By eBPF SIG
Recently, at the Apsara Conference 2022 OpenAnolis Forum-eBPF & Linux Stability Session, Wenan Mao (a maintainer of the eBPF Technology Exploration SIG) delivered a technical speech on Coolbpf Application Practice. The following article highlights the main points of that speech:


With the development of BPF technology, it has become easier to develop a BPF program. Although BPF has provided convenience, it has been pursuing another aspect: portability. BPF portability is defined as a BPF program successfully written and verified by the kernel, which can run in different kernel versions.
There are two challenges in performing the BPF portability:
BPF CO-RE (Compile Once-Run Everywhere) is a way to achieve portability.
The following components are provided to support CO-RE:
Three main types of information need to be relocated:

The steps to develop BPF CORE with libbpf are listed below:
There are roughly the following function calls:
<name>__open(): Create and open the BPF application. After that, you can set the skel->rodata variable.
<name>__load(): Instantiate, load, and verify BPF application parts
<name>__attach(): Attach all auto-attachable BPF programs. When an event and network run message arrives, the bpf program will be triggered.
<name>__destroy(): Detach all BPF programs and use all the resources they use
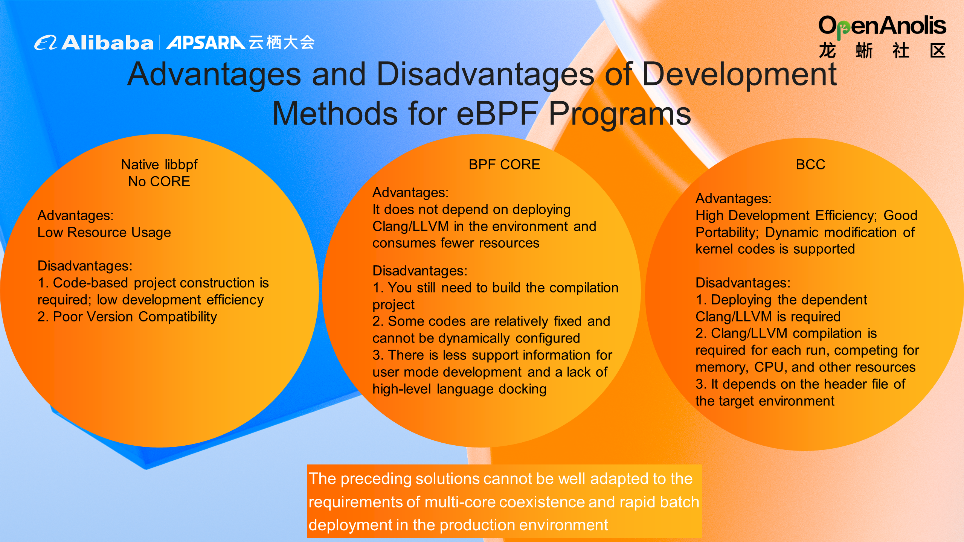
There are three main development methods for eBPF programs, each of which has advantages and disadvantages:
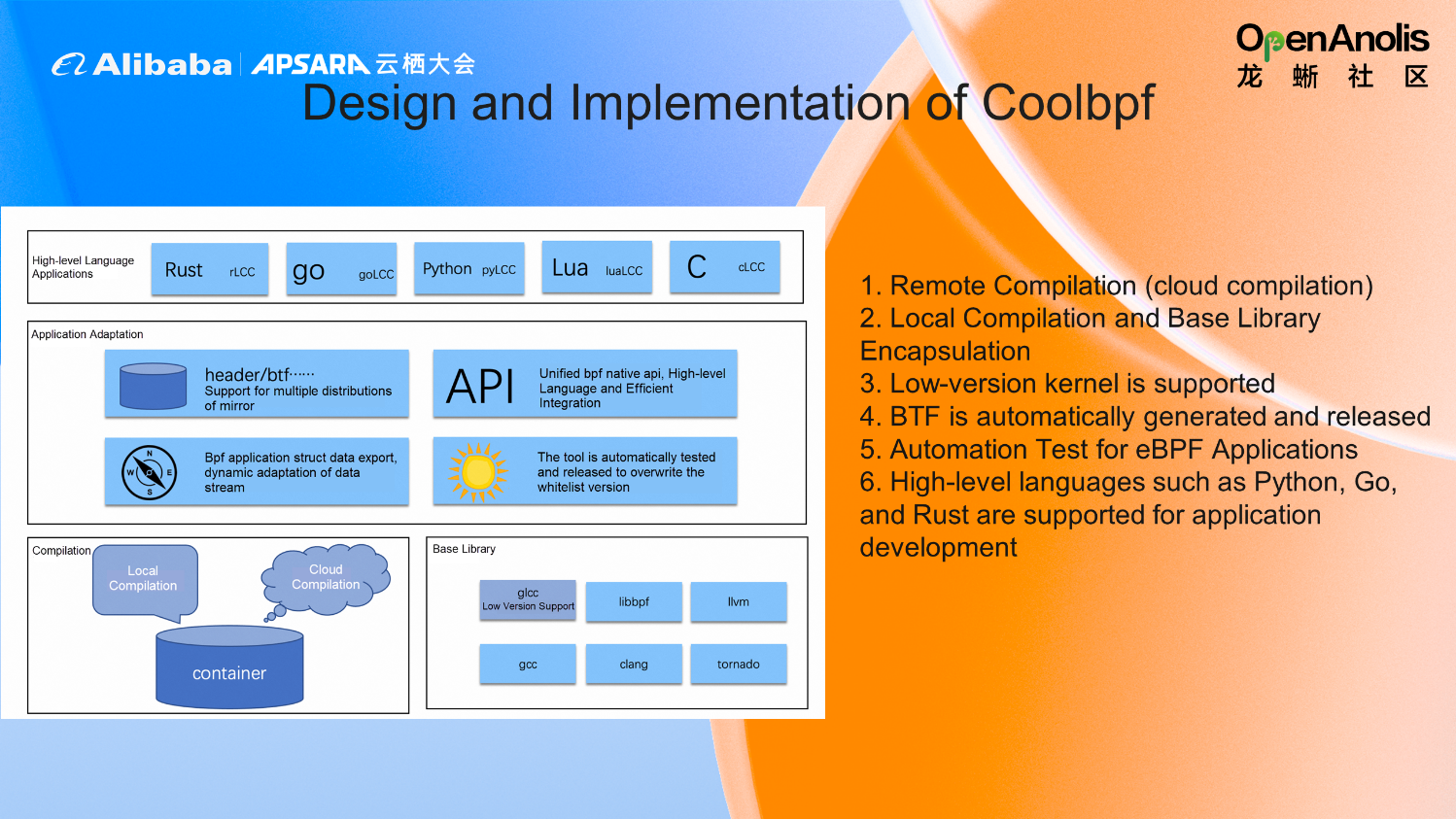
Coolbpf provides remote compilation (cloud compilation). Remote compilation means the target machine running the program is not on the same machine as the machine compiling the program, which can solve the problem of resource occupation. Local compilation and basic library encapsulation are provided, which is convenient for users to call the basic library for writing. Low-version kernel is supported. Coolbpf also provides automatic generation and release of BTF, and users can directly use it by downloading without manual adaptation. It provides automated testing and supports high-level languages (such as Python, Go, and Rust) for application development.
Coolbpf naturally supports the CORE capability of BPF, which solves the problems of compilation and resource consumption. At the same time, the complex libbpf development steps described earlier are completely simplified. Users only need to focus on their functional development, not environment building and redundant code development.
