By Aaron Handoko, Solution Architect Alibaba Cloud
To create intelligent search, OpenSearch is a one-stop Solution as a Service (SaaS) technology that is applicable to industry-specific search scenarios and provides a dedicated conversational search service for enterprises. There are 5 edition of Open Search and we are going to use LLM-Based Conversational Search Edition in this blog.

The diagram above is the architecture of the LLM Based Open Search including how data is being retrieved and processed as well as how the vector search algorithm is used to get the most relevant content to the user’s question.
LLM-Based Conversational Search Edition can automatically generate conversational search results in various formats such as texts, reference images, and reference links based on business data. The conversational search service is intelligent and high-quality.
Instance Name:
Storage Capacity: The amount of GB needed for dataset
In this blog we will show how to manage dataset for LLM Conversational Search using
1) OpenSearch Console
2) SDK Python
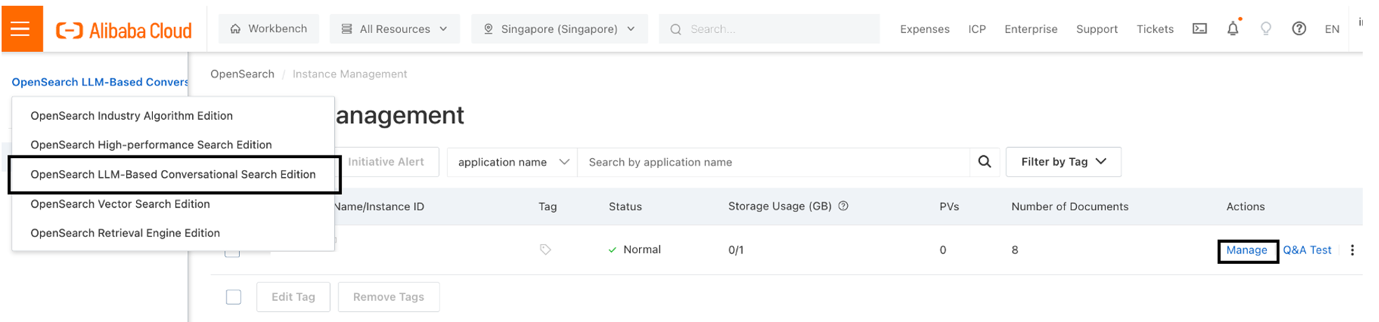
Figure 1. The Console of OpenSearch
A. Choose the Data Configuration on the left-hand side. You can choose to import data using API or File. Choose Import File then choose between Structured Data (data example can be found here) and Unstructured Data (pdf, docx, doc, html). Upload the data that you want to set as the dataset.
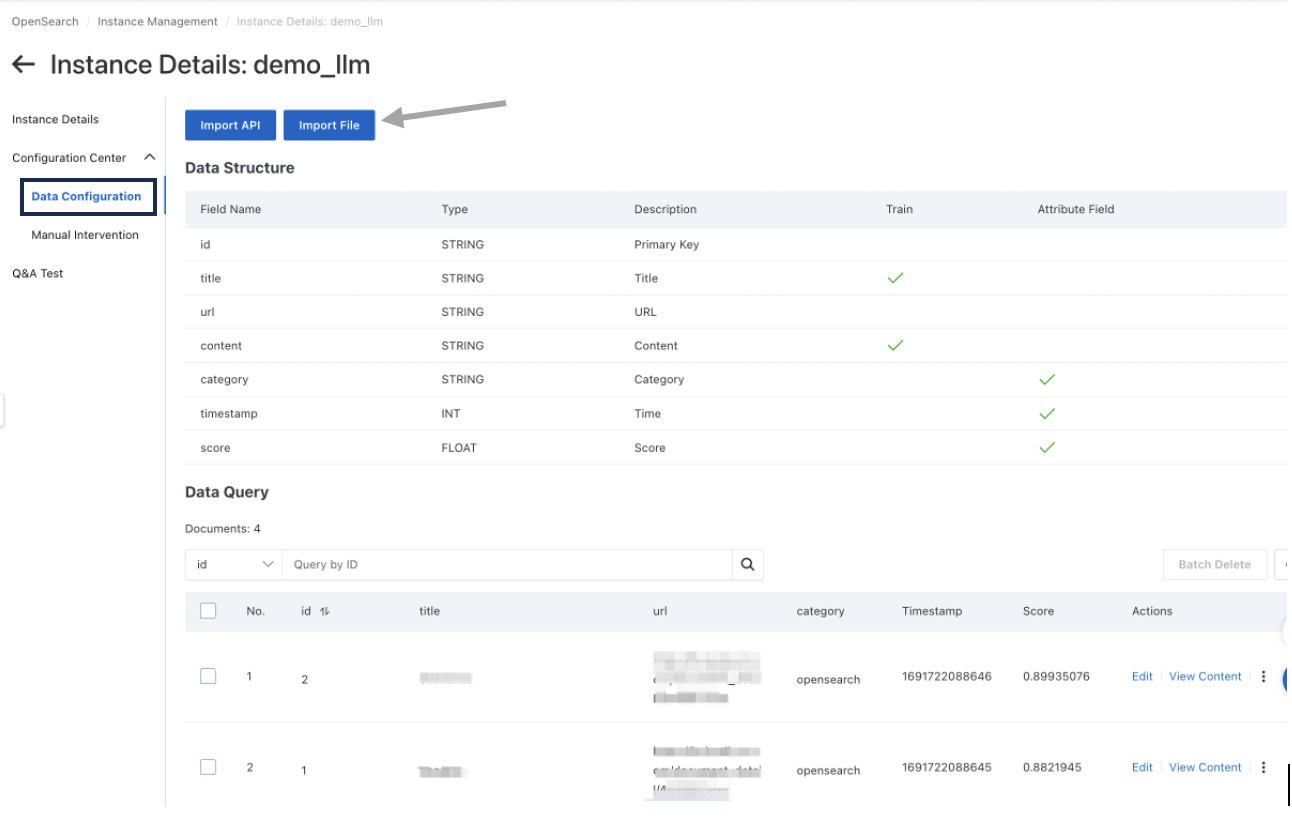
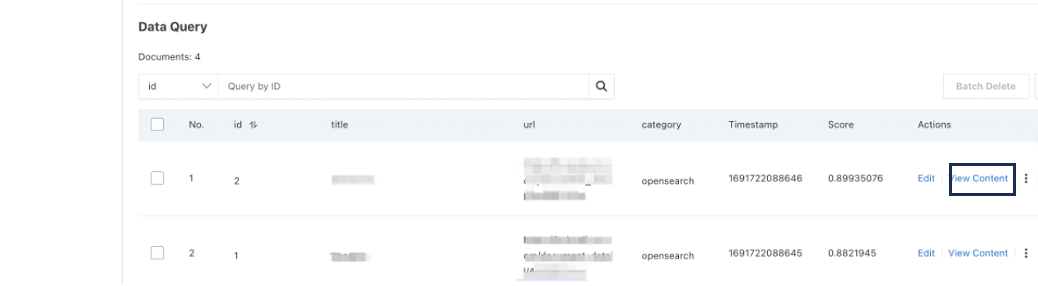
B. After the dataset is uploaded, the data will be shown in the console. Check the content of the data by clicking View Content.
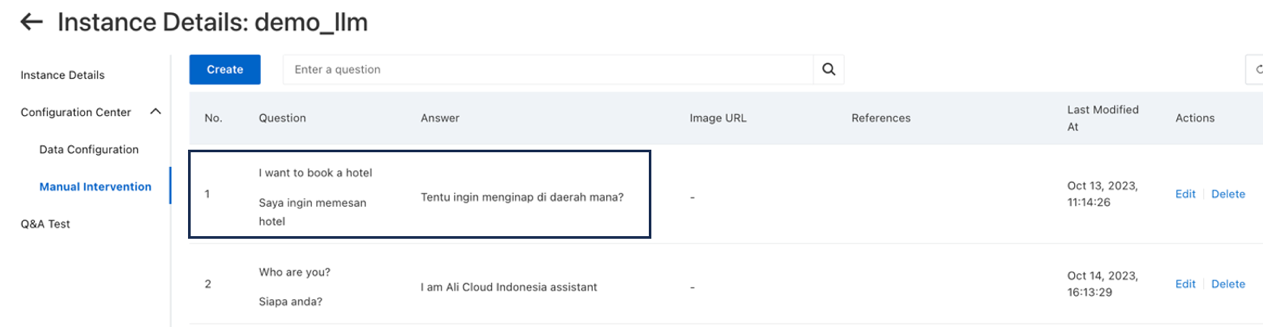
C. We can also set up manual intervention if we want the LLM to provide specific answer to a question. Click Create. The picture below shows the example of question and answer.
