By Wei Li, Apache RocketMQ Committer, RocketMQ Python Client Project Owner, Apache Doris Contributor, and TencentDB Development Engineer
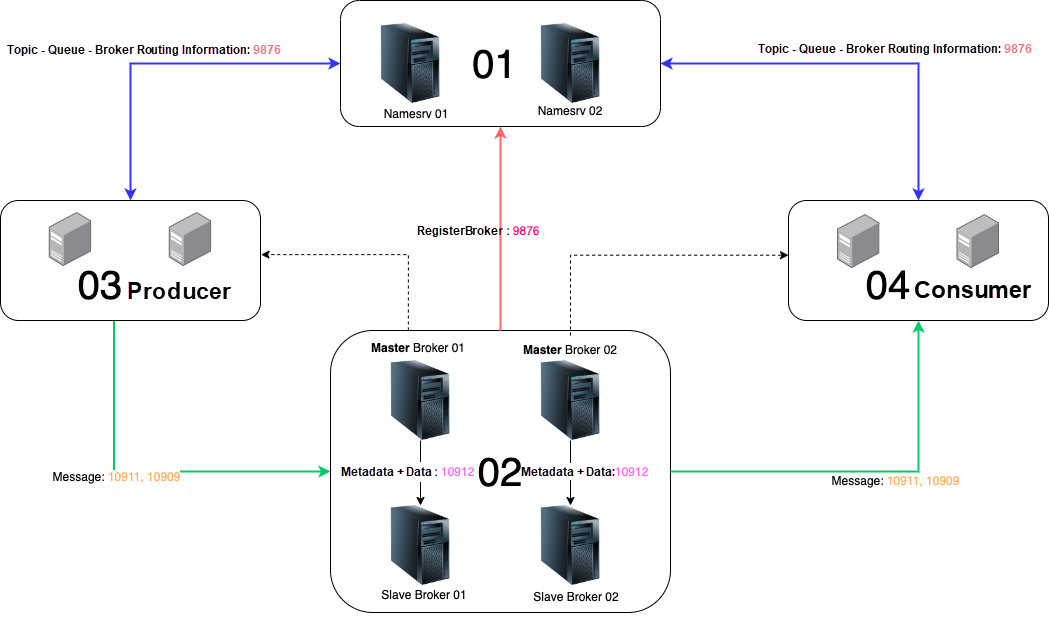
The following table briefly describes the communication between each component in 4.9.X.
| Component and data flow | Description |
| Namesrv | A stateless application that stores the topic routing information. Topic route: topic-queue-broker. |
| Broker | A stateful application that handles data computation and storage. The data it computes includes producer requests, consumer requests, management requests, and broker system services, such as index building and message expiry. The data it stores includes messages and indexes. |
| Broker -> namesrv | The broker periodically reports the broker information and the topic information in the current broker to the namesrv. |
| Producer | An application that produces messages. |
| Producer <-> namesrv | The producer obtains the topic routing information that includes the broker IP address from the namesrv. |
| Producer <-> broker | The producer sends messages directly to the broker by using topic routing information. The producer periodically sends heartbeats to the broker to report the current producer instance information. |
| Consumer | An application that consumes messages. |
| Consumer <-> namesrv | The consumer obtains the topic routing information that includes the broker IP address from the namesrv. |
| Consumer <-> broker | The consumer pulls messages from the specified broker for consumption by using topic routing information. The consumer periodically sends heartbeats to the broker to report the current consumer instance information. |
Consumer consumes messages. Consumer <-> namesrv
Consumer <-> broker
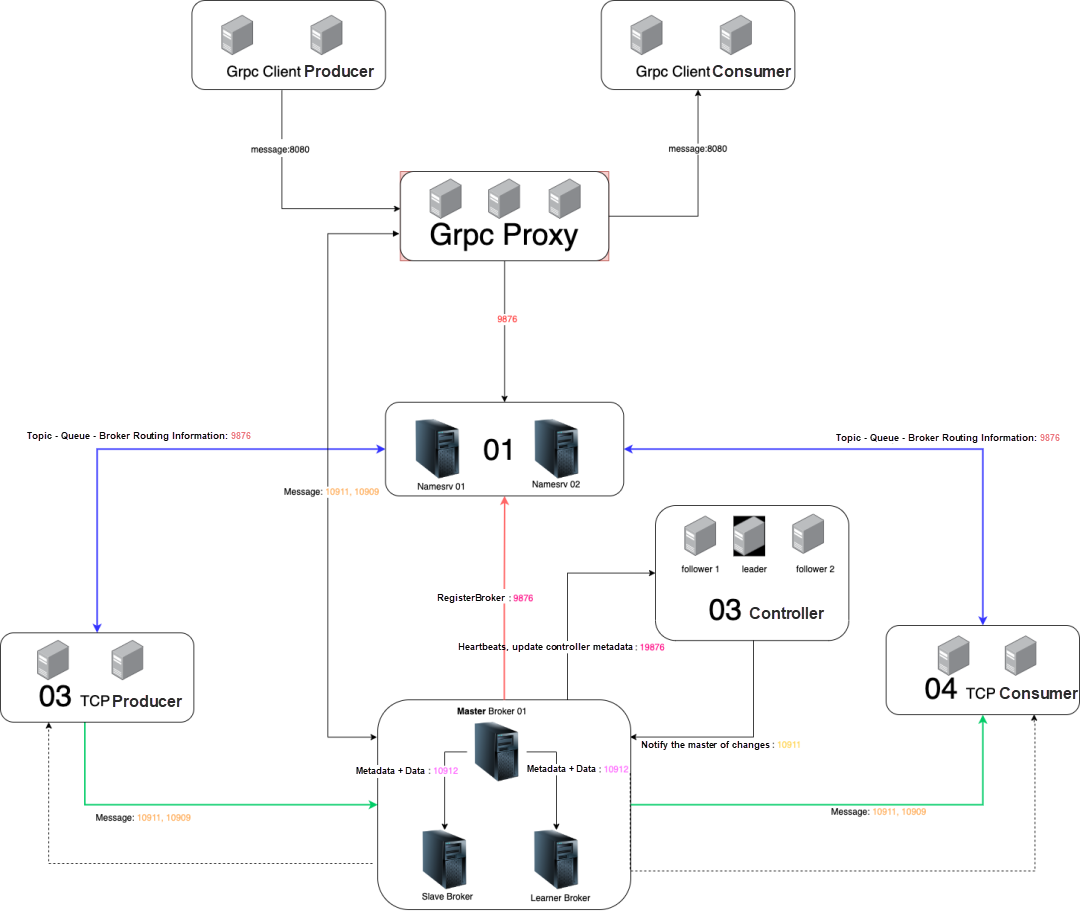
The following table briefly describes the communication between each component in 5.0.0.