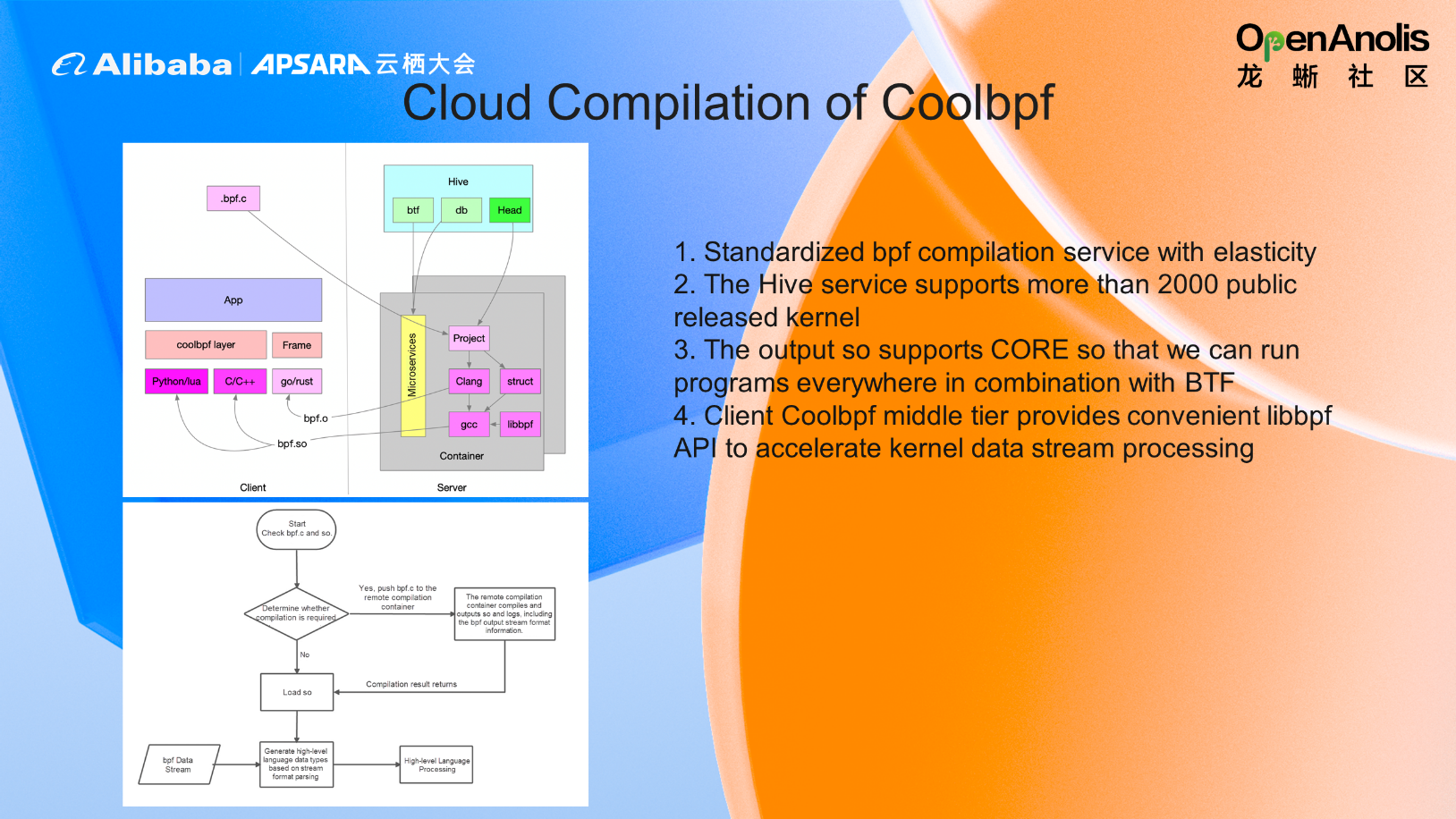
Coolbpf provides standardized bpf compilation services. When bpf.c is submitted to a remote build server, the server services advanced applications with the return point bpf.so or bpf.o for different languages, depending on the kernel version. Therefore, you only need to load bpf.so in your high-level language code to run the program. Instead of manually triggering Libbpf's open(), load(), attach(), and other functions, it is automatically completed by the init() function of the high-level language program. This way, users can quickly build and deploy the project and only need to focus on the processing after data output.
