LinkBench is an open-source database benchmark developed by Google to evaluate database performance. LinkBench creates a set of test data around a social graph and then perform data operations such as querying, adding or disconnecting relationships.
For more information about LinkBench, refer to the following articles:
https://www.facebook.com/notes/facebook-engineering/linkbench-a-database-benchmark-for-the-social-graph/10151391496443920
http://www.oschina.net/translate/linkbench-a-database-benchmark-for-the-social-graph
The test model of LinkBench is very typical in the social relationships of users. I will provide a copy of PostgreSQL database performance test data under this model and the test method.
After seeing this test data, you can compare it with the test data of other databases to see the performance differences.
This data can be represented in a social graph, where objects (graph nodes) such as people, posts, comments, and pages are connected by associations (directed edges of the graph) that model different relationships between the nodes.
Different types of associations can represent friendship between two users, a user liking another object, ownership of a post, or any other relationship.
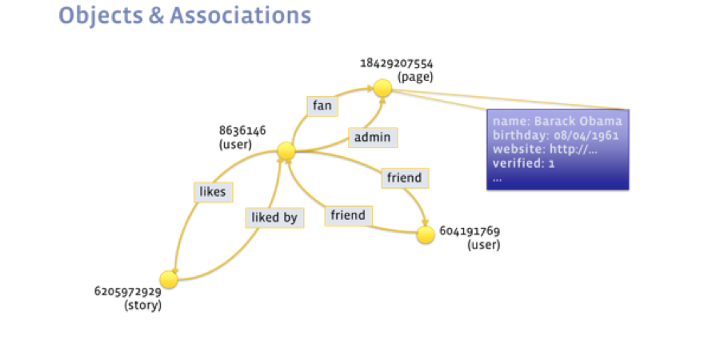
LinkBench is a graph-serving benchmark, not a graph-processing benchmark - the difference being that the former simulates the transactional workload from an interactive social network service while the latter simulates an analytics workload.
This benchmark is not about finding graph communities or graph partitioning, but rather serving real-time queries and updates on a graph database.
For example, a general form of graph query would be to find all the edges of type A from node X into which update operations can insert, delete, or update graph nodes or edges.
An example graph update operation is "insert a friendship edge from user 4 to user 63459821."
By classifying database queries into a small number of core operations for associations (edges) and objects (nodes), we could break down and analyze the mix of social graph operations for a production database.
The simple graph retrieval and update operations listed below are used to store and retrieve social graph data.
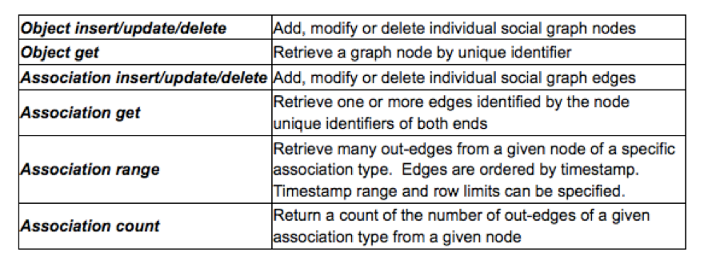
Note that the workload is heavy on edge operations and reads, particularly edge range scans.
Examples of edge range scans are "retrieve all comments for a post order from most to least recent" or "retrieve all friends for a user."
Optimization Tips:
This question is about storing data. If comments of an article have been aggregated, a small number of blocks need to be scanned and the performance is good. Similarly, if friends of a user have been aggregated, retrieving friends of a user will not encounter performance problems.
Aggregation through clusters can also reduce rows to be scanned.