D. Q&A Test. This is the platform to do testing for the Conversational Search Edition by typing the questions on the box provided. On the right-hand side there are numerous parameters that you can choose.
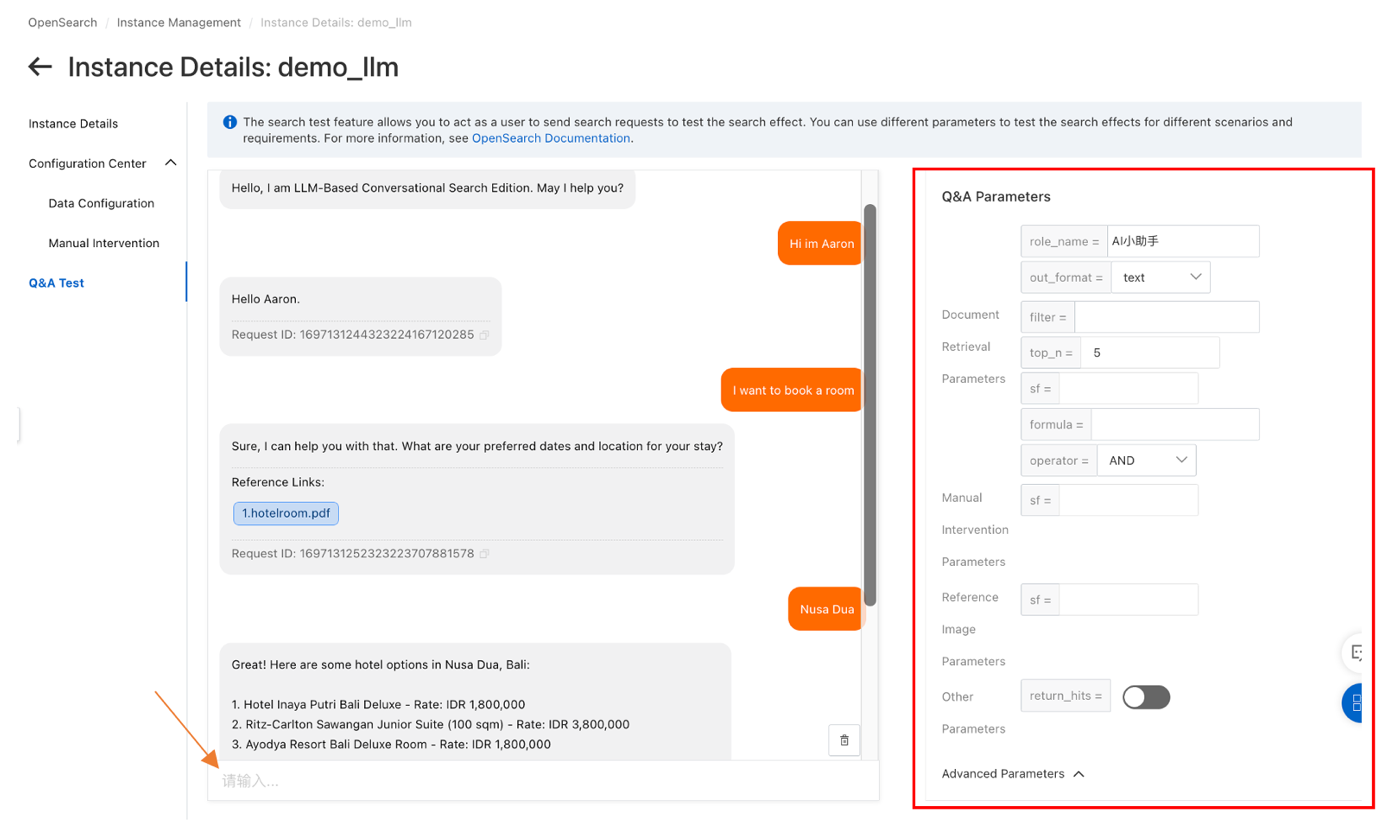
Q&A Parameters information can be found here.
