如果您的数据表经常需要进行GROUP BY、JOIN操作或为了避免数据倾斜,您可以在建表时设置分布键(Distribution Key),合适的分布键可以帮助数据均匀分布在所有计算节点上,显著提高计算和查询性能。本文为您介绍Hologres中为表设置Distribution Key。
Distribution Key介绍
在Hologres中,Distribution Key属性指定了表数据的分布策略,系统会保证Distribution Key相同的记录被分配到同一个Shard上。建表时设置语法如下:
-- Hologres V2.1版本起支持的语法
CREATE TABLE <table_name> (...) WITH (distribution_key = '[<columnName>[,...]]');
-- 所有版本支持的语法
BEGIN;
CREATE TABLE <table_name> (...);
call set_table_property('<table_name>', 'distribution_key', '[<columnName>[,...]]');
COMMIT;参数说明如下:
参数 | 说明 |
table_name | 设置分布键的表名称。 |
columnName | 设置分布键的字段名称。 |
Distribution Key是非常重要的分布式概念,合理设置Distribution Key可以达到如下效果:
显著提高计算性能。
不同的Shard可以进行并行计算,从而提高计算性能。
显著提高每秒查询率(QPS)。
当您以Distribution Key做过滤条件时,Hologres可以直接筛选出数据相关的Shard进行扫描。否则Hologres需要让所有的Shard参与计算,影响QPS。
显著提高Join性能。
当两张表在同一个Table Group内,并且Join的字段是Distribution Key时,那么数据分布保证表A一个Shard内的数据和表B同一Shard内的数据对应,只需要直接在本节点Join本节点数据(Local Join)即可,可以显著提高执行效率。
使用建议
Distribution Key设置原则总结如下:
Distribution Key尽量选择分布均匀的字段,否则容易因为数据倾斜导致负载倾斜,使得查询效率变低,排查数据倾斜请参见查看Worker倾斜关系。
选择
Group By频繁的字段作为Distribution Key。Join场景中,设置Join字段为Distribution Key,实现Local Join,避免数据Shuffle。同时进行Join的表需要在同一个Table Group内。
不建议为一个表设置多个Distribution Key,建议设置的Distribution Key不超过两个字段。设置多字段为Distribution Key,查询时若没有全部命中,容易出现数据Shuffle。避免使用两列值相同的字段作为分布键,否则会导致数据都分布在一个shard上,造成数据倾斜。
支持单列或者多列设置为Distribution Key,指定列时如设置单列,命令语句中不要保留多余空格;如设置多个列,则以半角逗号(,)分隔,同样不要保留多余空格。指定多列为Distribution Key时,列的顺序不影响数据的布局和查询性能。
表设置了主键(PK)时,Distribution Key必须为PK或者PK中的部分字段(不能为空,即不指定任何列),因为要求同一记录的数据只能属于一个Shard。如果没有额外指定Distribution Key,默认将PK设置为Distribution Key。
使用限制
设置Distribution Key需要在建表时设置,建表后如需修改Distribution Key需要重新建表并导入数据。
不支持修改Distribution Key对应列的值,如需修改请重新建表。
不支持将Float、Double、Numeric、Array、Json及其他复杂数据类型的字段设为Distribution Key。
表未设置PK时,Distribution Key没有限制,可以为空(不指定任何列)。如果为空,即随机Shuffle,数据随机分布到不同Shard上。从Hologres V1.3.28版本开始,Distribution Key禁止为空,示例用法如下。