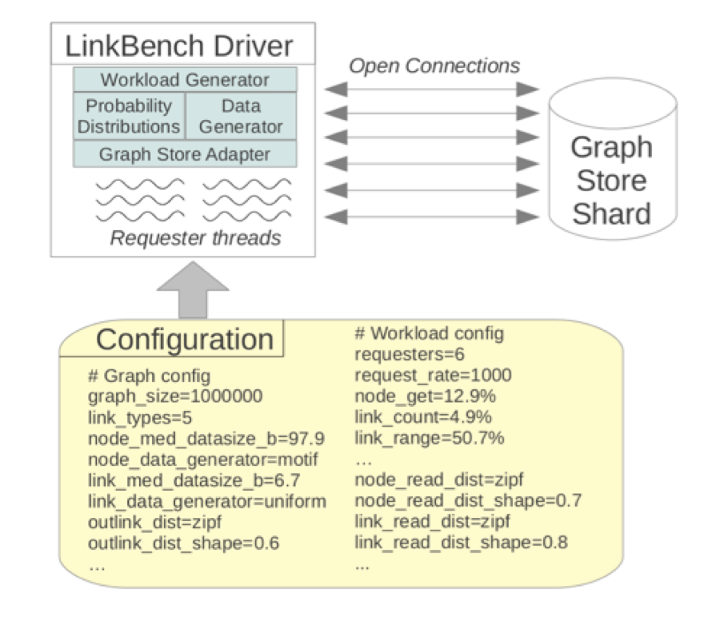
The actual benchmark is driven by the LinkBench driver, a Java program that generates the social graph and the operation mix.
Originally this tool only supports MySQL. Currently this tool has extended support for PostgreSQL. However, make sure to use PostgreSQL 9.5 or later, because queries include UPSET(insert on conflict), a new feature in PostgreSQL 9.5.
https://github.com/mdcallag/linkbench
Install LinkBench
mkdir ~/app
cd ~/app JDK
cd ~
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/jdk8-downloads-2133151.html
get
Java SE Development Kit 8u102
Linux x64 173.03 MB jdk-8u102-linux-x64.tar.gz
tar -zxvf jdk-8u102-linux-x64.tar.gz
mv jdk1.8.0_102 /home/digoal/app/ apache-maven
http://maven.apache.org/download.cgi
wget http://mirrors.cnnic.cn/apache/maven/maven-3/3.3.9/binaries/apache-maven-3.3.9-bin.tar.gz
tar -zxvf apache-maven-3.3.9-bin.tar.gz
mv apache-maven-3.3.9 /home/digoal/app/ Set up the environment
export JAVA_HOME=/home/digoal/app/jdk1.8.0_102
export PATH=/home/digoal/app/apache-maven-3.3.9/bin:/home/digoal/app/jdk1.8.0_102/bin:$PATH
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/home/digoal/app/apache-maven-3.3.9/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH Install LinkBench
git clone https://github.com/mdcallag/linkbench Pack linkbench
$ cd linkbench
$ mvn clean package -P pgsql -D skipTests
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] BUILD SUCCESS
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Total time: 5.146 s
[INFO] Finished at: 2016-09-11T13:07:55+08:00
[INFO] Final Memory: 39M/1582M
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Generate the environment variable configuration file
$ vi ~/.bash_profile
# append
export JAVA_HOME=/home/digoal/app/jdk1.8.0_102
export PATH=/home/digoal/app/linkbench/bin:/home/digoal/app/apache-maven-3.3.9/bin:/home/digoal/app/jdk1.8.0_102/bin:$PATH
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/home/digoal/app/apache-maven-3.3.9/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
export CLASSPATH=.:/home/digoal/app/linkbench/target/FacebookLinkBench.jar $ linkbench
Using java at: /home/digoal/app/jdk1.8.0_102/bin/java
Did not select benchmark mode
usage: linkbench [-c <file>] [-csvstats <file>] [-csvstream <file>] [-D
<property=value>] [-L <file>] [-l] [-r]
-c <file> Linkbench config file
-csvstats,--csvstats <file> CSV stats output
-csvstream,--csvstream <file> CSV streaming stats output
-D <property=value> Override a config setting
-L <file> Log to this file
-l Execute loading stage of benchmark
-r Execute request stage of benchmark The benchmark runs in two phases:
1. The load phase, where an initial graph is generated and loaded in bulk;
2. The request phase, where many request threads concurrently access the database with a mix of operations. During the request phase latency and throughput statistics for operations are collected and reported.