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| Model | The LLM model that you can use. In Singapore region you can choose openbuddy_llama2_13b and opensearch-falcon-7b. |
| Multi-round Conversations (session) | Conversation that understands multiple interaction with the customer. The number of questions needed for the model to make a decision. |
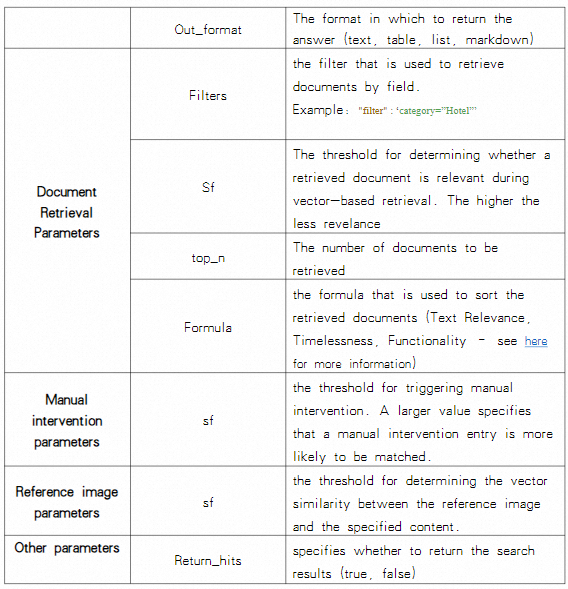
Extended Parameters information can be found here.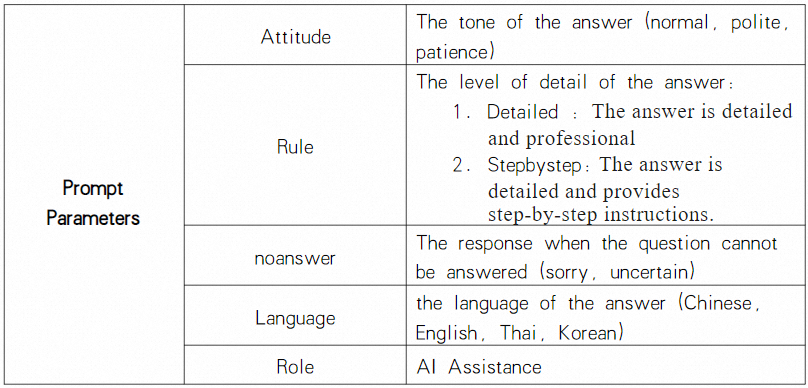
In this blog we will integrate LLM using Python SDK. For Java or PHP language can be found here. [Java, PHP]
a) Clone the github repository containing helper code and simple application code
git clone https://github.com/aaronhandoko01/OpenSearchLLM.git
b) Install the necessary libraries
pip install alibabacloud_tea_util
pip install alibabacloud_opensearch_util
pip install alibabacloud_credentials
c) Create environmental variable for the Alibaba Cloud Access Key and Secret.
i) For Mac or Ubuntu users we can run the following code
export ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID=<access_key_id>
export ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET=<access_key_secret>
ii) For Windows user we can do the following
1) Create an environment variable file, add the ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID and ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables to the file, and then set the environment variables to your AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret.
