As the saying goes, prevention is better than cure. For medical professionals, the ability to detect diseases early is priceless as many diseases can be nipped in the bud if detected early. Recent developments in artificial intelligence for the medical industry have helped medical professionals make more accurate and faster detections.
In June 2019, Alibaba's medical artificial intelligence (AI) mastered the cardiovascular recognition technology, which allows it to accurately extract coronary artery vessels from CTA images within merely 0.5 seconds. This technology is approximately 100 times more efficient than conventional methods.
As a popular application of medical AI, medical imaging diagnosis covers a wide disease spectrum, including the liver, lung, bones, mammary glands, thyroid glands, heart, and other organs. Cardiovascular diseases are commonly recognized as a tough field that only few people can have access to.
Before making achievements in the heart, Alibaba has been making world-class breakthroughs in lung nodule detection and liver nodule diagnosis. So far, Alibaba's new technologies such as lung nodule detection and computer-assisted orthopedic treatment have been put into commercial use.
Once breakthroughs are made in the horizontal disease spectrum and vertical technological application, medical AI will drive the technological revolution in imaging.
Without medical imaging, modern medicine would not be as effective as it is today. Before Roentgen discovered X-rays, we could not see examines our bones and organs accurately. Today, medical professionals spend a significant amount of their time analyzing medical images every day. In large hospitals in China, imaging doctors may spend more than 10 hours analyzing images every day.

Physical exhaustion from executing these repetitive tasks has become one of the major reasons for misdiagnosis and missed diagnoses.
Fortunately, a new technological revolution is taking place, with AI knocking at the door of modern medicine. With trillions of gigabytes of medical images generated every year, imagine how many intellectual resources can be reserved if computers can assist doctors in processing these images. By then, doctors will be able to focus on more important things, such as spending more time on patients.
For specific organs and diseases, AI can conquer them one by one. However, for all kinds of organs, the data capacity, algorithms, and computing capabilities need to be improved by several orders of magnitude. In addition, medical diagnosis is a set of chains with a self-consistent system, complex procedures, and continuous enhancements. It is rather difficult to nest new technologies into it.
Lung nodule detection is currently the best known territory of medical imaging AI. A tumor may start with merely a nodule, but many lung cancer patients are diagnosed at a late stage of the disease when they undergo a routine checkup.
To fight against this malignant tumor, it is best to have early detection, early diagnosis, and early treatment. However, lung nodules are often too subtle to detect. Most nodules are smaller than 10 mm at the early stage, and usually do not cause obvious discomfort.
To screen for lung nodules, over 200 chest computed tomography (CT) images are scanned in each case. However, a doctor can process only a maximum of dozens of images every day. During the high-intensity fatigue work, it is inevitable that doctors will make mistakes in manual operations. This is the ideal scenario for AI to give full play to its advantages.
In July 2017, Alibaba AI broke the world record at the international authoritative LUng Nodule Analysis 2016 (LUNA 16) challenge, winning the championship with an average recall rate of 89.7% (the percentage of successfully detected nodules in sample data).
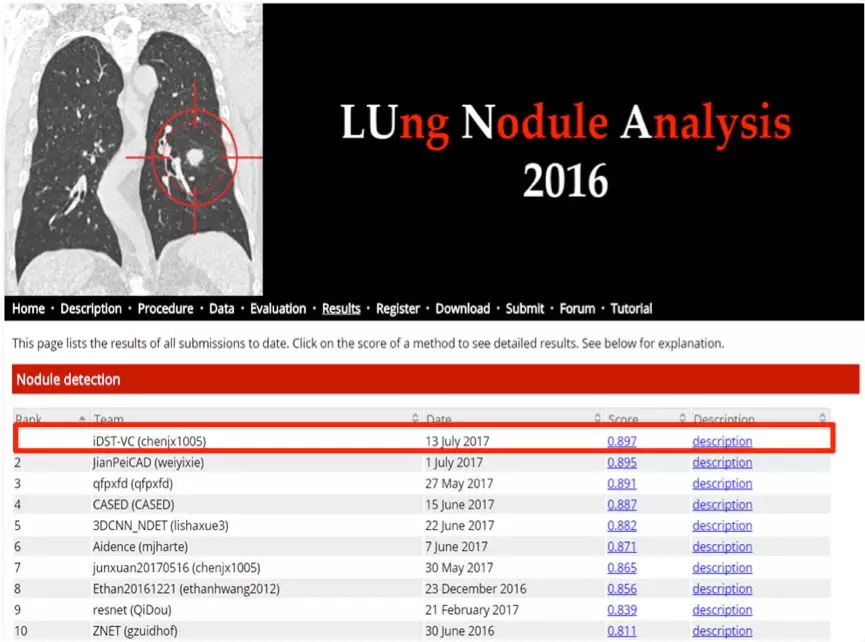
Ranking at the Official Website of LUNA16
The challenge requires participating teams to search 888 lung CT samples for lung nodules. The samples contain 1,186 lung nodules, and more than 75% of them are smaller than 10 mm. Without manual intervention, Alibaba AI automatically read the CT sequences of the patients and directly output the detected lung nodules.