--从1.3.28版本开始,写法将会被禁止 CALL SET_TABLE_PROPERTY('<tablename>', 'distribution_key', '');Distribution Key列的值中有
null时,当作“”(空串)看待,即Distribution Key为空。
技术原理
Distribution Key指定了表的分布策略。根据实际的业务场景,存在以下情形。
设置Distribution Key
为表设置了Distribution Key之后,数据会根据Distribution Key被分配到各个Shard上,算法为Hash(distribution_key)%shard_count,结果为对应的Shard。系统会保证Distribution Key相同的记录会被分配到同一个Shard上,示例如下。
V2.1版本起支持的建表语法:
--设置a列为distribution key,系统会对a列的值做hash操作,再取模,即hash(a)%shard_count = shard_id,结果相同的一组数据分布在同一个Shard内 CREATE TABLE tbl ( a int NOT NULL, b text NOT NULL ) WITH ( distribution_key = 'a' ); --设置a、b两列为distribution key,系统对a,b两个列的值做hash操作,再取模,即hash(a,b)%shard_count = shard_id,结果相同的一组数据分布在同一个Shard内 CREATE TABLE tbl ( a int NOT NULL, b text NOT NULL ) WITH ( distribution_key = 'a,b' );所有版本支持的建表语法:
--设置a列为distribution key,系统会对a列的值做hash操作,再取模,即hash(a)%shard_count = shard_id,结果相同的一组数据分布在同一个Shard内 begin; create table tbl ( a int not null, b text not null ); call set_table_property('tbl', 'distribution_key', 'a'); commit; --设置a、b两列为distribution key,系统对a,b两个列的值做hash操作,再取模,即hash(a,b)%shard_count = shard_id,结果相同的一组数据分布在同一个Shard内 begin; create table tbl ( a int not null, b text not null ); call set_table_property('tbl', 'distribution_key', 'a,b'); commit;
数据分布示意图如下: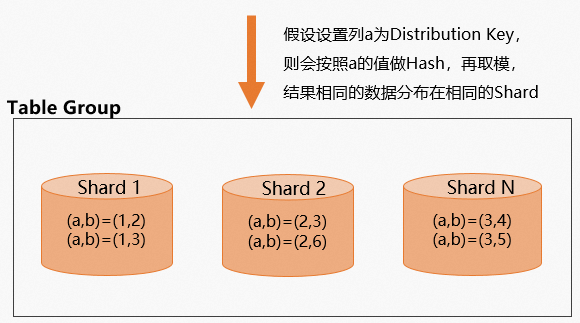 但在设置Distribution Key时,需要关注设置为Distribution Key字段的数据最好是分布均匀的。Hologres的Shard数和Worker节点数有一定的关联关系,详情请参见基本概念。如果设置了数据分布不均匀的字段作为Distribution Key之后,那么数据会集中分布在某些Shard上,导致大部分的计算集中到部分Worker上,出现长尾效应,查询效率降低。排查以及处理数据的倾斜情况详情请参见查看Worker倾斜关系。
但在设置Distribution Key时,需要关注设置为Distribution Key字段的数据最好是分布均匀的。Hologres的Shard数和Worker节点数有一定的关联关系,详情请参见基本概念。如果设置了数据分布不均匀的字段作为Distribution Key之后,那么数据会集中分布在某些Shard上,导致大部分的计算集中到部分Worker上,出现长尾效应,查询效率降低。排查以及处理数据的倾斜情况详情请参见查看Worker倾斜关系。
不设置Distribution Key
不设置Distribution Key时,数据将会被随机分布在各个Shard,相同的数据可能会在相同Shard,也可能在不同的Shard,示例如下。
--不设置distribution key