2) Restart Windows for the AccessKey pair to take effect.
d) BaseRequest.py is a helper code to configure the SDK call. The code below can be found in the github or here.
import time
from typing import Dict, Any
from Tea.core import TeaCore
from Tea.exceptions import TeaException, UnretryableException
from Tea.model import TeaModel
from Tea.request import TeaRequest
from alibabacloud_credentials import models as credential_models
from alibabacloud_credentials.client import Client as CredentialClient
from alibabacloud_opensearch_util.opensearch_util import OpensearchUtil
from alibabacloud_tea_util import models as util_models
from alibabacloud_tea_util.client import Client as UtilClient
class Config(TeaModel):
"""
Config
The environment-related configurations.
"""
def __init__(
self,
endpoint: str = None,
protocol: str = None,
type: str = None,
security_token: str = None,
access_key_id: str = None,
access_key_secret: str = None,
user_agent: str = ""
):
self.endpoint = endpoint
self.protocol = protocol
self.type = type
self.security_token = security_token
self.access_key_id = access_key_id
self.access_key_secret = access_key_secret
self.user_agent = user_agent
class Client:
"""
OpensearchClient
The OpenSearch client that is used to specify request parameters and send the request.
"""
_endpoint: str = None
_protocol: str = None
_user_agent: str = None
_credential: CredentialClient = None
def __init__(self, config: Config):
if UtilClient.is_unset(config):
raise TeaException(
{
'name': 'ParameterMissing',
'message': "'config' can not be unset"
}
)
if UtilClient.empty(config.type):
config.type = 'access_key'
credential_config = credential_models.Config(
access_key_id=config.access_key_id,
type=config.type,
access_key_secret=config.access_key_secret,
security_token=config.security_token
)
self._credential = CredentialClient(credential_config)
self._endpoint = config.endpoint
self._protocol = config.protocol
self._user_agent = config.user_agent
def _request(self, method: str, pathname: str, query: Dict[str, Any], headers: Dict[str, str], body: Any, runtime: util_models.RuntimeOptions,) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
Process the request.
:param request: TeaRequest
:param runtime: util_models.RuntimeOptions
:return: Dict[str, Any]
"""
runtime.validate()
_runtime = {
'timeouted': 'retry',
'readTimeout': runtime.read_timeout,
'connectTimeout': runtime.connect_timeout,
'httpProxy': runtime.http_proxy,
'httpsProxy': runtime.https_proxy,
'noProxy': runtime.no_proxy,
'maxIdleConns': runtime.max_idle_conns,
'retry': {
'retryable': runtime.autoretry,
'maxAttempts': UtilClient.default_number(runtime.max_attempts, 3)
},
'backoff': {
'policy': UtilClient.default_string(runtime.backoff_policy, 'no'),
'period': UtilClient.default_number(runtime.backoff_period, 1)
},
'ignoreSSL': runtime.ignore_ssl
}
_last_request = None
_last_exception = None
_now = time.time()
_retry_times = 0
while TeaCore.allow_retry(_runtime.get('retry'), _retry_times, _now):
if _retry_times > 0:
_backoff_time = TeaCore.get_backoff_time(_runtime.get('backoff'), _retry_times)
if _backoff_time > 0:
TeaCore.sleep(_backoff_time)
_retry_times = _retry_times + 1
try:
_request = TeaRequest()
accesskey_id = self._credential.get_access_key_id()
access_key_secret = self._credential.get_access_key_secret()
security_token = self._credential.get_security_token()
_request.protocol = UtilClient.default_string(self._protocol, 'HTTP')
_request.method = method
_request.pathname = pathname
_request.headers = TeaCore.merge({
'user-agent': UtilClient.get_user_agent(self._user_agent),
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Date': OpensearchUtil.get_date(),
'host': UtilClient.default_string(self._endpoint, f'opensearch-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com'),
'X-Opensearch-Nonce': UtilClient.get_nonce()
}, headers)
if not UtilClient.is_unset(query):
_request.query = UtilClient.stringify_map_value(query)
if not UtilClient.is_unset(body):
req_body = UtilClient.to_jsonstring(body)
