This article will address how new retail methodology and technology can be applied to a retail booth, or pop-up store scenario.
A retail booth, also known as a popup store, is a location in the shopping mall where rental is more temporary in nature. The main advantage is the lower risk in testing out new products or new venue, because of the often shorter term rental binding, and lower renovation/decoration costs.
Roadshow is a particular use of a retail booth location for doing promotional events, especially for the launch of new products or performing promotion corresponding to seasonal needs. Conceptually, roadshows and retail booths are slightly different, but in this discussion, we will simply call the both of them as a "retail booth".
There are typically 4 key business objectives of incorporating new retail into existing businesses:
These objectives essentially encapsulate how technologies are applied in to the booth.
Let's have a closer look at a typical user journey from online to offline, i.e. from getting promotional/marketing messages to reaching the store and leaving afterwards:
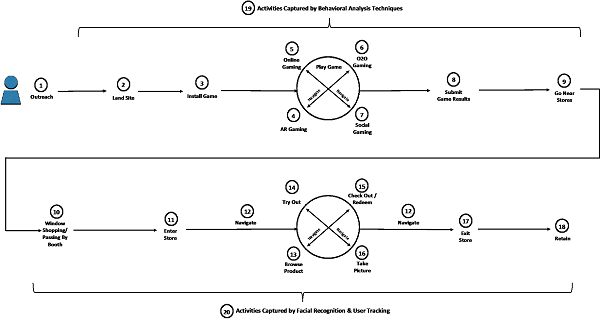
In a nutshell, there are 4 main technology areas involved in New Retail:
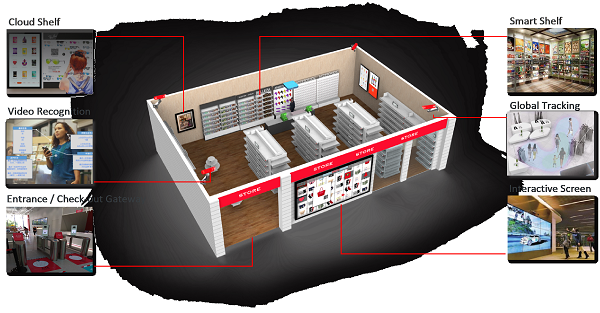
Specifically, around the booth, there are several applicable technologies that can be used:
In this blog, we explore how the blockchain is necessary for the new retail industry to create a consistent platform for storing and sharing of information.
With the emergence of a new retail in the internet era, traditional business models have evolved to meet the demands introduced by new retail. Businesses from all industries have also adjusted and upgraded their services to adapt to new situations. In recent years, a new marketing and operations concept, known as the supply-to-business (S2B) model, has taken the retail market by storm and has been regarded as one of the most advanced business model available.
In the context of the rapid development of new retail, the application of blockchain will be a breakthrough in the implementation of the S2B model. But what exactly are the impacts of blockchain and the S2B model on the retail industry? As a breakthrough and extension, how will blockchain support new retail and how will it inspire the retail sector?
The S2B model was developed to cope with the constantly evolving demands of customers. Precisely, it is S2B2C, a powerful data-based supply chain platform (S) connected to thousands of businesses (B), that directly serves customers. By utilizing the power of the internet, S2B2C helps users interact more effectively and at a lower cost.
As a whole, suppliers and small businesses co-serve customers. In the Internet era, "co-serve" has two meanings. First, when serving customers, small businesses have to use specific services provided by suppliers. Apart from SaaS-based tools, suppliers should also offer some value-added services based on the integration of the upstream supply chains to help businesses to serve customers better.
Second, suppliers must have information about the process in which small businesses serve customers and receive real-time feedback from small businesses so that suppliers can improve services for small businesses. This requires that the process by which small enterprises serve customers is updated online. Also, suppliers and small businesses achieve network- and software-based automatic collaboration to better serve customers. For example, a supplier supplies goods to a micro-business but is not involved in the process in which the micro business serves customers. In this case, no higher value gets created, and this is not S2B2C. The S2B model will soon become a backdrop of the retail industry.
Let's analyze the S2B model in the new retail era from macro perspectives. In the new retail era, the application of blockchain offers an attractive opportunity for development and breakthrough. Regarding the norm requirements, the core of the model lies in that production is driven by consumption and backed by robust and scientific supply chain systems.
Alibaba Dpath, a traffic isolation solution, is developed to provide support for new retail scenarios during the Double 11 Shopping Festival.
During this year's Double Eleven Shopping Festival, technical preparations had to be changed from previous years to support New Retail. The Business Division required that traffic from new retail will enter independent servers and be isolated from other common traffic. Although conceptually straightforward, this poses higher requirements on the stability of new retail systems.
We have proposed a solution known as Dpath (dedicated path) to cope with these new requirements. The general idea of Dpath can be described as follows:
We'll introduce how Dpath works in three steps:
Simply put, the information we need is the machines, apps, and the relation between them in a dedicated environment. Such information is stored in the configuration center in JSON format. A sample are as follows:
{
"enable": true,
"envRules": [
{
"envName": "newRetail",
"failoverPolicy": 0,
"envAppRules": [
{
"appName": "app1",
"ips": [ ],
"machineGroups": [
"app1_newRetail_host"
]
},
{
"appName": "app2",
"ips": [ ],
"machineGroups": [
"app2_newRetail_host"
]
},
{
"appName": "app3",
"ips": [ ],
"machineGroups": [
"app3_newRetail_host"
]
},
{
"appName": "newRetailEntryApp",
"ips": [ ],
"machineGroups": [
"newRetailEntryApp_host"
]
}
]
}
]
} The above configuration information describes a dedicated environment called newRetail, which has four apps, app1, app2, app3, and newRetailEntryApp, and their corresponding machines.