begin;
create table tbl (
a int not null,
b text not null
);
commit;数据分布示意图如下: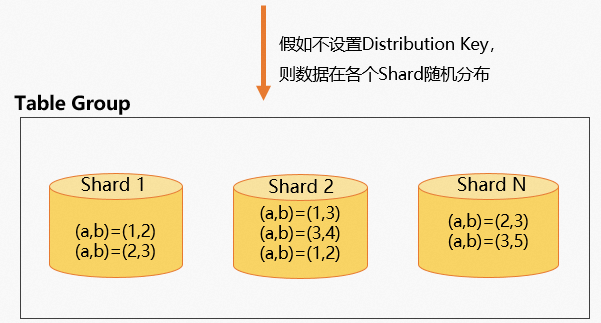
Group By聚合场景设置Distribution Key
为表设置了Distribution Key,那么相同的数据就分布在相同的Shard上,同时对于Group By聚合场景,数据在计算时按照设置的Distribution Key重新分布,因此可以将Group By频繁的字段设置为Distribution Key,这样数据在Shard内就已经聚合,减少数据在Shard间的重分配,提高查询性能,示例如下。
V2.1版本起支持的建表语法:
CREATE TABLE agg_tbl ( a int NOT NULL, b int NOT NULL ) WITH ( distribution_key = 'a' ); --示例查询,对a列做聚合查询 select a,sum(b) from agg_tbl group by a;所有版本支持的建表语法:
begin; create table agg_tbl ( a int not null, b int not null ); call set_table_property('agg_tbl', 'distribution_key', 'a'); commit; --示例查询,对a列做聚合查询 select a,sum(b) from agg_tbl group by a;
通过查看执行计划(explain SQL),如下所示执行计划结果中没有redistribution算子,说明数据没有重分布。
两表关联场景设置Distribution Key
两表Join字段设置为Distribution Key
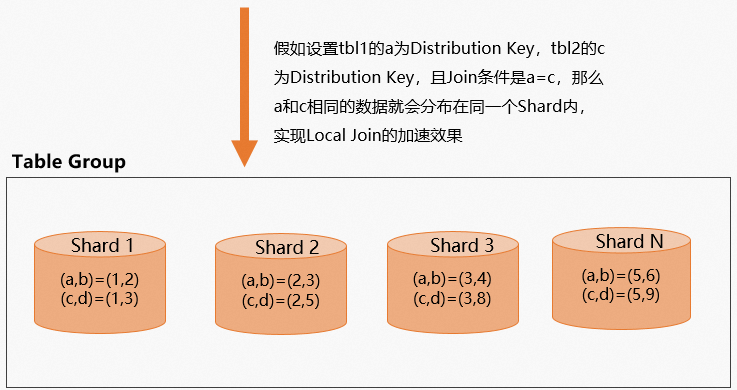
在两表关联(Join)的场景,如果两表Join字段分别在对应表里都设置为Distribution Key,那么Join字段相同的数据就会分布在相同的Shard,这样就能实现Local Join,从而实现查询加速的效果,示例如下。
建表DDL。
V2.1版本起支持的建表语法:
--tbl1按照a列分布,tbl2按照c列分布,当tbl1与tbl2以a=c关联条件join时,对应的数据分布在同一个Shard内,这种查询可以实现Local Join的加速效果 BEGIN; CREATE TABLE tbl1 ( a int NOT NULL, b text NOT NULL ) WITH ( distribution_key = 'a' ); CREATE TABLE tbl2 ( c int NOT NULL, d text NOT NULL ) WITH ( distribution_key = 'c' ); COMMIT;所有版本支持的建表语法:
--tbl1按照a列分布,tbl2按照c列分布,当tbl1与tbl2以a=c关联条件join时,对应的数据分布在同一个Shard内,这种查询可以实现Local Join的加速效果 begin; create table tbl1( a int not null, b text not null ); call set_table_property('tbl1', 'distribution_key', 'a'); create table tbl2( c int not null, d text not null ); call set_table_property('tbl2', 'distribution_key', 'c'); commit;
查询语句。
select * from tbl1 join tbl2 on tbl1.a=tbl2.c;
数据分布示意图如下。
 通过查看执行计划(explain SQL),如下所示执行计划结果中没有
通过查看执行计划(explain SQL),如下所示执行计划结果中没有redistribution算子,说明数据没有重分布。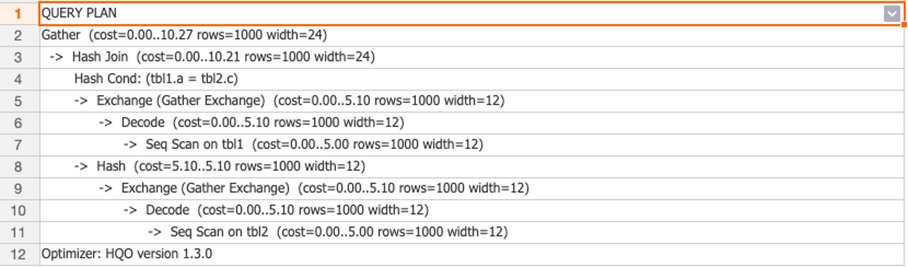
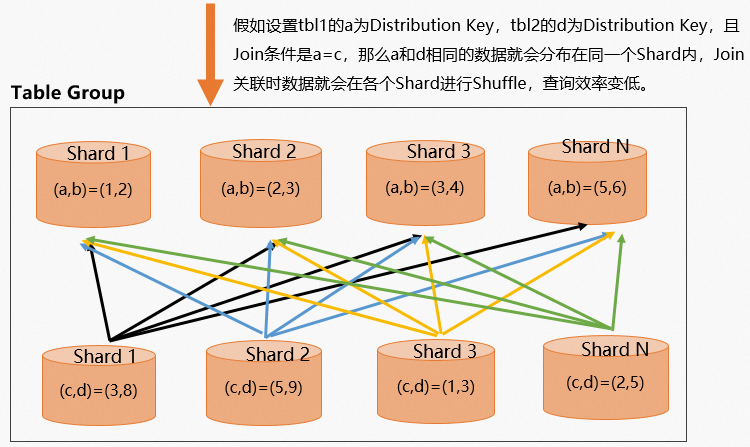
