By Cui Xiang
The for-each node provided by DataWorks allows you to retrieve the last query result or output statement from an assignment node or parameter. Built-in variables can be used to access specific data during each traversal. The number of rows or length of the output determines the number of traversals. DataWorks has a maximum limit of 128 executions and doesn't support concurrent execution. However, you can exceed this limit and achieve concurrent execution using the following solution.
DataWorks determines the number of traversals based on the number of rows in a two-dimensional array or the number of data split by commas in a one-dimensional array. By transforming the output results of the assignment node and combining the output mode of the assignment node with the result set of the arrays, concurrent fetching and execution can be indirectly implemented through the built-in variables of the for-each node.
Assuming the upstream output result set is a one-dimensional array with data 1, 2, 3, 4:
Before transformation: Each traversal reads a piece of data through the variable ${dag.foreach.current}, and the traversal is performed 4 times by default.
Expected: The traversal is performed twice, with each traversal defining two tasks to concurrently read some data from the current traversal values.
The following section describes the key configurations. For more information, see For-each nodes.
1. Transform the original data.
Split the original output results 1, 2, 3, 4 of the assignment node into two groups by commas: 1#2, 3#4. The number of groups is determined by the number of commas, and the number of data items spliced by # in each group determines the number of inner nodes in the for-each node.
This output statement divides the data into two groups using commas, resulting in 2 traversals of the for-each node. The # further splits each data group.
2. Define the node to obtain the target value.
During each traversal, retrieve each group of data (the first group: 1#2; the second group: 3#4) using the variable ${dag.foreach.current}. Split each group of data using a function, and each task reads the divided data from the function.
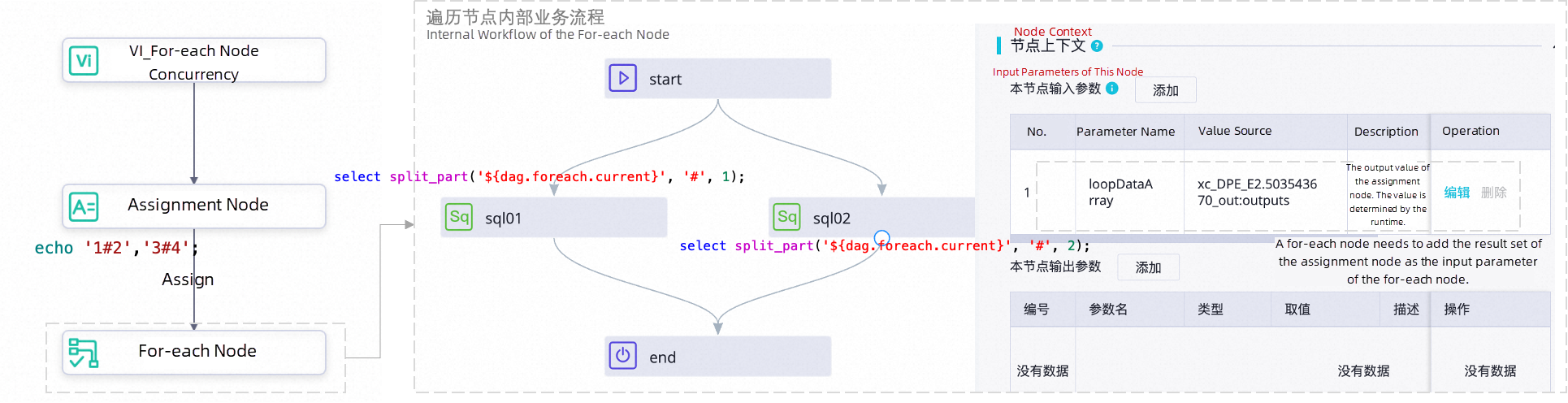
| Number of traversalsvalue | Current traversal data | Use the function to split the current traversal data |
| First traversal |
${dag.foreach.current}: 1#2 |
Take 1: split_part('${dag.foreach.current}', '#', 1)Take 2: split_part('${dag.foreach.current}, '#', 2)
|
| Second traversal |
${dag.foreach.current}: 3#4 |
Take 3: split_part('${dag.foreach.current}, '#', 1)Take 4: split_part('${dag.foreach.current}, '#', 2)
|
Go to Operation Center to choose Backfill Data > Backfill the Current Node and Downstream Nodes, run the assignment node and for-each node at the same time, and check the running status of each for-each node by viewing its inner nodes.
