer to Step 1 to rebind the instance to the source code hosting platform.
Log on to the Container Registry console.
In the top navigation bar, select a region.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Instances.
On the Instances page, click the Enterprise Edition instance that you want to manage.
In the left-side navigation pane of the management page of the Container Registry Enterprise Edition instance, choose .
On the Repositories page, find the created image repository and click Manage in the Actions column.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Build. In the Build Rules section, click Add Build Rule. In the Build Information step of the Add Build Rule wizard, configure parameters and then click Next. The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Description
Type
Specify the type of the source code repository. Valid values: Branch and Tag.
Branch/Tag
Select or enter a branch or a tag. Regular expressions are supported. If you specify the release-(?<imageTag>\w*) regular expression, the system automatically builds an image of V1 when the source code in the release-v1 branch is updated. You cannot manually build the image. For more information about how to specify regular expressions, see Use regular expressions in named capturing groups.
NoteAfter you specify regular expressions, images can be built only by the system. You cannot manually build images.
Build Context Directory
Specify the directory in which the Dockerfile resides. This is the subdirectory of the branch or tag directory. For example, if the branch directory is master/ and the Dockerfile is in the master/ directory, the value is master/Dockerfile.
Dockerfile Filename
Specify the name of the Dockerfile. The default name is Dockerfile.
In the Tag step, configure the parameters, click Save, and then click Next.
NoteClick Add Configuration to add image tags. You can add up to three image tags.
Parameter
Description
Image Tag
The tag of the image. Example: latest. You can enable named capturing groups. For example, if you specify a named capturing group for Branch/Tag, you can use the captured content.
Build Time
The time (UTC+8) when source code is pushed. Example: 20201015 or 202010151613.
NoteThis parameter is optional. If you set this parameter, only the system can build images. You cannot manually build images.
Commit ID
The number of characters to be obtained from the commit ID of the most recently pushed code. By default, the first six characters are used. You can adjust the slider to change the number of characters.
NoteThis parameter is optional. If you set this parameter, only the system can build images. You cannot manually build images.
In the Build Configurations step, configure parameters and then click Confirm. The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Description
Build Architecture
The architecture for which you want to build images. You can select multiple architectures. If you select multiple architectures, multiple container images for the architectures are built for each image tag.
Build Parameters
The runtime parameters of the image building. Each building parameter is a key-value pair that is case-sensitive. You can configure a maximum of 20 building parameters. You can set a building parameter to modify the environment variables in a Dockerfile and make the same Dockerfile show different status.
Trigger the image building rule.
You can use one of the following methods to trigger an image building rule:
In the Build Rules section of the Build page, find the image building rule and click Build in the Actions column.
Submit code to the master branch of the source code repository to trigger the building rule.
NoteIn the Build Log section of the Build page, find the triggered image building task and click Cancel in the Actions column to cancel the image building task.
In the Build Log section of the Build page, find the triggered image building task and click Log in the Actions column to view the image building log.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Image Tag. If the image that you created is displayed, the image is built.