两表Join字段未都设置为Distribution Key
在两表关联(Join)的场景,如果两表Join字段在对应表里未都设置为Distribution Key,那么查询时数据就会在各个Shard Shuffle(执行计划会根据关联的两个表大小,来判断是进行Shuffle还是Broadcast)。如下示例,设置
tbl1的a字段为Distribution Key,tbl2的d字段为Distribution Key,而Join条件是a=c,那么c字段就会在每个Shard Shuffle一遍,从而导致查询效率变低。建表DDL。
V2.1版本起支持的建表语法:
BEGIN; CREATE TABLE tbl1 ( a int NOT NULL, b text NOT NULL ) WITH ( distribution_key = 'a' ); CREATE TABLE tbl2 ( c int NOT NULL, d text NOT NULL ) WITH ( distribution_key = 'd' ); COMMIT;所有版本支持的建表语法:
begin; create table tbl1( a int not null, b text not null ); call set_table_property('tbl1', 'distribution_key', 'a'); create table tbl2( c int not null, d text not null ); call set_table_property('tbl2', 'distribution_key', 'd'); commit;
查询语句。
select * from tbl1 join tbl2 on tbl1.a=tbl2.c;
数据分布示意图如下。
 通过查看执行计划(explain SQL),如下所示执行计划中有
通过查看执行计划(explain SQL),如下所示执行计划中有redistribution算子,说明数据进行了重分布,表明Distribution Key设置的不合理,需要重新设置。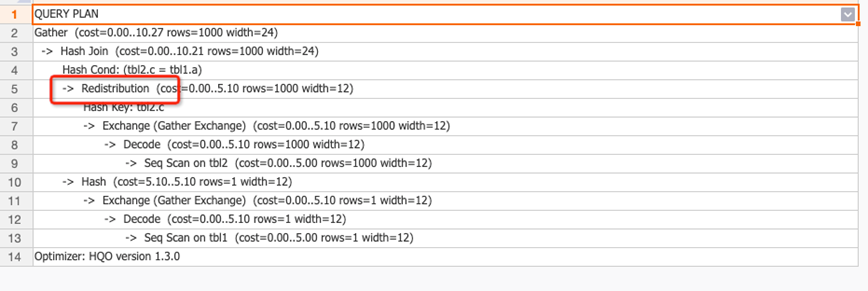
多表关联场景设置Distribution Key
多表关联的场景比较复杂,可以遵循如下原则:
每个表的Join字段都相同,那么将Join字段都设置为Distribution Key。
每个表的Join字段不同,优先考虑大表间的Join,将大表的Join字段设置为Distribution Key。
通过以下几种情况举例说明(本文中以三个表Join为例说明,大于三个表的Join情况可以参考本示例)。
三个表的Join字段相同
在三个表Join的场景中,三个表的Join字段都相同,那么这种情况是最简单的,可以直接将三个表的Join字段都设置为Distribution Key,实现Local Join的能力。
V2.1版本起支持的建表语法:
BEGIN; CREATE TABLE join_tbl1 ( a int NOT NULL, b text NOT NULL ) WITH ( distribution_key = 'a' ); CREATE TABLE join_tbl2 ( a int NOT NULL, d text NOT NULL, e text NOT NULL ) WITH ( distribution_key = 'a' ); CREATE TABLE join_tbl3 ( a int NOT NULL, e text NOT NULL, f text NOT NULL, g text NOT NULL ) WITH ( distribution_key = 'a' ); COMMIT; --3表join查询 SELECT * FROM join_tbl1 INNER JOIN join_tbl2 ON join_tbl2.a = join_tbl1.a INNER JOIN join_tbl3 ON join_tbl2.a = join_tbl3.a;所有版本支持的建表语法:
begin; create table join_tbl1( a int not null, b text not null ); call set_table_property('join_tbl1', 'distribution_key', 'a'); create table join_tbl2( a int not null, d text not null, e text not null ); call set_table_property('join_tbl2', 'distribution_key', 'a'); create table join_tbl3( a int not null, e text not null, f text not null, g text not null ); call set_table_property('join_tbl3', 'distribution_key', 'a'); commit; --3表join查询 SELECT * FROM join_tbl1 INNER JOIN join_tbl2 ON join_tbl2.a = join_tbl1.a INNER JOIN join_tbl3 ON join_tbl2.a = join_tbl3.a;
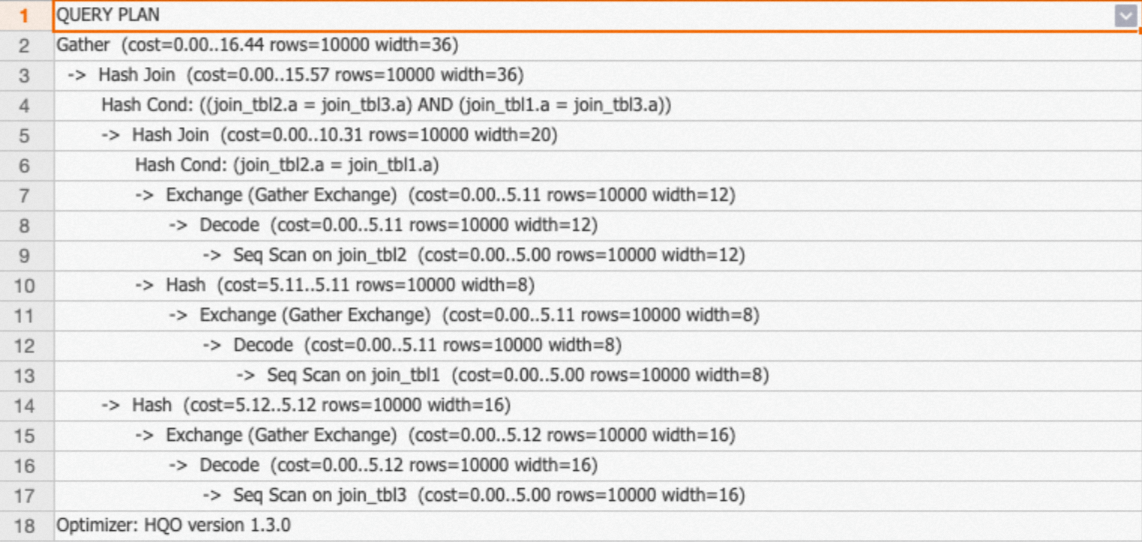
通过查看执行计划(explain SQL),如下所示执行计划中:
没有
redistribution算子,说明数据没有重分布,实现了Local Join。exchange算子代表文件级别聚合到Shard级别聚合,这样就只需要对应Shard的数据,提升数据的查询效率。
三个表的Join字段不同
在实际业务中,多表关联时会有Join字段不相同的场景,这个时候可以根据如下原则来设置Distribution Key:
核心优化原则是优先考虑大表间的Join,设置大表的Join字段为Distribution Key;小表因其数据量较少,无需过多考虑。
表数据量大致相同的情况,可以设置Group By频繁的Join字段为Distribution Key。
如下示例,有三个表相互Join,Join的字段不完全一样,这个时候选择大表的Join字段为Distribution Key,
join_tbl_1这个表数据量有一千万条,join_tbl_2和join_tbl_3分别有一百万条,以join_tbl_1为主要优化对象。V2.1版本起支持的建表语法:
BEGIN; -- join_tbl_1为1kw数据量 CREATE TABLE join_tbl_1 ( a int NOT NULL, b text NOT NULL ) WITH ( distribution_key = 'a' ); -- join_tbl_2为100w数据量 CREATE TABLE join_tbl_2 ( a int NOT NULL, d text NOT NULL, e text NOT NULL ) WITH ( distribution_key = 'a' ); -- join_tbl_3为100w数据量 CREATE TABLE join_tbl_3 ( a int NOT NULL, e text NOT NULL, f text NOT NULL, g text NOT NULL ); WITH ( distribution_key = 'a' ); COMMIT; --join key不相同时,选择大表的join key为distribution key。 SELECT * FROM join_tbl_1 INNER JOIN join_tbl_2 ON join_tbl_2.a = join_tbl_1.a INNER JOIN join_tbl_3 ON join_tbl_2.d = join_tbl_3.f;所有版本支持的建表语法:
begin; --join_tbl_1为1kw数据量 create table join_tbl_1( a int not null, b text not null ); call set_table_property('join_tbl_1', 'distribution_key', 'a'); --join_tbl_2为100w数据量 create table join_tbl_2( a int not null, d text not null, e text not null ); call set_table_property('join_tbl_2', 'distribution_key', 'a'); --join_tbl_3为100w数据量 create table join_tbl_3( a int not null, e text not null, f text not null, g text not null ); --call set_table_property('join_tbl_3', 'distribution_key', 'a'); commit; --join key不相同时,选择大表的join key为distribution key。 SELECT * FROM join_tbl_1 INNER JOIN join_tbl_2 ON join_tbl_2.a = join_tbl_1.a INNER JOIN join_tbl_3 ON join_tbl_2.d = join_tbl_3.f;
通过查看执行计划(explain SQL),如下所示执行计划表明:
在
join_tbl_2和join_tbl_3表之间有redistribution算子,因为join_tbl_3是小表,Join字段与Distribution Key不一致,所以数据进行了重分布。join_tbl_1和join_tbl_2表之间没有redistribution算子,因为两表将Join字段都设置为Distribution Key,因此数据不会重分布。

使用示例
V2.1版本起支持的建表语法:
--单表设置为distribution key CREATE TABLE tbl ( a int NOT NULL, b text NOT NULL ) WITH ( distribution_key = 'a' ); --设置多个distribution key CREATE TABLE tbl ( a int NOT NULL, b text NOT NULL ) WITH ( distribution_key = 'a,b' ); --join场景,设置join key为distribution key BEGIN; CREATE TABLE tbl1 ( a int NOT NULL, b text NOT NULL ) WITH ( distribution_key = 'a' ); CREATE TABLE tbl2 ( c int NOT NULL, d text NOT NULL ) WITH ( distribution_key = 'c' ); COMMIT; SELECT b, count(*) FROM tbl1 JOIN tbl2 ON tbl1.a = tbl2.c GROUP BY b;所有版本支持的建表语法:
--设置一个distribution key begin; create table tbl (a int not null, b text not null); call set_table_property('tbl', 'distribution_key', 'a'); commit; --设置多个distribution key begin; create table tbl (a int not null, b text not null); call set_table_property('tbl', 'distribution_key', 'a,b'); commit; --join场景,设置join key为distribution key begin; create table tbl1(a int not null, b text not null); call set_table_property('tbl1', 'distribution_key', 'a'); create table tbl2(c int not null, d text not null); call set_table_property('tbl2', 'distribution_key', 'c'); commit; select b, count(*) from tbl1 join tbl2 on tbl1.a = tbl2.c group by b;