_request.headers['Content-MD5'] = OpensearchUtil.get_content_md5(req_body)
_request.body = req_body
if not UtilClient.is_unset(security_token):
_request.headers["X-Opensearch-Security-Token"] = security_token
_request.headers['Authorization'] = OpensearchUtil.get_signature(_request, accesskey_id, access_key_secret)
_last_request = _request
_response = TeaCore.do_action(_request, _runtime)
obj_str = UtilClient.read_as_string(_response.body)
if UtilClient.is_4xx(_response.status_code) or UtilClient.is_5xx(_response.status_code):
raise TeaException({
'message': _response.status_message,
'data': obj_str,
'code': _response.status_code
})
obj = UtilClient.parse_json(obj_str)
res = UtilClient.assert_as_map(obj)
return {
'body': res,
'headers': _response.headers
}
except TeaException as e:
if TeaCore.is_retryable(e):
_last_exception = e
continue
raise e
raise UnretryableException(_last_request, _last_exception)import time, os
from typing import Dict, Any
from Tea.exceptions import TeaException
from Tea.request import TeaRequest
from alibabacloud_tea_util import models as util_models
# from opensearch.V3_cases.doc_search.BaseRequest import Config, Client
from BaseRequest import Config, Client
class LLMSearch:
def __init__(self, config: Config):
self.Clients = Client(config=config)
self.runtime = util_models.RuntimeOptions(
connect_timeout=10000,
read_timeout=10000,
autoretry=False,
ignore_ssl=False,
max_idle_conns=50,
max_attempts=3
)
self.header = {}
def searchDoc(self, app_name: str,body:Dict, query_params: dict={}) -> Dict[str, Any]:
try:
response = self.Clients._request(method="POST", pathname=f'/v3/openapi/apps/{app_name}/actions/knowledge-search',
query=query_params, headers=self.header, body=body, runtime=self.runtime)
return response
except TeaException as e:
print(e)
class LLMDocumentPush:
def __init__(self, config: Config):
self.Clients = Client(config=config)
self.runtime = util_models.RuntimeOptions(
connect_timeout=10000,
read_timeout=10000,
autoretry=False,
ignore_ssl=False,
max_idle_conns=50,
max_attempts=3
)
self.header = {}
def docBulk(self, app_name: str,doc_content: list) -> Dict[str, Any]:
try:
response = self.Clients._request(method="POST",
pathname=f'/v3/openapi/apps/{app_name}/actions/knowledge-bulk',
query={}, headers=self.header,
body=doc_content, runtime=self.runtime)
return response
except Exception as e:
print(e)
def search_llm(app_name, ops, question):
# --------------- Search for documents ---------------
docQuery = {
"question": {
"text": question,
"type": "TEXT",
"session": 10,
# "content": "Legal Agreement Form.pdf"
},
"options": {
"retrieve": {
"doc": {
"disable": False, # Specifies whether to disable the document retrieval feature. Default value: false.
"filter": 'category="Hotel"', # Filters documents based on the specified category during document retrieval. By default, this parameter is left empty.
"sf": 1.3, # The threshold of vector relevance for document retrieval. Default value: 1.3. The greater the value is, the less relevant the retrieved documents are.
"top_n": 5, # The number of documents to be retrieved. Default value: 5. Valid values: (0,50].
"formula" : "", # By default, documents are retrieved based on vector similarity.
# "rerank_size" : 5, # The number of documents to be fine sorted. By default, you do not need to specify this parameter, and the system determines the number of documents to be fine sorted.
"operator":"AND" # The operator between text tokens. In this example, the OR operator is used between text tokens when text documents are retrieved. Default value: AND.
},
"entry": {
"disable": False, # Specifies whether to disable the intervention data retrieval feature. Default value: false.
"sf": 0.3 # The vector relevance for intervention data retrieval. Default value: 0.3.
},
},
"chat": {
"stream" : False, # Specifies whether to enable HTTP chunked transfer encoding. Default value: false.
"disable" : False, # specifies whether to disable the chat model. Default value: false.
"model" : "opensearch-llama2-13b", # The LLM model. Valid values: Qwen and opensearch-llama2-13b.