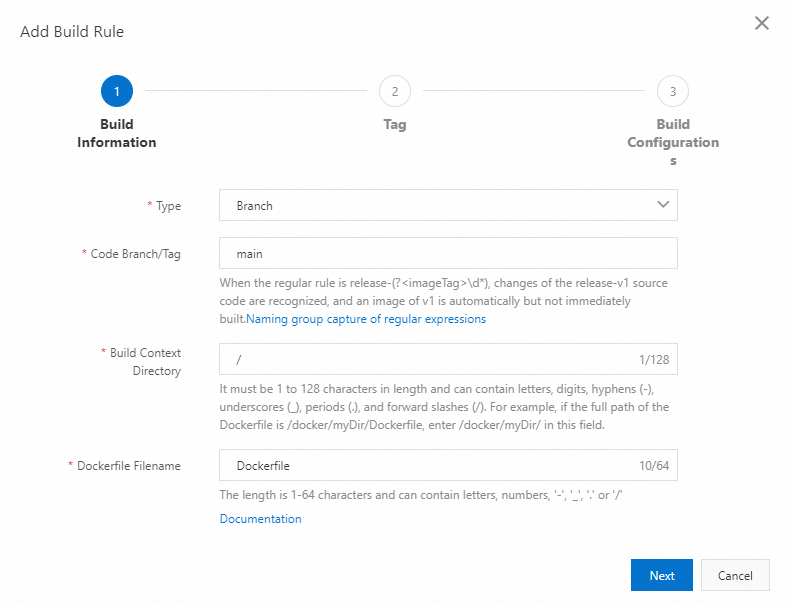
Example 1: Build an image based on the branch that is named main (you can manually build images)
Configure the building rule based on the following settings:
Type: Branch
Branch/Tag: main
Build Context Directory: /
Dockerfile Filename: Dockerfile
Image Tag: latest
When you click Build or the source code in the main branch is updated, the system builds an image. The file named Dockerfile in the / directory of the main branch is used to build the image. The tag of the created image is latest. The following figure shows the configuration of the building rule.
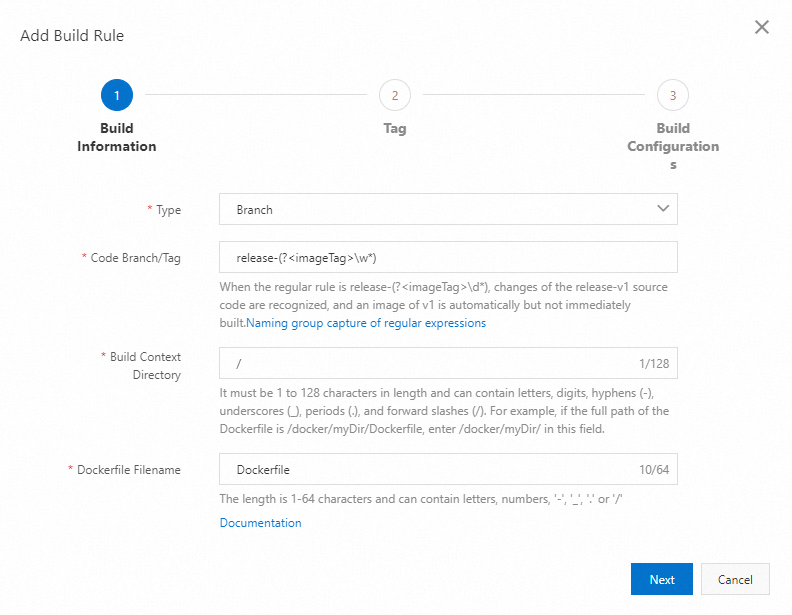
Example 2: Build an image based on the branch that matches a regular expression (you cannot manually build images)
Configure the building rule based on the following settings:
Type: Branch
Branch/Tag: release-(?<imageTag>\w*)
Build Context Directory: /
Dockerfile Filename: Dockerfile
Image Tag: ${imageTag}
Build Time: yyyyMMddHHmm
Commit ID: 30
If the source code is updated in the branch whose name starts with release-, the system automatically builds an image. The file named Dockerfile in the / directory of the branch is used to build the image.
For example, if the source code in the branch whose name starts with release-v1 is updated, the regular rule of release-(?<imageTag>\w*) captures v1 in the branch name, sends v1 to the imageTag variable, and uses v1 in the image tag. In this example, the tag of the created image is v1-202010151625-d4ef3dc3b77a011a5779eec7efdd45. The following figure shows the configuration of the building rule.
What to do next
You can perform the following operations after the image is built:
You can pull the image from Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) clusters without using secrets. For more information, see Use the aliyun-acr-credential-helper component to pull images without using a Secret.
You can use the image to create applications in ACK clusters. For more information, see Create a stateless application by using a Deployment.
You can use the P2P acceleration feature in ACK clusters to accelerate image pulling. For more information, see Use the P2P acceleration feature in ACK Serverless and ACK clusters.