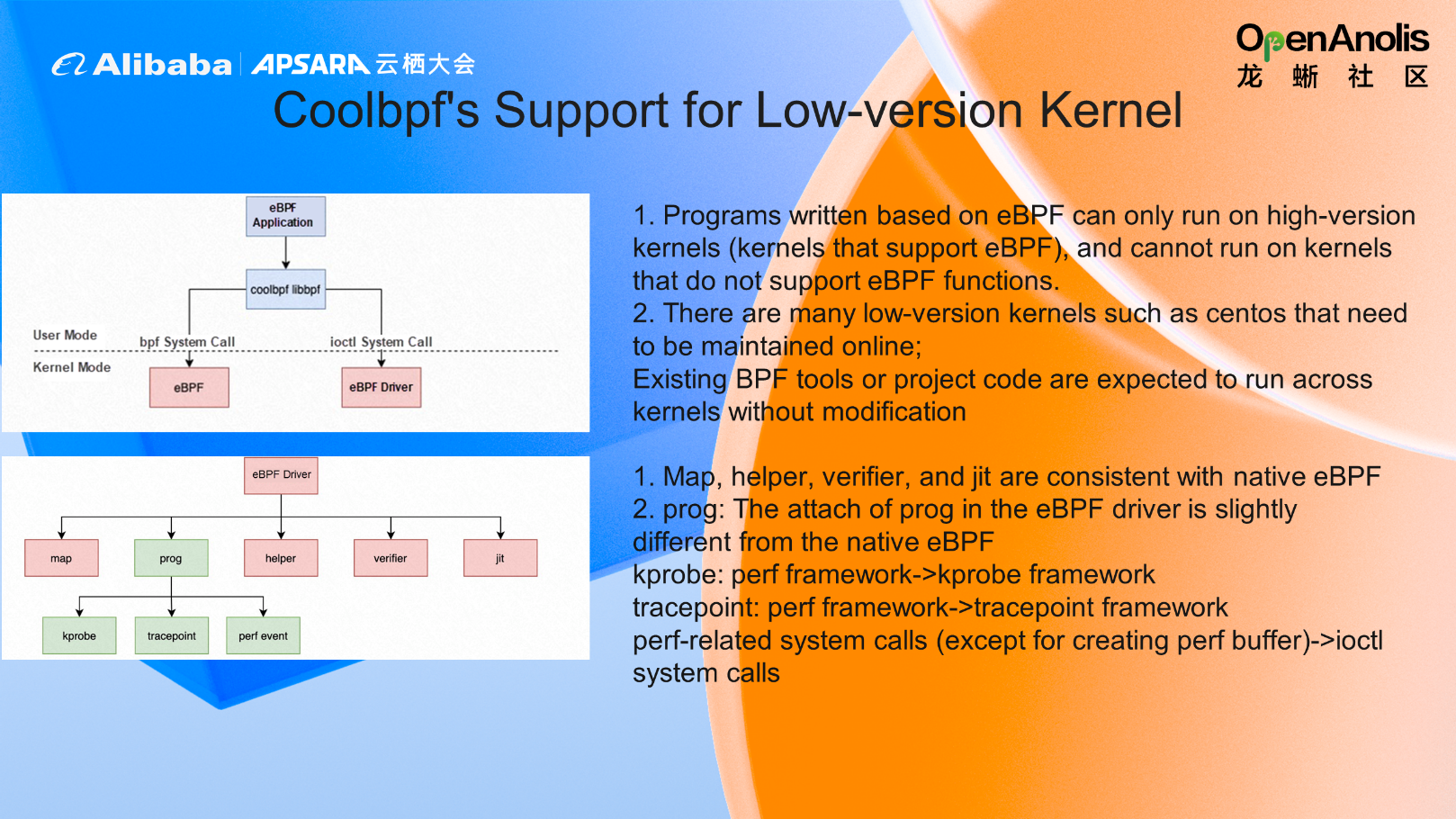
Coolbpf also supports low-version kernels without eBPF features, and we provide the eBPF driver to help it run safely on low-version kernels. We implement the eBPF verifier verification part in a driver on the higher version, which will perform various security checksums to ensure the security of eBPF compared with kernel modules. In addition, we convert all the original libbpf-based calls to IOCTL system calls.
The previously supported helper function, map creation, and program loading are all converted into the implementation of kprobe or tracepoint in lower versions. In addition, perf event and jit are supported. This way, the same user program, loading such a driver, can safely run on the lower version kernel without modifying the eBPF program code.

Raptor is an observable tool based on Coolbpf. It can run on earlier version kernels (such as AliOS and CentOS 3.10). It can be used as an SDK for third parties to collect data.