2017 is named "lung nodule's year" in the AI industry, because most existing breakthroughs in the AI-assisted lung nodule detection technology are made this year. Till now, at least a dozen of Chinese companies have claimed to have implemented lung nodule detection algorithms.
Lung nodule detection has become an entry-level field of medical imaging AI. There are two reasons in terms of the algorithm threshold. First, lung nodule images are relatively "easy to read", because images are intuitive with well-organized features and few interference factors. Second, there are many public lung nodule-related data, which is easy to obtain and reduces the costs of machine training.
Unfortunately, for many medical AI systems, lung nodules are both a starting point and an endpoint.
After 2017, Alibaba AI continued its high-speed advancements and successively won two world-class competitions, including liver nodule diagnosis and coronary artery extraction. They announced Alibaba AI's unparalleled advantages in the algorithm field.
In December 2018, Alibaba AI stood out from nearly a hundred of teams by winning two first places in the global Liver Tumor Segmentation Challenge (LiTS).
The liver is an organ where human tubes are most densely distributed, including multiple tubular systems, such as portal veins, hepatic veins, hepatic arteries, and the bile duct system. Liver nodules have varied shapes, and the gray-level distribution between nodules vary widely. The gray level of the nodules is similar to or even not clearly separated from that of surrounding tissues. Therefore, liver nodules are more challenging than lung nodules for the "eyesight" of the AI.
Alibaba's AI copes with the diversity of liver nodules through network structure analysis where inter- and intra-layer information of CT images are integrated. This involves technologies such as atrous spatial pyramid pooling (ASPP) and sub-pixel convolution. At present, the Alibaba team is undertaking further study on how to determine benign and malignant liver nodules.
Half a year later, at the Rotterdam coronary artery centerline extraction competition in 2019, Alibaba AI won the first place in the fully automatic extraction. The related papers have been accepted in advance by MICCAI 2019, the world's leading conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention.
Accurate extraction of the coronary artery centerline from CTA images is essential for imaging diagnosis of coronary heart diseases. The general process is as follows: The doctor reconstructs a 3D image of the blood vessels based on 2D images to form a curved planar reconstruction view, manually extracts the coronary vessels, finds and marks vascular patches, and determines the nature of the vasculopathy to determine the treatment means.
The coronary artery is 164 mm long on average and has complex geometric characteristics and tiny blood vessels. Compared with the static scanning of lung nodule images, the reconstruction of 3D images for the beating heart is much tougher. By contrast, most conventional coronary artery centerline extraction methods are time-consuming and involve redundant man-machine interaction.
Alibaba AI proposed a discriminant coronary tracking model consisting of a 3D convolutional neural network. The model makes full use of 3D spatial features to iteratively search images for complete vessels without man-machine interaction. It takes 0.5 seconds on average to extract a single coronary artery vessel and less than 20 seconds to extract a complete coronary tree, which is nearly 100 times more efficient than conventional methods.
The complexity of cardiovascular disease diagnosis leads to scarce application of AI-based medical imaging recognition in this field. Alibaba's technological breakthroughs allow AI to assist doctors in diagnosing cardiovascular diseases in the near future.
Medical imaging for lung, liver, and cardiovascular diseases requires a more advanced algorithm, and there is no shortcut to algorithm breakthroughs. Alibaba DAMO Academy has gathered the most powerful AI R&D talent pool in China to develop such algorithms. DAMO Academy currently has 10 IEEE fellows and more than 20 well-known university professors, with more than half of the scientists holding a doctoral degree from famous universities.
Algorithms alone are far from enough to promote technologies. The real challenge is to make algorithms work reliably and consistently for every scenario possible. Many problems need to be solved when it comes to medical AI, for example, proving the accuracy of the model in a real medical environment, solving real clinical concerns, and establishing service models and business models.