| Component and data flow | Description |
| Namesrv | A stateless application that stores the topic routing information. Topic route: topic-queue-broker. In 5.0.0, the namesrv supports controller modules. If you set the enableControllerInNamesrv value to true, a controller instance gets embedded and started in the namesrv process. |
| Broker | A stateful application that handles data computation and storage. The data it computes includes producer requests, consumer requests, management requests, and broker system services, such as index building and message expiry. The data it stores includes messages and indexes. In 5.0.0, the broker can perform primary, secondary, and learner switchover. If you set the asyncLearner value to true, the broker switches to the learner mode. It only synchronizes data and does not elect the master. |
| Broker -> namesrv | The broker periodically reports the broker information and the topic information in the current broker to the namesrv. |
| Remoting producer | An application that produces messages. |
| Remoting producer <-> namesrv | The producer obtains the topic routing information that includes the broker IP address from the namesrv. |
| Remoting producer <-> broker | The producer sends messages directly to the broker by using topic routing information. The producer periodically sends heartbeats to the broker to report the current producer instance information. |
| Remoting consumer | An application that consumes messages. |
| Remoting consumer <-> namesrv | The consumer obtains the topic routing information that includes the broker IP address from the namesrv. |
| Remoting consumer <-> broker | The consumer pulls messages from the specified broker for consumption by using topic routing information. The consumer periodically sends heartbeats to the broker to report the current consumer instance information. |
| New module in 5.0.0, controller | Similar to the Kafka controller, the RocketMQ controller is responsible for electing the broker master and notifying all brokers. |
| New module in 5.0.0, broker <-> controller | The broker periodically reports the broker information to the Controller. The broker synchronizes the replica status. After the controller elects a new broker master, it notifies all brokers. |
| New Module in 5.0.0, proxy | A stateless application. The new client accesses the proxy through the gRPC interface to send and subscribe to messages. The Remoting Protocol is supported in the community. The proxy supports brokers. If you set the proxyMode value to LOCAL, a broker instance gets started in the proxy process. |
| New module in 5.0.0, proxy <-> broker | The proxy communicates with the broker by using the Remoting Protocol. You can use the proxy as a remoting client. |
| New Module in 5.0.0, new client | The new client supports production, consumption, and management features. It also supports the gRPC Protocol. |
| New module in 5.0.0, new client <-> proxy | The new client accesses the proxy to send, subscribe to, and manage messages. |
Remoting consumers consume messages. Remoting consumers <-> namesrv
Controller in RocketMQ is similar to Kafka Controller, responsible for electing and notifying the Broker Master.
Broker <-> Controller
Proxy is a stateless application. The new clients access the Proxy through the gRPC interface to send and receive messages.
Proxy supports embedding Broker.
If proxyMode=LOCAL is set, a Broker instance will be started within the Proxy process.
Proxy <-> BrokerProxy
Communicates with the Broker using the Remoting protocol, where Proxy acts as a Remoting client.
New Client
A new client that supports production, consumption, and management functions. Currently supports the gRPC Protocol.
New Client <-> Proxy
The new client accesses the Proxy for message sending, receiving, and management.
How to Configure TLS-encrypted Transmission in RocketMQ 5.0?

508 posts | 48 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Native - June 7, 2024
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - November 20, 2023
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - February 15, 2023
Alibaba Cloud Native - June 12, 2024
Alibaba Cloud Native - November 13, 2024
Alibaba Cloud Native - June 7, 2024

508 posts | 48 followers
Follow ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ
ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ
ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ is a distributed message queue service that supports reliable message-based asynchronous communication among microservices, distributed systems, and serverless applications.
Learn More Architecture and Structure Design
Architecture and Structure Design
Customized infrastructure to ensure high availability, scalability and high-performance
Learn More Function Compute
Function Compute
Alibaba Cloud Function Compute is a fully-managed event-driven compute service. It allows you to focus on writing and uploading code without the need to manage infrastructure such as servers.
Learn More DevOps Solution
DevOps Solution
Accelerate software development and delivery by integrating DevOps with the cloud
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud Native Community