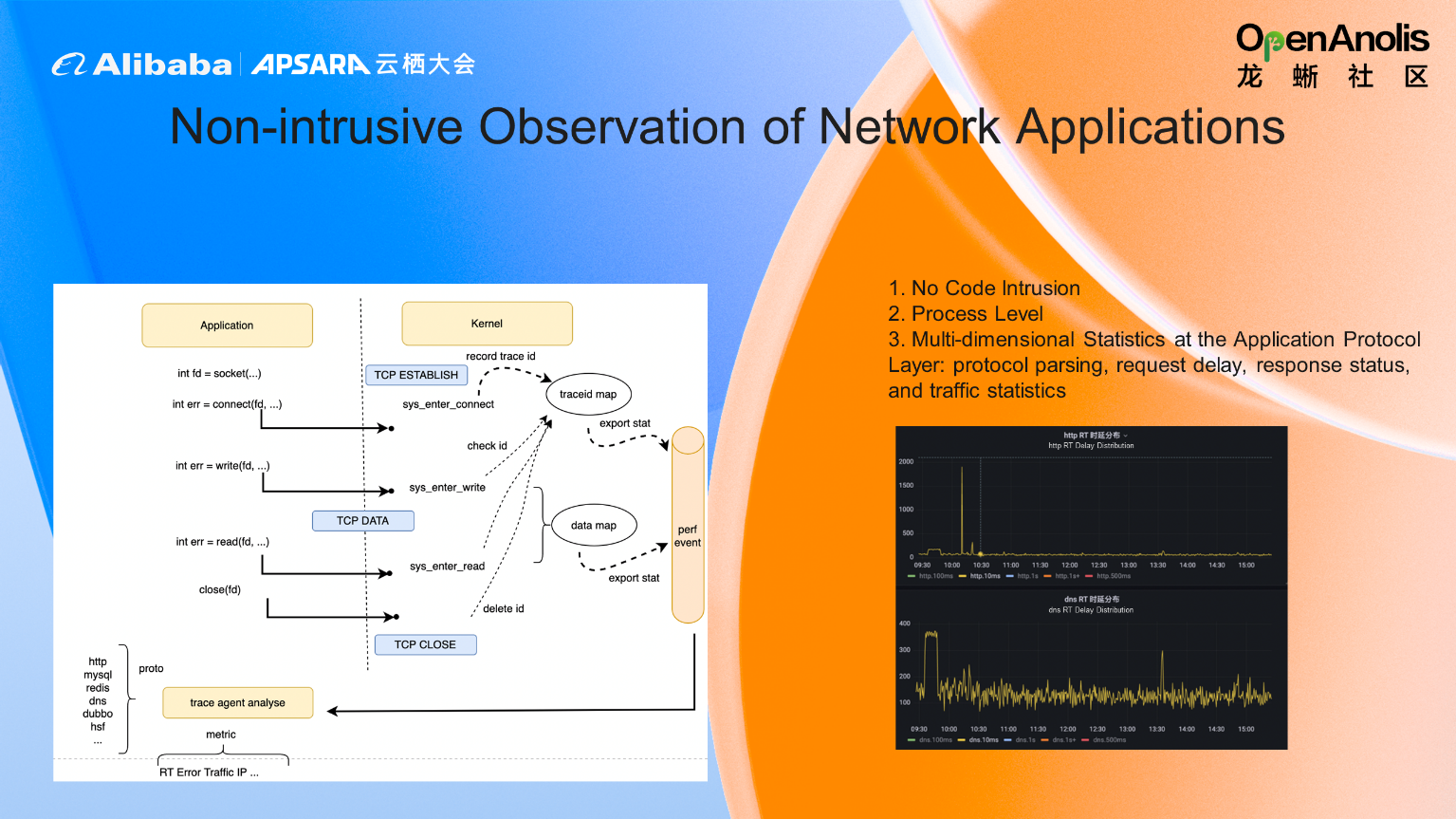
In this network application observation, the interactive data content and quintuple information are determined by monitoring the data interaction, request, and response information in the system call. They are sent to the user mode through the interactive mode of the map, so the observation is done in a non-intrusive way. Finally, the observation results are presented (such as traffic statistics and request delay).