"prompt_config": {
"attitude": "normal",
"rule": "stepbystep",
"noanswer": "sorry",
"language": "English",
"role": True,
"role_name": "AI Assistant"
# "out_format": "text"
}
},
}}
res1 = ops.searchDoc(app_name=app_name, body=docQuery)
# print("ANSWER ", res1["body"]["result"]["data"][0]["answer"])
return res1["body"]["result"]["data"][0]["answer"]
# print(res1)
def push_doc(app_name, ops):
document = [
{
"fields": {
"id": "1",
"title": "Benefits",
"url": "https://help.aliyun.com/document_detail/464900.html",
"content": "Industry Algorithm Edition: Intelligence: Industry Algorithm Edition provides rich built-in and customized algorithm models and introduces industry retrieval and sorting algorithms based on the search needs of different industries.",
"category": "opensearch",
"timestamp": 1691722088645,
"score": 0.8821945219723084
},
"cmd": "ADD"
},
{
"fields": {
"id": "2",
"title": "Scenarios",
"url": "https://help.aliyun.com/document_detail/464901.html",
"content": "Industry Algorithm Edition: Features: provides industry built-in capabilities such as semantic understanding and machine learning-based algorithms, and supports lightweight custom models and search guidance. This helps you build intelligent search services in a quick manner",
"category": "opensearch",
"timestamp": 1691722088646,
"score": 0.8993507402088953
},
"cmd": "ADD"
}
]
# Delete a record.
deletedocument = {"cmd": "DELETE", "fields": {"id": 2}}
documents = document
res5 = ops.docBulk(app_name=app_name, doc_content=documents)
return res5
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Specify the endpoint of the OpenSearch API. The value does not contain the http:// prefix.
endpoint = "opensearch-ap-southeast-1.aliyuncs.com"
# Specify the request protocol. Valid values: HTTPS and HTTP.
endpoint_protocol = "HTTP"
# Specify your AccessKey pair.
# Obtain the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret from environment variables.
# You must configure environment variables before you run this code. For more information, see the "Configure environment variables" section of this topic.
access_key_id = os.environ.get("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID")
access_key_secret = os.environ.get("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET")
# Specify the authentication method. Default value: access_key. A value of sts indicates authentication based on Resource Access Management (RAM) and Security Token Service (STS).
# Valid values: sts and access_key.
auth_type = "access_key"
# If you use authentication based on RAM and STS, you must specify the security_token parameter. You can call the AssumeRole operation of Alibaba Cloud RAM to obtain an STS token.
security_token = "<security_token>"
# Specify common request parameters.
# The type and security_token parameters are required only if you use the SDK as a RAM user.
Configs = Config(endpoint=endpoint, access_key_id=access_key_id, access_key_secret=access_key_secret,
security_token=security_token, type=auth_type, protocol=endpoint_protocol)
# Create an OpenSearch instance.
app_name = "demo_llm"
# print(res1)
while True:
print("\t\tWELCOME TO CHAT")
print("1. Q&A Feature: ")
print("2. Push Document: ")
choice = int(input("Option: "))
if choice ==1:
ops = LLMSearch(Configs)
print("What can I help?")
while True:
question = input("\n")
if not question.lower() == 'exit':
print("\n\nResponse: ", search_llm(app_name, ops, question))
else:
break
elif choice == 2:
ops = LLMDocumentPush(Configs)
print("STATUS: ", push_doc(app_name, ops))
else:
breakTo push the document into OpenSearch we create LLMDocumentPush class and call the function push_doc. To create Q&A function we create LLMSearch class and use search_llm function. The parameters for the LLM Q&A can be modified in the search_llm function.