At the end of March, Alibaba Cloud partnered with Intel and LinkDoc to hold the first season of the "Tianchi Medical AI Competition", with the subject of intelligent recognition and lung nodule diagnosis. The competition is intended to explore the application of early imaging diagnosis for lung cancer. Physicians from 16 top-level hospitals formed an expert steering group, and 2,887 teams from 20 countries or regions registered for the competition. The entire competition lasted for half a year, and some excellent algorithms were finally converted into practical solutions.
The three organizers performed their respective duties. Alibaba Cloud provided a machine learning and training platform that supports hundreds of gigabytes of memory at a single point, with more than thirty-two 128x128x128 or larger 3D images rapidly processed in each iteration. Intel provided a high-performance computing cluster built on the second generation of strong fusion core processors, to ensure high-intensity computing capabilities. LinkDoc partnered with 16 hospitals to provide 2,000 "scientific research-level chest CT data sets", which is the largest sample scale in the world.
This non-commercial event mobilized the wisdom of the entire industry and promoted algorithm optimization and technological accumulation for lung nodule detection. However, the greater value is beyond the competition leaderboard: Professional physicians and algorithm engineers work together to explore ways of collaboration between imaging and AI and focus on the feasibility of embedding AI algorithms into the medical process.
"Openness" has always been Alibaba's pursuit for the AI industry ecosystem. Alibaba's AI platform can provide small and medium-sized enterprises with AI infrastructure and AI algorithm packages , including services such as standard algorithm access, runtime environment hosting, and online and offline resource interconnection. It helps enterprises build exclusive smart applications in a rapid and cost-effective manner.
Both holding competitions as a leader and providing the infrastructure on the backend are compliant with Alibaba's platform visions and ecosystem strategies. Perhaps it is this open thinking that enables Alibaba's AI engineers to always discover pain points earlier than others in the industry and better understand the demand-oriented innovation in products.
For example, while the accuracy of AI-assisted lung nodule detection approaches the theoretical extreme value, why are doctors not interested? Why does a hospital deploy various algorithms of multiple companies at the same time, but does not particularly depend on any of them?
The answers are not complicated. Even if the performance in real scenarios is not lower than that in the laboratory, the individual lung nodule detection technology cannot improve the overall efficiency of imaging doctors. There are various types of lung diseases, and lung nodules are merely one of them. It is unlikely that doctors read the images only to check lung nodules. Therefore, machines cannot really relieve the burden on doctors.
Based on this, after winning the championship in the top competition about lung nodule detection, the Alibaba team immediately got down to the R&D of comprehensive lung diagnosis solutions. Now, the imaging diagnosis of six common lung lesions is available: lung density increase, lung cable, lung bubble, atherosclerosis, lymph node calcification, and lung nodules. The comprehensive solution covers early screening for most lung diseases, which imposes a very practical effect for both imaging departments in hospitals and physical examination organizations. This technology is now available to the public through Alibaba Cloud, serving nearly 10 million users in total.
There is no doubt that AI-assisted medical imaging is the future of medical development trends. However, developers still need to prove the value of AI and enable the medical AI service model to catch up with the pace of technological advancement.
Malaysia Future Makers: Alibaba Cloud Partners with Well-Known Malaysian Enterprises

2,597 posts | 774 followers
FollowMichael Njunge - November 29, 2022
Alibaba Clouder - March 27, 2019
Alibaba Clouder - April 29, 2020
Alibaba Cloud Community - May 31, 2024
Alibaba Clouder - June 25, 2018
Alibaba Cloud Community - January 13, 2025

2,597 posts | 774 followers
Follow Big Data Consulting for Data Technology Solution
Big Data Consulting for Data Technology Solution
Alibaba Cloud provides big data consulting services to help enterprises leverage advanced data technology.
Learn More Big Data Consulting Services for Retail Solution
Big Data Consulting Services for Retail Solution
Alibaba Cloud experts provide retailers with a lightweight and customized big data consulting service to help you assess your big data maturity and plan your big data journey.
Learn More ApsaraDB for HBase
ApsaraDB for HBase
ApsaraDB for HBase is a NoSQL database engine that is highly optimized and 100% compatible with the community edition of HBase.
Learn More Offline Visual Intelligence Software Packages
Offline Visual Intelligence Software Packages
Offline SDKs for visual production, such as image segmentation, video segmentation, and character recognition, based on deep learning technologies developed by Alibaba Cloud.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Clouder
Start building with 50+ products and up to 12 months usage for Elastic Compute Service
Get Started for Free Get Started for Free