The exact behavior of the driver in both phases is controlled by a configuration file, and many aspects of the benchmark can be easily altered using this file.
The configuration file template is config/LinkConfigPgsql.properties.
This article does not include OS parameter optimization.
$ wget https://ftp.postgresql.org/pub/source/v9.6rc1/postgresql-9.6rc1.tar.bz2
$ tar -jxvf postgresql-9.6rc1.tar.bz2
$ cd postgresql-9.6rc1
$ ./configure --prefix=/home/postgres/pgsql9.6rc1 --enable-debug
$ gmake world -j 32
$ gmake install-world Environment variable configuration
$ vi ~/env_pg.sh
# add by digoal
export PS1="$USER@`/bin/hostname -s`-> "
export PGPORT=1921
export PGDATA=/data01/pgdata/pg_root_96
export LANG=en_US.utf8
export PGHOME=/home/postgres/pgsql9.6rc1
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$PGHOME/lib:/lib64:/usr/lib64:/usr/local/lib64:/lib:/usr/lib:/usr/local/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
export DATE=`date +"%Y%m%d%H%M"`
export PATH=$PGHOME/bin:$PATH:.
export MANPATH=$PGHOME/share/man:$MANPATH
export PGHOST=$PGDATA
export PGDATABASE=postgres
alias rm='rm -i'
alias ll='ls -lh'
unalias vi
$ . ~/env_pg.sh 1. Initialize the database
initdb -D $PGDATA -E UTF8 --locale=C -U postgres2. Create a database
$> psql
DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS linkdb;
CREATE DATABASE linkdb ENCODING='latin1' template template0;
--drop user linkbench to create new one
DROP USER IF EXISTS linkdb;
-- You may want to set up a special database user account for benchmarking:
CREATE USER linkdb password 'password';
-- Grant all privileges on linkdb to this user
GRANT ALL ON database linkdb TO linkdb; 3. Connect to linkdb and create tables and index
$> \c linkdb linkdb
--add Schema keep the same query style (dbid.table_name)
DROP SCHEMA IF EXISTS linkdb CASCADE;
CREATE SCHEMA linkdb;
-- FIXME:Need to make it partitioned by key id1 %16
-- Partition tables are recommended, or you can directly use a single table
-- For partition tables, the constraint check(mod(id1,16)=0) is required for the sub-table ID1...
-- src/main/java/com/facebook/LinkBench/LinkStorePgsql.java needs to be modified and re-compiled
-- In addition to id1=... add the same query criterion as the constraint, for example, where id1=val and mod(id1,16) = mod(val,16) ...
-- This allows the optimizer of PostgreSQL to filter id1=val
CREATE TABLE linkdb.linktable (
id1 numeric(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',
id2 numeric(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',
link_type numeric(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',
visibility smallint NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',
data varchar(255) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
time numeric(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',
version bigint NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',
PRIMARY KEY (link_type, id1,id2)
);
-- this is index for linktable
CREATE INDEX id1_type on linkdb.linktable(
id1,link_type,visibility,time,id2,version,data);
CREATE TABLE linkdb.counttable (
id numeric(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',
link_type numeric(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',
count int NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',
time numeric(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',
version numeric(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',
PRIMARY KEY (id,link_type)
);
CREATE TABLE linkdb.nodetable (
id BIGSERIAL NOT NULL,
type int NOT NULL,
version numeric NOT NULL,
time int NOT NULL,
data text NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(id)
); Note that each value cannot have a trailing space in the configuration file of LinkBench. Otherwise parsing errors may occur.
