By Alex Mungai Muchiri, Alibaba Cloud Tech Share Author. Tech Share is Alibaba Cloud's incentive program to encourage the sharing of technical knowledge and best practices within the cloud community.
By definition, localization is the spread of a product across multiple markets. When localization is at play, market share is always a major consideration factor. Doing it right sends a signal to your target clients that your product offering was designed with their needs and lifestyle in mind. Many surveys have continuously proved that local languages are the first choice for consumers in markets where English is not spoken. It is especially important if it is a software product in question. A recent survey by MediaPost.com yielded the following results:
The same research shows that most buyers, accessing web content in their own language far outweighs the cost of goods. Personally, I have found that most people I know who are living in non-English speaking countries find it hard to cope with the content on local websites. Therefore, most will tell you that they are constantly on the lookout for localized sites. Accordingly, those websites that are better localized. A properly localized website even scores better on search engines.
If you are a website or business owner, you have probably thought about creating a multilingual website for your company or business. For instance, you may be setting up a travel website about museums in Europe that targets Spanish, German, and English speakers. Building such a website requires consideration of the structure, geographic and content of the website.

It is important to consider getting domains that are specific to your target country, which are called top-level domains (TLDs). You can have a domain such as ilovebackpacking.co.uk, ichlieberucksackreisen.de, and irdemochilero.es. The method of using country-specific is also known as geo-targeting and is very useful for targeting those markets.
However, geo-targeting is slightly different from language targeting, a subject that is covered later in this article. For instance, you may have content targeted for German-speaking people in Germany, Switzerland, or even Austria. The TLD method requires that you have a .de TLD for those users. When users are targeted in their own language, they are more likely to trust your website. However, buying domains for all countries may become very expensive especially for a small business. Furthermore, updating and maintaining all those domains is a very tedious process.
If you are looking to localize web content minus all the costs for maintaining multiple domains, consider buying a single domain to host all versions of your website. There are two available options for you in this case:
If you still need for information on subdirectories and subdomains, this article will help you understand the topic better. So, which option should you follow? Geographic targeting or language targeting?
The Set Geographic Target tool in Webmaster Tools is an amazing tool for use in a geographically targeted website. It can help you reach a certain region in the world easily by setting the geographic targets for subdirectories and subdomains. It allows you to make settings such as /es/ for Spain etc. However, geographic targeting is only limited to certain geographic regions of the world. In such a case, language targeting is the better alternative. So, how to go about it?
From a search engine perspective, presenting similar content in multiple languages is not similar to duplicating content. However, an organisation of content is much important in such a case. Following one of the recommended organization methods above would save much of the problems associated with multilingual websites. It is important that languages are not mixed up on the same page since search engines may find it difficult to discern between the content. Importantly also, content and navigation in the same language should be on the same page. Perform a language-specific site search to determine the number of pages on your website that are in a certain language. Google includes such a feature, but you shall have to use the TLD for the specific language. For example, if we wanted the results of our Spanish site, use google.es and choose below the search box for Google to only display Spanish results.
This article has explored the design of a data model to achieve the objective of localization. It will also give you a better way to manage content that is offered in a variety of languages.
The first thing to consider is content translation when undertaking a content localization project. Also, you will need a very robust database that is well designed to efficiently store content that has been translated into various languages.
Let us say that you are working on a travel portal that supports several languages. The first consideration is creating fields to store text, PackageTitle, and PackageDescription, that are in various languages. You will also need a CustomerMaster table to store text fields to serve other categories required in the various languages. The examples below are some of the ways to design websites that are capable of content translation as well as the merits and the demerits with the chosen method.
The approaches that have been selected for this article could be expanded to other tables in the models. Your needs should inform the approach you choose for your multilingual portal.
This first approach is one of the simplest challenges from a development perspective. It is as simple as adding a column for the respective language in the column field.
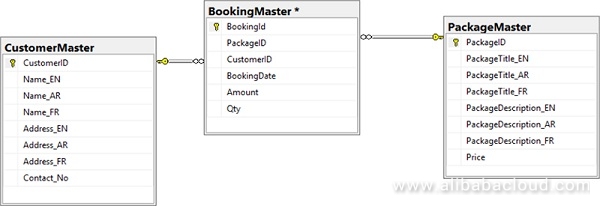
Pros:
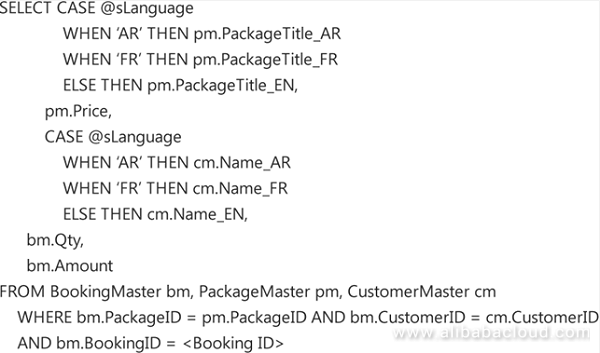
The sample SQL method below demonstrates this method:

Cons:
The second approach involves creating translated and non-translated fields in entity layers. Specifically, we use entity tables that contain any number of translated fields. Such fields are split into either translated and non-translated in separate layers. The method is uniquely positioned to separate all individual layers of data.
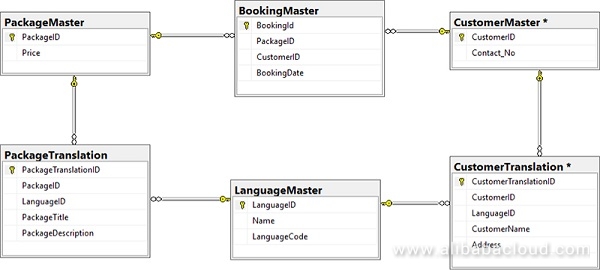
Pros:

Localization is very important for multinational brands that seek to enter new markets. However, it is important to look at future prospects before settling on a particular localization solution. You should keep in mind that localization is not only about presenting your website in local languages. It is about capturing the culture, lifestyle, and behaviors of local people.
Alibaba Cloud ApsaraDB for RDS can host your database solution securely on the cloud. Whether it is MySQL, PostgreSQL, or any other database system, you can host your multi-lingual website on Alibaba Cloud. Don't have an Alibaba Cloud account yet? Sign up for an account and try over 40 products for free worth up to $1200.
Rupal_Click2Cloud - November 6, 2024
Alibaba Clouder - September 19, 2018
Alibaba EMR - August 28, 2019
Alibaba Clouder - August 2, 2018
Alibaba Clouder - October 10, 2020
Kalpesh Parmar - November 12, 2025
 PolarDB for MySQL
PolarDB for MySQL
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for MySQL is a cloud-native relational database service 100% compatible with MySQL.
Learn More Web Hosting Solution
Web Hosting Solution
Explore Web Hosting solutions that can power your personal website or empower your online business.
Learn More AnalyticDB for MySQL
AnalyticDB for MySQL
AnalyticDB for MySQL is a real-time data warehousing service that can process petabytes of data with high concurrency and low latency.
Learn More Web Hosting
Web Hosting
Explore how our Web Hosting solutions help small and medium sized companies power their websites and online businesses.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alex