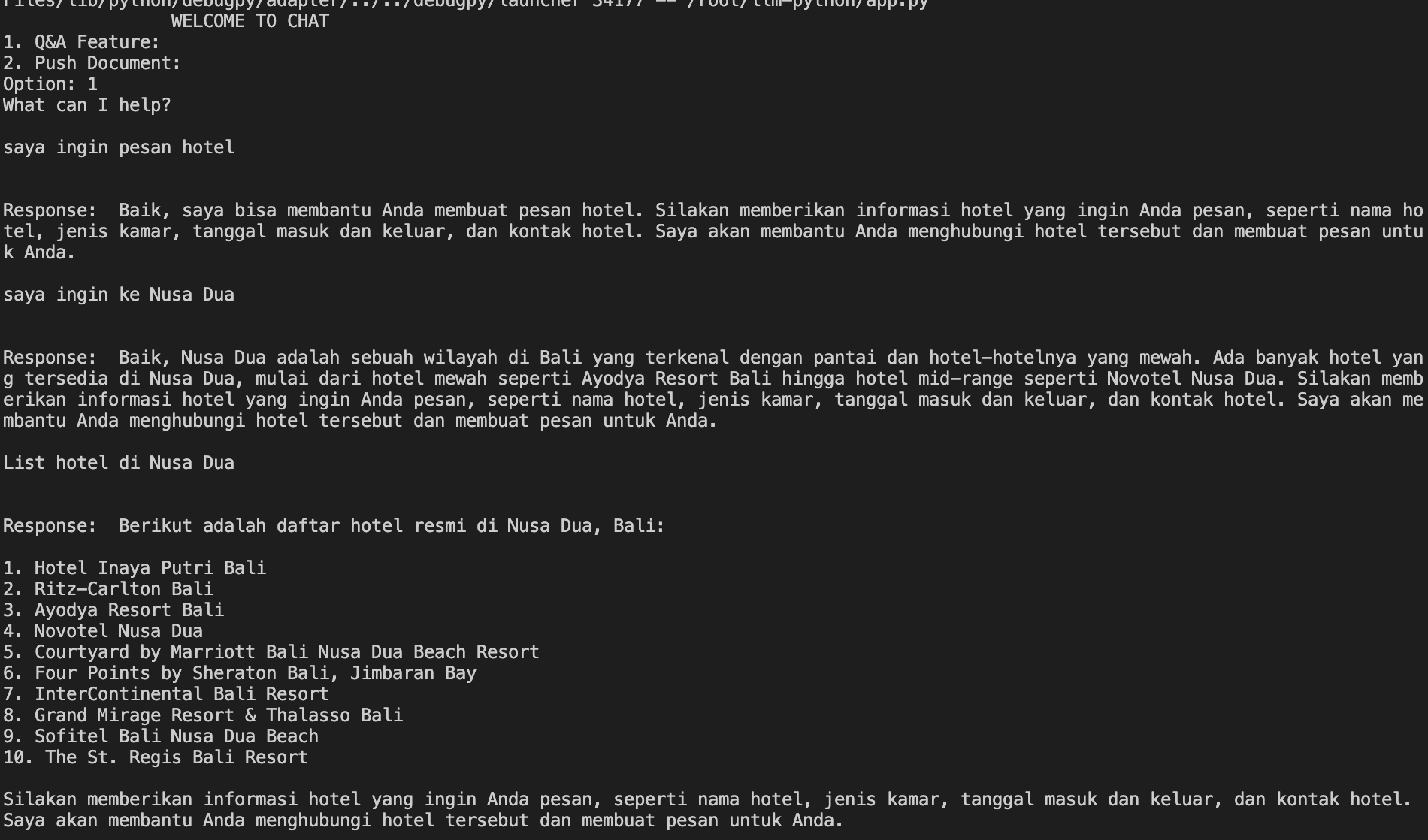
Here is the example of the simple terminal application using Bahasa Indonesia Language:
104 posts | 18 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Indonesia - November 22, 2023
Farruh - March 22, 2024
Alibaba Cloud Community - August 28, 2023
Alibaba Cloud Community - January 4, 2024
Alibaba Cloud Data Intelligence - December 27, 2024
OpenSearch - June 21, 2023
104 posts | 18 followers
Follow OpenSearch
OpenSearch
OpenSearch helps develop intelligent search services.
Learn More EMAS HTTPDNS
EMAS HTTPDNS
EMAS HTTPDNS is a domain name resolution service for mobile clients. It features anti-hijacking, high accuracy, and low latency.
Learn More Tongyi Qianwen (Qwen)
Tongyi Qianwen (Qwen)
Top-performance foundation models from Alibaba Cloud
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud Indonesia
Start building with 50+ products and up to 12 months usage for Elastic Compute Service
Get Started for Free Get Started for Free