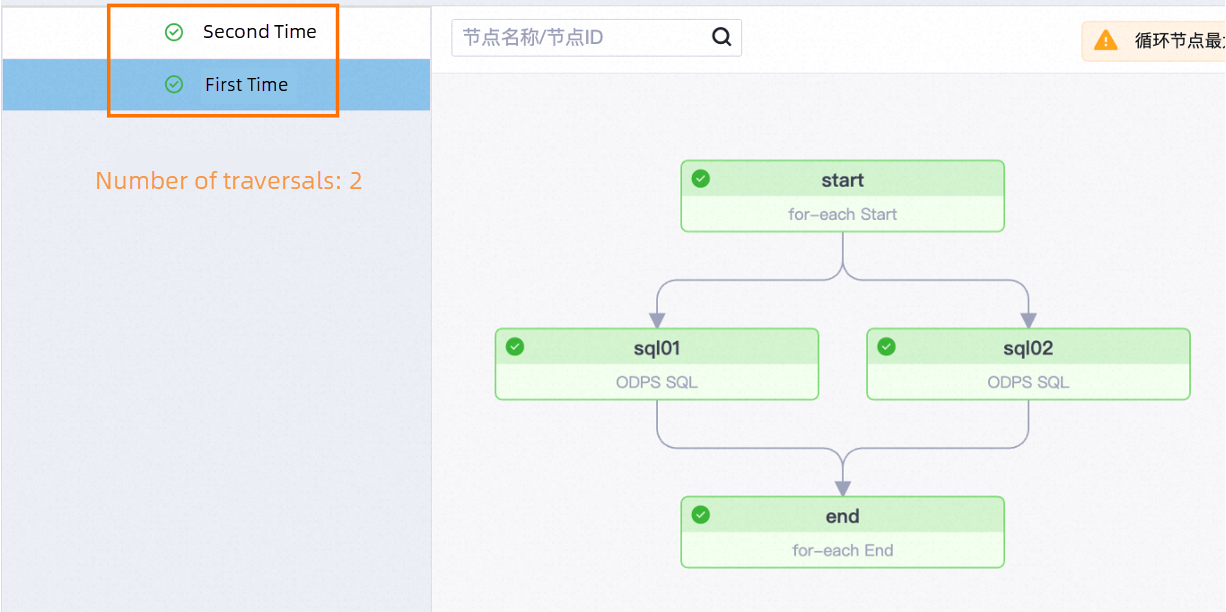
| Number of traversalsNode names | sql01 | sql02 |
| First traversal | 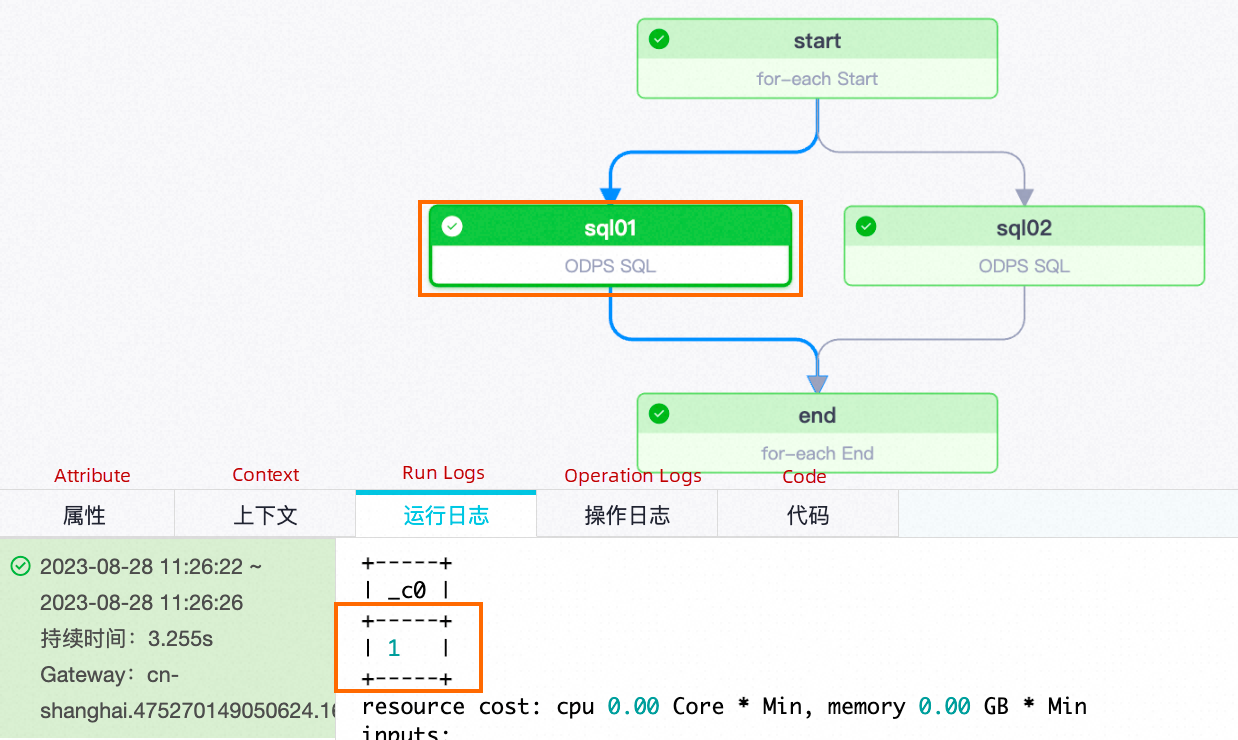 |
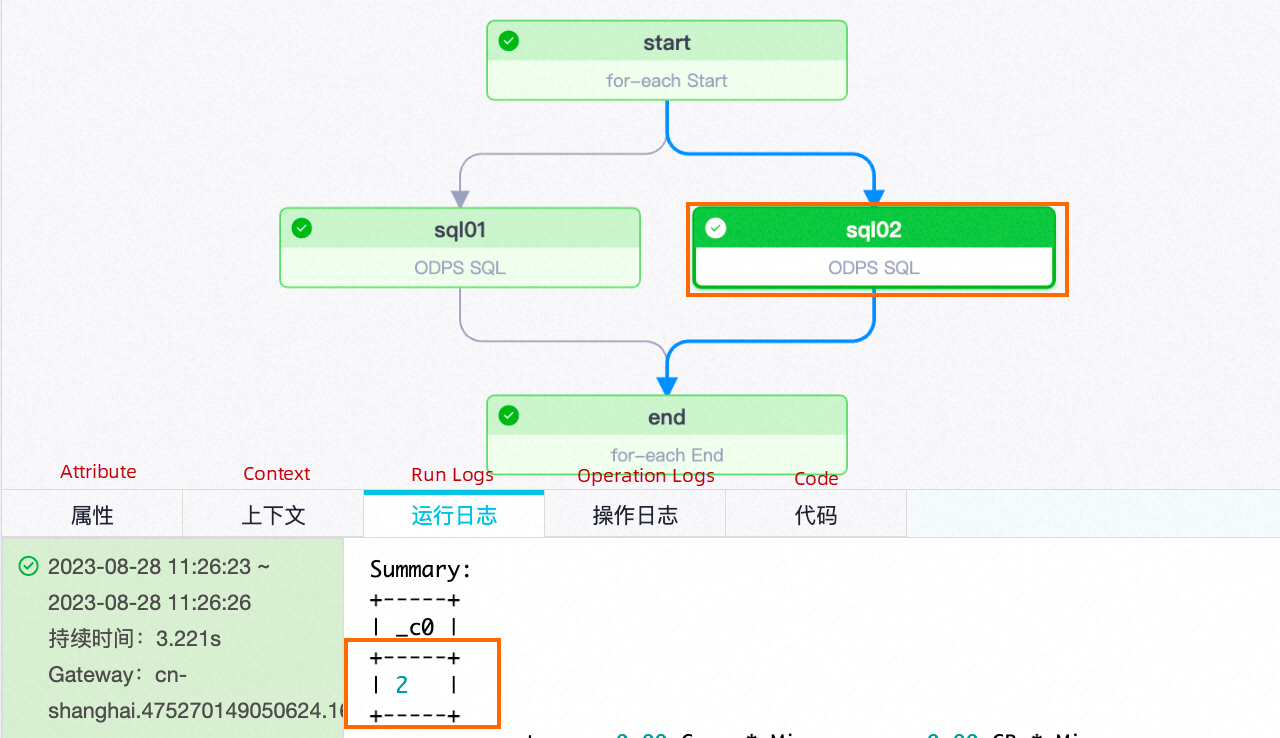 |
| Second traversal | 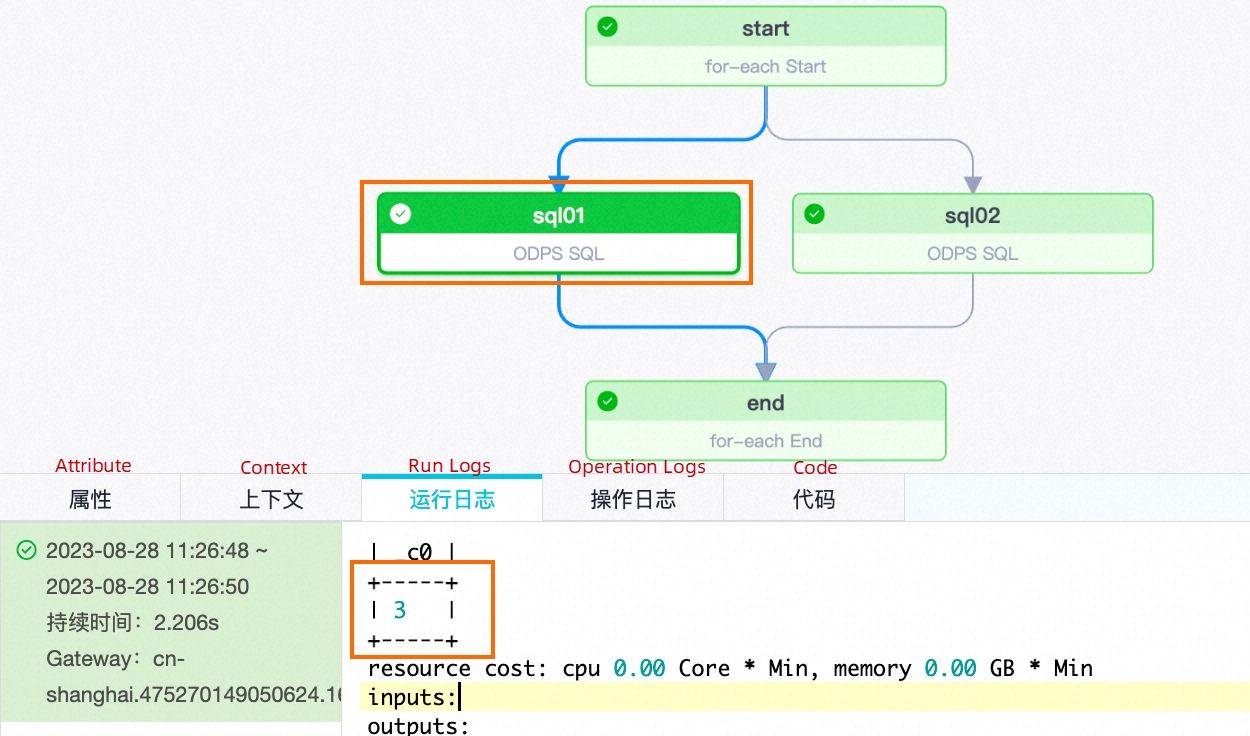 |
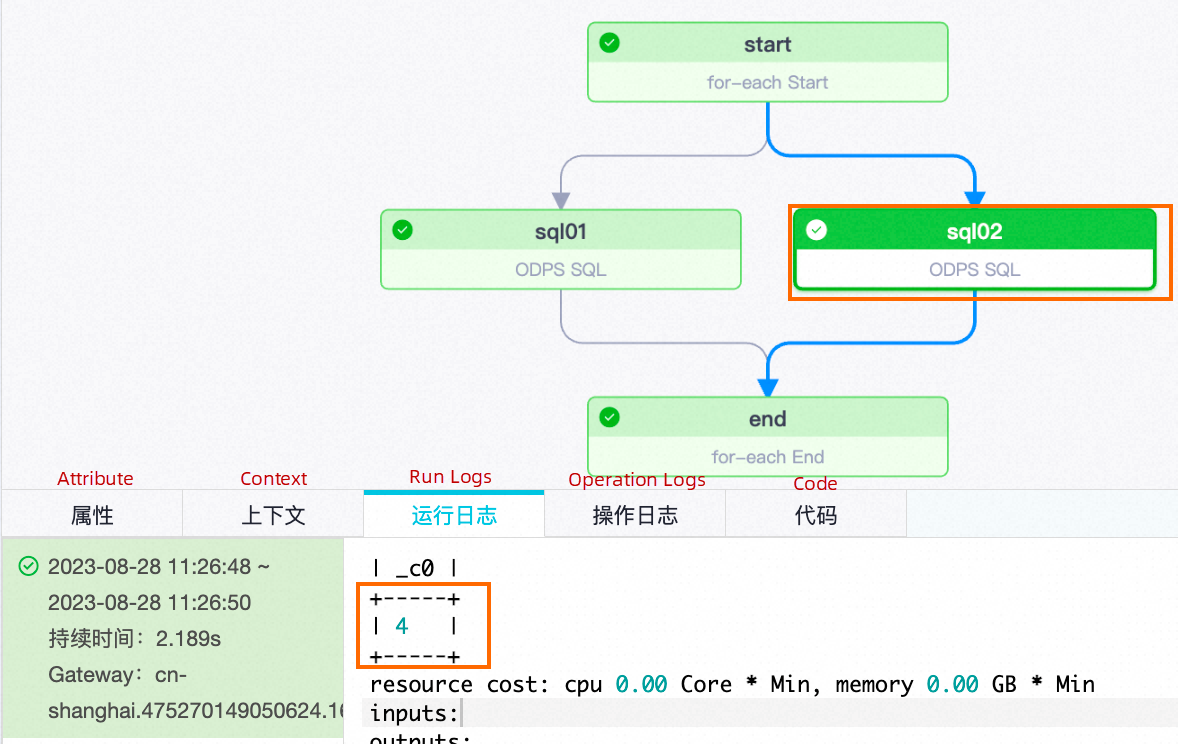 |
Disclaimer: The views expressed herein are for reference only and don't necessarily represent the official views of Alibaba Cloud.

1,345 posts | 471 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Community - October 20, 2023
Alibaba Clouder - September 3, 2019
Alibaba Clouder - April 11, 2018
PM - C2C_Yuan - May 20, 2024
Alibaba Cloud MaxCompute - April 26, 2020
Alibaba Cloud MaxCompute - June 24, 2019

1,345 posts | 471 followers
Follow Bastionhost
Bastionhost
A unified, efficient, and secure platform that provides cloud-based O&M, access control, and operation audit.
Learn More Managed Service for Grafana
Managed Service for Grafana
Managed Service for Grafana displays a large amount of data in real time to provide an overview of business and O&M monitoring.
Learn More Big Data Consulting for Data Technology Solution
Big Data Consulting for Data Technology Solution
Alibaba Cloud provides big data consulting services to help enterprises leverage advanced data technology.
Learn More Big Data Consulting Services for Retail Solution
Big Data Consulting Services for Retail Solution
Alibaba Cloud experts provide retailers with a lightweight and customized big data consulting service to help you assess your big data maturity and plan your big data journey.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud Community