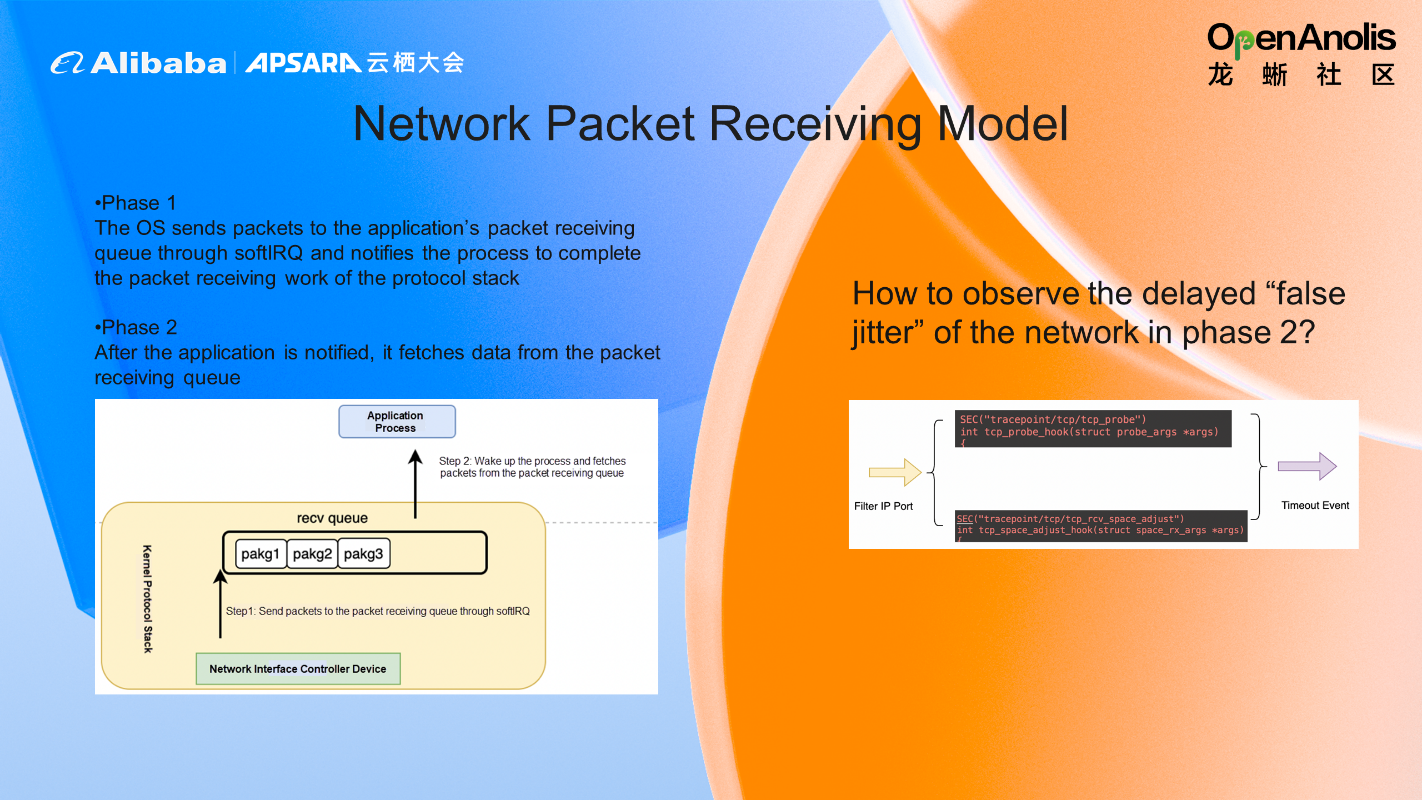
Let's look at a specific problem and understand how Coolbpf finds the network jitter problem in the packet-receiving phase. We know the network packet receiving is divided into two phases:
Phase 1: The OS sends packets to the application's packet-receiving queue through softIRQ and notifies the process to complete the packet-receiving work of the protocol stack.
Phase 2: The application fetches data from the packet-receiving queue after being notified.
We can write a BPF program in Coolbpf. Then, we only need to monitor two tracepoints (tcp_probe and tcp_rcv_space_adjust) to find the delay problem in phase 2.