The Dpath toolkit subscribes to the configuration, and each middleware can use the Dpath toolkit to get the required information.
Dpath uses the dpath_env attribute carried by the trace module (the trace function of the entire link, which can transmit data on the link) to identify the corresponding dedicated environment for the current traffic. With regards to how to map a request information to a dedicated environment, the business division will do it with business logic.
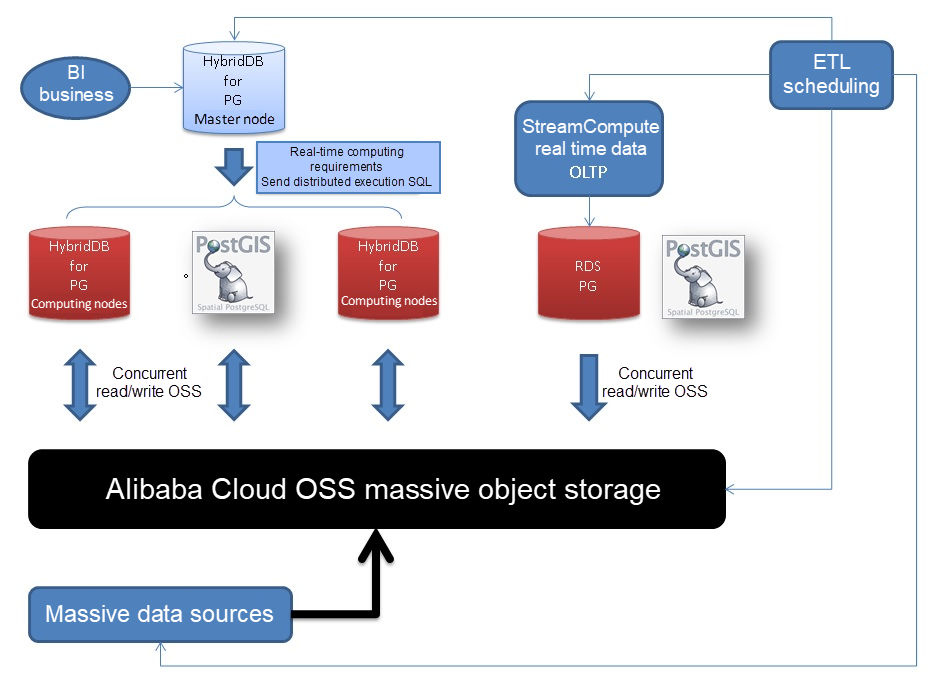
In today's retail industry, data must be used to its greatest value if online and offline business are to be integrated and inventories optimized.
Here, online business refers to cloud platforms and offline business refers to stores or manufacturers. New logistics will eliminate inventories to reduce the volume of stock-ups.
The disappearance of E-commerce platforms means the decentralization of existing E-commerce platforms, where merchants will possess their own independent platforms and no longer settle their business on large-scale platforms like Tmall, JD.com, and Amazon. For example, if everyone owns a store on an E-commerce platform for centralized sales, the sales are restricted.
Data must be used to its greatest value if online and offline business are to be integrated and inventories eliminated. For example, it can be used to predict sales volume ahead of time. Connecting online and offline business also brings new challenges to data operation, and leads to gridded operation based on geographic locations.
A single server-based service for application deployment, security management, O&M monitoring, and more
Elastic and secure virtual cloud servers to cater all your cloud hosting needs.
In this use case, a leader in the apparel industry adopted a hybrid cloud solution based on Application Real-Time Monitoring Service (ARMS) to build a real-time monitoring system for its retail industry.
Business value of the ARMS-based monitoring system
ApsaraDB for RDS offers four editions: Basic Edition, High-availability Edition, Cluster Edition, and Enterprise Edition. This topic describes how to view the edition of an RDS instance and provides a comparison between various editions.
For more information about the instance families that are supported by each edition, see Instance families.
This course is designed to help traditional IT companies who want to migrate their IT infrastructure to the cloud. You will fully understand Alibaba Cloud's various solution recommendations for server migration, database migration, storage migration and available tools for different business scenarios and migration objects. Therefore, it will be much easier to do the assessment, design and implementation of the migration.
This course aims to help users and engineers who want to migrate databases from third-party cloud platforms to Alibaba Cloud. By learning this course, you can get a comprehensive understanding of what cross-platform database migration is, the DTS, a common tool of database migration on Alibaba Cloud, and the scenarios for migrating cloud databases from third-party cloud platforms to Alibaba Cloud ApsaraDB for RDS, so as to provide a reference for database migration across cloud platforms.
Best Practice for Creating and Managing User Access Permissions
What is Serverless Computing? Challenges, Architecture and Applications

2,593 posts | 793 followers
FollowAlibaba Clouder - September 26, 2018
Alibaba Clouder - January 22, 2020
Alibaba Cloud Indonesia - November 27, 2023
Alibaba Clouder - November 30, 2018
Alibaba Cloud Community - September 27, 2025
Alibaba Clouder - October 9, 2020

2,593 posts | 793 followers
Follow ROS(Resource Orchestration Service)
ROS(Resource Orchestration Service)
Simplify the Operations and Management (O&M) of your computing resources
Learn More GPU(Elastic GPU Service)
GPU(Elastic GPU Service)
Powerful parallel computing capabilities based on GPU technology.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Clouder