Configure how much test data is to be imported
$ vi ~/app/linkbench/config/FBWorkload.properties
# end node id for initial load (exclusive)
# With default config and MySQL/InnoDB, 1M ids ~= 1GB
maxid1 = 1000000001
# Configure about 1 billion node records (about 1 TB) Configure the database connection method, report frequency, thread, operations tested on each thread, maximum test duration, and stress testing
$ vi ~/app/linkbench/config/LinkConfigPgsql.properties
workload_file = config/FBWorkload.properties
linkstore = com.facebook.LinkBench.LinkStorePgsql
nodestore = com.facebook.LinkBench.LinkStorePgsql
# Database connection information
host = xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
user = linkdb
password = linkdb
port = 1922
dbid = linkdb
# Database tables
linktable = linktable
counttable = counttable
nodetable = nodetable
# INFO output level
debuglevel = INFO
# Print frequency
progressfreq = 300
displayfreq = 1800
# Number of records allowed to be loaded and requested on each thread
load_progress_interval = 500000
req_progress_interval = 500000
maxsamples = 10000
# Number of threads to be loaded
loaders = 64
generate_nodes = true
loader_chunk_size = 2048
# Number of requests enabled (Multiplying by 2 to get the number of connections)
requesters = 192
# Number of requests for each thread
requests = 5000000
requestrate = 0
maxtime = 100000
warmup_time = 0
max_failed_requests = 100 $ cd ~/app/linkbench
$ ./bin/linkbench -c config/LinkConfigPgsql.properties -l The steps are the same as those described in the preceding "Configure the load template" section
./bin/linkbench -c config/LinkConfigPgsql.properties -r INFO 2016-09-12 01:19:07,229 [main]: LOAD_NODE_BULK count = 390625 p25 = [8000,9000]ms p50 = [8000,9000]ms p75 = [9000,10000]ms p95 = [10000,100000]ms p99 = [10000,100000]ms max = 1259341.029ms mean = 9759.494ms
INFO 2016-09-12 01:19:07,229 [main]: LOAD_LINKS_BULK count = 1708831 p25 = [10000,100000]ms p50 = [10000,100000]ms p75 = [10000,100000]ms p95 = [10000,100000]ms p99 = [10000,100000]ms max = 1292335.24ms mean = 33558.09ms
INFO 2016-09-12 01:19:07,229 [main]: LOAD_COUNTS_BULK count = 301615 p25 = [10000,100000]ms p50 = [10000,100000]ms p75 = [10000,100000]ms p95 = [10000,100000]ms p99 = [10000,100000]ms max = 1318474.297ms mean = 66637.2ms
INFO 2016-09-12 01:19:07,229 [main]: LOAD PHASE COMPLETED. Loaded 100000000 nodes (Expected 100000000). Loaded 437452202 links (4.37 links per node). Took 4060.6 seconds. Links/second = 107731 Query performance for one-way metrics
INFO 2016-09-11 21:49:47,069 [main]:
ADD_NODE
count = 2471774
p25 = [0.4,0.5]ms Less than 0.5 milliseconds for 25% requests
p50 = [0.5,0.6]ms Less than 0.6 milliseconds for 50% requests
p75 = [0.6,0.7]ms Less than 0.7 milliseconds for 75% requests
p95 = [1,2]ms Less than 2 milliseconds for 95% requests
p99 = [4,5]ms Less than 5 milliseconds for 99% requests
max = 213.324ms Maximum RT
mean = 0.715ms Average RTp25 indicates that the RT for 0-25% of requests is between a and b (milliseconds) and p50 indicates that the RT for 25-50% of requests is between a and b (milliseconds)
Overall test statistics (including QPS)
INFO 2016-09-11 21:49:47,070 [main]:
REQUEST PHASE COMPLETED.
96000000 requests done in 796 seconds.