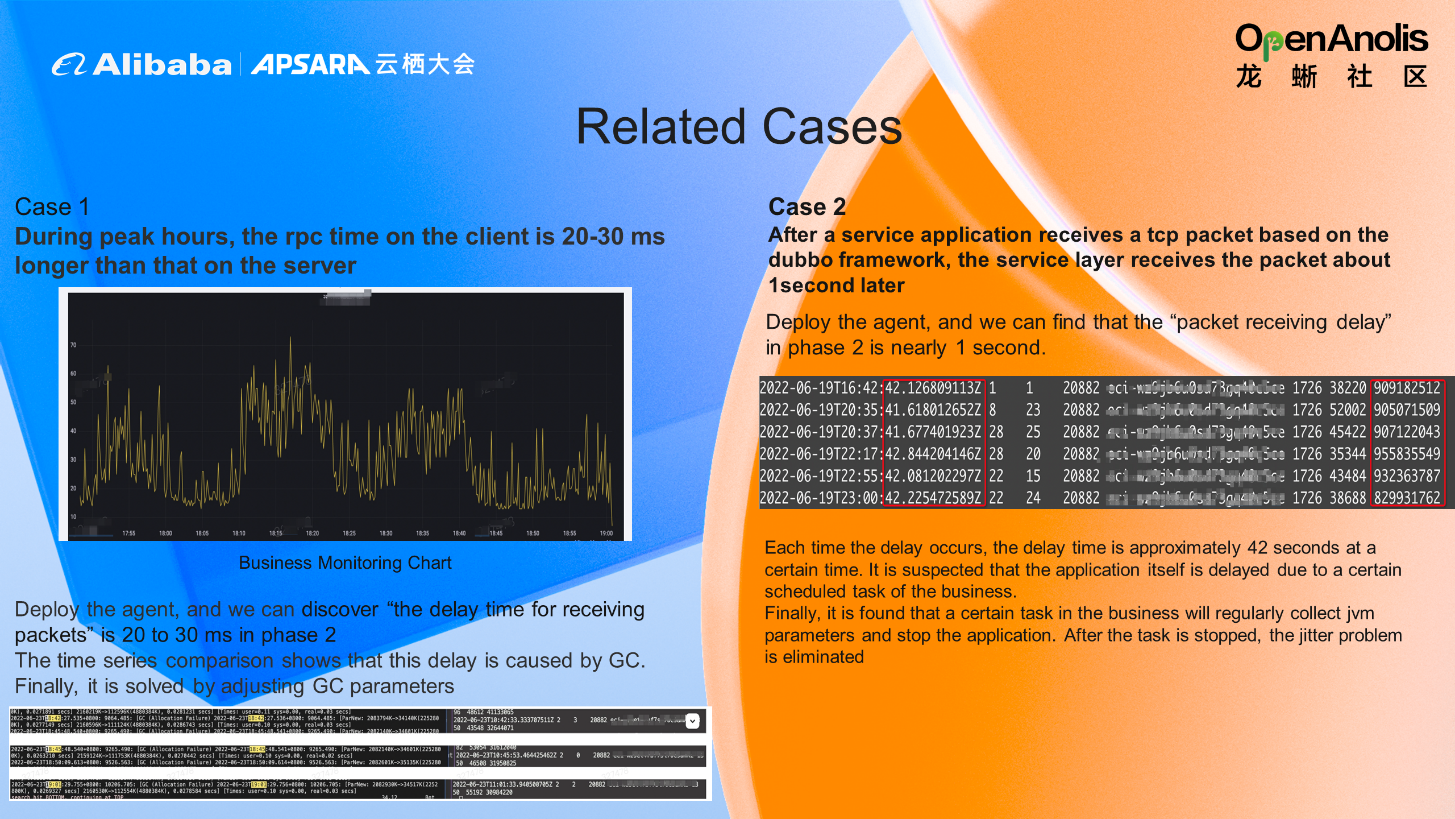
In this case, a business application receives packets slowly. The kernel side has received the tcp packet, but the application side does not receive it until nearly one second later.
Observation Method: Deploy the eBPF agent, and we can see the packet receiving delay time in Phase 2 is nearly one second.
Cause: Each time the delay occurs, the delay time is approximately 42 seconds at a certain time. It is suspected the application is delayed due to a scheduled task of the business. Finally, it is found that a certain task of the business will regularly collect jvm parameters and stop the business.
Solution: After the task is stopped, the jitter problem is eliminated.
Please see the following links for more information:
Link Address of eBPF Technology Exploration SIG:
https://openanolis.cn/sig/ebpfresearch
eunomia-bpf: The Lightweight Development Framework for eBPF and WebAssembly Is Now Available!

102 posts | 6 followers
FollowOpenAnolis - July 27, 2023
OpenAnolis - November 29, 2022
OpenAnolis - December 24, 2024
OpenAnolis - April 7, 2023
OpenAnolis - June 25, 2025
OpenAnolis - February 2, 2023

102 posts | 6 followers
Follow Networking Overview
Networking Overview
Connect your business globally with our stable network anytime anywhere.
Learn More Alibaba Cloud Linux
Alibaba Cloud Linux
Alibaba Cloud Linux is a free-to-use, native operating system that provides a stable, reliable, and high-performance environment for your applications.
Learn More Edge Network Acceleration
Edge Network Acceleration
Establish high-speed dedicated networks for enterprises quickly
Learn More Apsara File Storage NAS
Apsara File Storage NAS
Simple, scalable, on-demand and reliable network attached storage for use with ECS instances, HPC and Container Service.
Learn MoreMore Posts by OpenAnolis