Requests/second = 120482 The test result for a 32-core machine
INFO 2016-09-11 21:49:47,069 [main]: ADD_NODE count = 2471774 p25 = [0.4,0.5]ms p50 = [0.5,0.6]ms p75 = [0.6,0.7]ms p95 = [1,2]ms p99 = [4,5]ms max = 213.324ms mean = 0.715ms
INFO 2016-09-11 21:49:47,069 [main]: UPDATE_NODE count = 7073914 p25 = [0.4,0.5]ms p50 = [0.5,0.6]ms p75 = [0.7,0.8]ms p95 = [2,3]ms p99 = [5,6]ms max = 154.589ms mean = 0.813ms
INFO 2016-09-11 21:49:47,069 [main]: DELETE_NODE count = 971421 p25 = [0.3,0.4]ms p50 = [0.4,0.5]ms p75 = [0.6,0.7]ms p95 = [2,3]ms p99 = [4,5]ms max = 80.185ms mean = 0.731ms
INFO 2016-09-11 21:49:47,070 [main]: GET_NODE count = 12414612 p25 = [0.4,0.5]ms p50 = [0.6,0.7]ms p75 = [0.9,1]ms p95 = [2,3]ms p99 = [5,6]ms max = 78.739ms mean = 0.943ms
INFO 2016-09-11 21:49:47,070 [main]: ADD_LINK count = 8631075 p25 = [1,2]ms p50 = [2,3]ms p75 = [3,4]ms p95 = [5,6]ms p99 = [9,10]ms max = 103.442ms mean = 2.657ms
INFO 2016-09-11 21:49:47,070 [main]: DELETE_LINK count = 2870975 p25 = [1,2]ms p50 = [2,3]ms p75 = [3,4]ms p95 = [6,7]ms p99 = [14,15]ms max = 134.991ms mean = 3.197ms
INFO 2016-09-11 21:49:47,070 [main]: UPDATE_LINK count = 7694028 p25 = [1,2]ms p50 = [2,3]ms p75 = [3,4]ms p95 = [5,6]ms p99 = [9,10]ms max = 91.146ms mean = 2.654ms
INFO 2016-09-11 21:49:47,070 [main]: COUNT_LINK count = 4690047 p25 = [0.4,0.5]ms p50 = [0.6,0.7]ms p75 = [1,2]ms p95 = [2,3]ms p99 = [5,6]ms max = 79.349ms mean = 1.026ms
INFO 2016-09-11 21:49:47,070 [main]: MULTIGET_LINK count = 504147 p25 = [0.7,0.8]ms p50 = [0.9,1]ms p75 = [1,2]ms p95 = [3,4]ms p99 = [6,7]ms max = 59.272ms mean = 1.325ms
INFO 2016-09-11 21:49:47,070 [main]: GET_LINKS_LIST count = 48678007 p25 = [0.7,0.8]ms p50 = [0.9,1]ms p75 = [1,2]ms p95 = [3,4]ms p99 = [6,7]ms max = 117.932ms mean = 1.386ms
INFO 2016-09-11 21:49:47,070 [main]: REQUEST PHASE COMPLETED. 96000000 requests done in 796 seconds. Requests/second = 120482 Each item represents a test case and the last row indicates the overall performance. For more information, see the preceding figures.
The result shows that LinkBench reaches 120,000 QPS.
A 32-core host is used in this test example.
https://github.com/mdcallag/linkbench
https://www.facebook.com/notes/facebook-engineering/linkbench-a-database-benchmark-for-the-social-graph/10151391496443920
PostgreSQL Family Tree Application Practices - Graph Relation Storage and Search
digoal - July 4, 2019
digoal - April 22, 2021
digoal - July 4, 2019
digoal - July 4, 2019
digoal - July 4, 2019
digoal - July 4, 2019
 ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL
ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL
An on-demand database hosting service for PostgreSQL with automated monitoring, backup and disaster recovery capabilities
Learn More PolarDB for PostgreSQL
PolarDB for PostgreSQL
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for PostgreSQL is an in-house relational database service 100% compatible with PostgreSQL and highly compatible with the Oracle syntax.
Learn More ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL
ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL
An on-demand database hosting service for MySQL with automated monitoring, backup and disaster recovery capabilities
Learn More ApsaraDB for OceanBase
ApsaraDB for OceanBase
A financial-grade distributed relational database that features high stability, high scalability, and high performance.
Learn MoreMore Posts by digoal